Assume: If the only expense incurred was freight-out of P3,000, compute the following for Parts B: 1. Beginning Inventory 2. Purchases during the month 3. Ending Inventory 4. Cost... Assume: If the only expense incurred was freight-out of P3,000, compute the following for Parts B: 1. Beginning Inventory 2. Purchases during the month 3. Ending Inventory 4. Cost of Sales 5. Sales 6. Gross Profit 7. Net Sales.
Understand the Problem
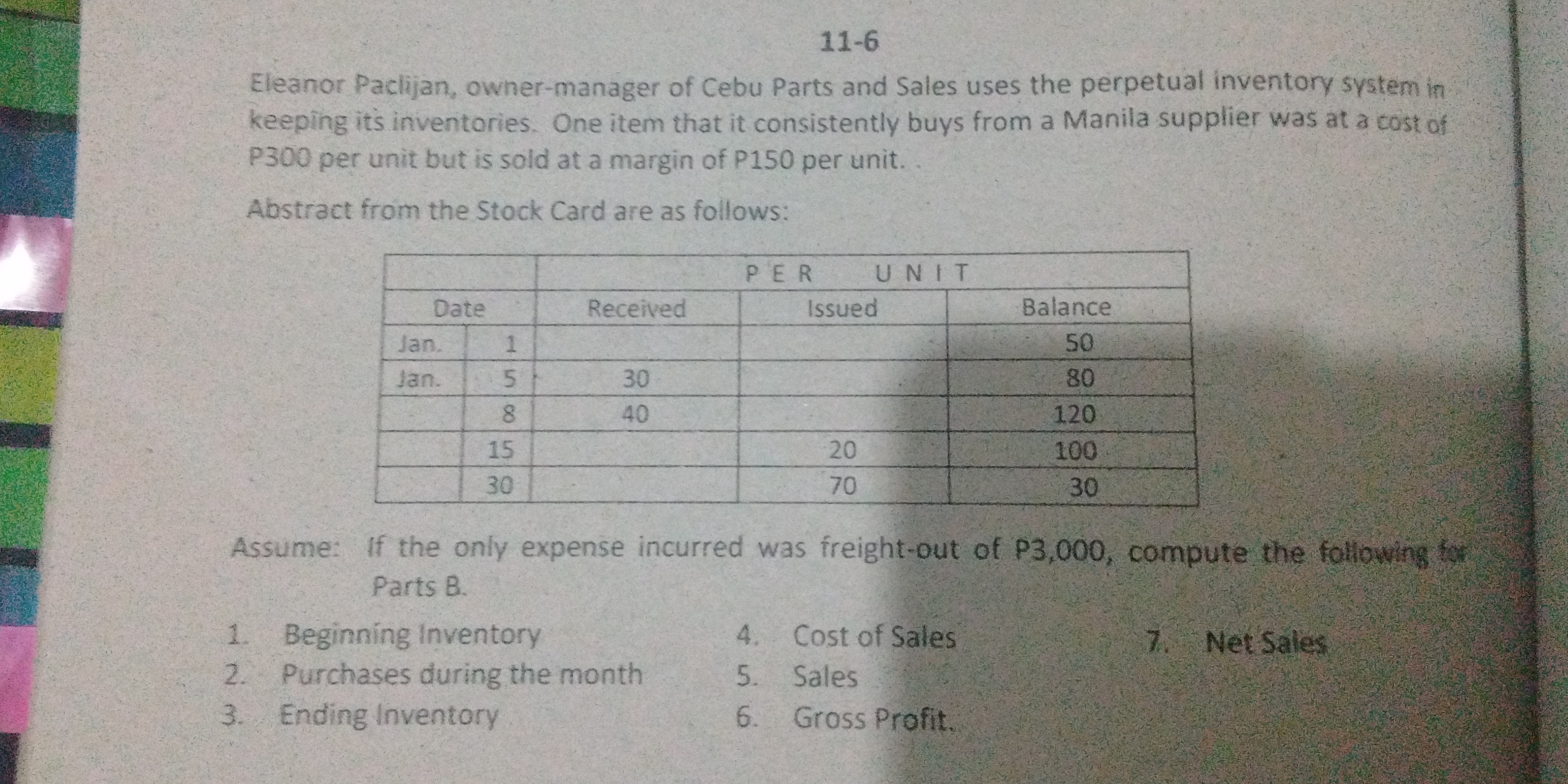
The question is asking to compute the beginning inventory, purchases during the month, ending inventory, cost of sales, sales, gross profit, and net sales for a company based on the given perpetual inventory data.
Answer
Net Sales: 69,000 P.
Answer for screen readers
- Beginning Inventory: 50 units
- Purchases During the Month: 140 units
- Ending Inventory: 30 units
- Cost of Sales: 48,000 P
- Sales: 72,000 P
- Gross Profit: 24,000 P
- Net Sales: 69,000 P
Steps to Solve
- Determine Beginning Inventory
From the stock card, the beginning inventory on January 1 is 50 units.
- Calculate Purchases During the Month
Next, sum the units received:
- 30 units on January 5
- 40 units on January 8
- 70 units on January 30
Total purchases = $30 + 40 + 70 = 140$ units.
- Calculate Ending Inventory
The ending inventory is given as 30 units on January 30.
- Calculate Cost of Sales
Cost of sales (Cost of Goods Sold - COGS) can be calculated as follows:
COGS = (Total available units - Ending inventory) * Cost per unit
Total available units = Beginning inventory + Purchases
$$ \text{Total available units} = 50 + 140 = 190 \text{ units} $$
Ending inventory = 30 units, so:
$$ \text{COGS} = (190 - 30) \times 300 = 160 \times 300 = 48,000 \text{ P} $$
- Calculate Sales
To find sales, we first calculate units sold:
Units sold = Total available units - Ending inventory
$$ \text{Units sold} = 190 - 30 = 160 \text{ units} $$
Now, multiply units sold by the selling price per unit:
$$ \text{Sales} = \text{Units sold} \times \text{Selling price} $$
Selling price = Cost + Margin = $300 + 150 = 450$ P
$$ \text{Sales} = 160 \times 450 = 72,000 \text{ P} $$
- Calculate Gross Profit
Gross profit is calculated as:
$$ \text{Gross Profit} = \text{Sales} - \text{COGS} $$
$$ \text{Gross Profit} = 72,000 - 48,000 = 24,000 \text{ P} $$
- Calculate Net Sales
Net sales can be calculated as:
$$ \text{Net Sales} = \text{Sales} - \text{Freight-out} $$
Freight-out = 3,000 P, so:
$$ \text{Net Sales} = 72,000 - 3,000 = 69,000 \text{ P} $$
- Beginning Inventory: 50 units
- Purchases During the Month: 140 units
- Ending Inventory: 30 units
- Cost of Sales: 48,000 P
- Sales: 72,000 P
- Gross Profit: 24,000 P
- Net Sales: 69,000 P
More Information
These values provide a financial snapshot of Eleanor Paclijan's business for the month, encompassing inventory management, cost tracking, and profit evaluation.
Tips
- Forgetting to convert total sales into net sales by deducting freight-out costs.
- Miscalculating units sold by not considering total available inventory correctly.
- Not keeping track of inventory balances accurately after transactions.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information