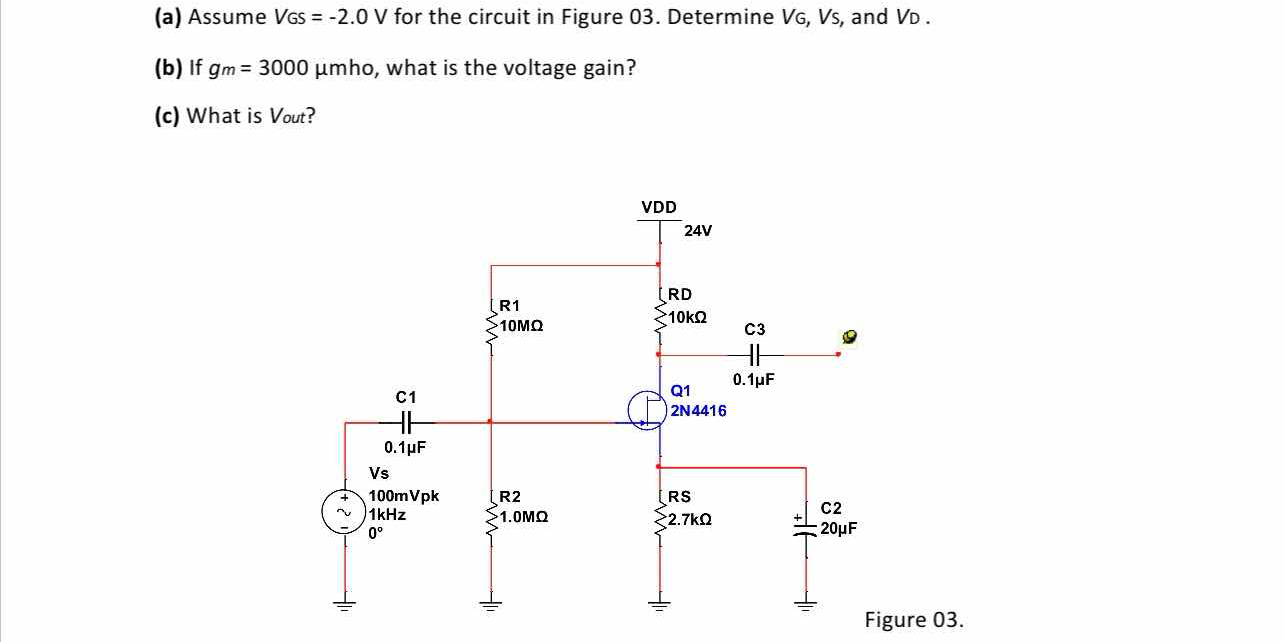
(a) Assume VGS = -2.0 V for the circuit in Figure 03. Determine VG, VS, and VD. (b) If gm = 3000 μmho, what is the voltage gain? (c) What is Vout?
Understand the Problem
The question asks for the calculation of certain voltages (VG, VS, VD) and the voltage gain of a circuit depicted in a provided figure, along with the output voltage (Vout) based on given parameters. This involves understanding circuit analysis and operational amplifier concepts.
Answer
VG ≈ -0.18 V, VS = -2.0 V, VD ≈ -30.6 V, Voltage Gain ≈ -6.3, Vout ≈ 12.6 V
Answer for screen readers
- ( V_G \approx -0.18 , V )
- ( V_S = -2.0 , V )
- ( V_D \approx -30.6 , V )
- Voltage Gain ( A_v \approx -6.3 )
- ( V_{out} \approx 12.6 , V )
Steps to Solve
- Determine VG To find the gate voltage (VG), use the voltage divider rule involving resistors R1 and R2. The input voltage (Vs) is provided, along with the resistor values.
The formula for VG is: $$ V_G = V_{S} \cdot \frac{R_2}{R_1 + R_2} $$ Substituting values: $$ V_G = -2.0 \cdot \frac{1.0 \text{MΩ}}{10.0 \text{MΩ} + 1.0 \text{MΩ}} = -2.0 \cdot \frac{1}{11} \approx -0.18 , \text{V} $$
-
Determine VS In this case, we already have the value of VS given as $V_S = -2.0 , V$.
-
Determine VD The drain voltage (VD) can be calculated using Ohm's law: $$ V_D = V_{DD} - I_D \cdot R_D $$ First, we need to calculate the drain current (ID). This can be approximated using: $$ I_D = g_m \cdot (V_G - V_S) $$ The transconductance ($g_m$) is given as $3000 , \mu mho = 3000 \times 10^{-6} , S$. Now, substituting for ID: $$ I_D = 3000 \times 10^{-6} \cdot (-0.18 - (-2.0)) = 3000 \times 10^{-6} \cdot 1.82 \approx 5.46 , mA $$ Now, substituting into the drain voltage formula: $$ V_D = 24V - (5.46 \times 10^{-3} A) \cdot 10^4 \Omega = 24 - 54.6 = -30.6 , V $$
-
Calculate Voltage Gain The voltage gain ($A_v$) is given by the formula: $$ A_v = -g_m \cdot \frac{R_D || R_S}{1} $$ Where $R_D || R_S = \frac{R_D \cdot R_S}{R_D + R_S}$. So we first find this parallel resistance: $$ R_{D || S} = \frac{10 \times 2.7}{10 + 2.7} \approx 2.1 , k\Omega $$ Now substituting values: $$ A_v = -3000 \times 10^{-6} \cdot 2.1 \times 10^{3} \approx -6.3 $$
-
Determine Vout We can find the output voltage using: $$ V_{out} = A_v \cdot V_s $$ Substituting the values: $$ V_{out} = -6.3 \cdot (-2.0) \approx 12.6 , V $$
- ( V_G \approx -0.18 , V )
- ( V_S = -2.0 , V )
- ( V_D \approx -30.6 , V )
- Voltage Gain ( A_v \approx -6.3 )
- ( V_{out} \approx 12.6 , V )
More Information
This analysis covers key output parameters in a transistor amplifier circuit, demonstrating how voltage levels change and how the amplifier alters input signals via voltage gain. Such configurations are common in operational amplifier designs and signal processing.
Tips
- Misinterpreting the voltage division rule when calculating VG can lead to incorrect numbers.
- Forgetting to take absolute values when working with negative voltages can confuse results.
- Neglecting to convert transconductance into appropriate units for calculations.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information