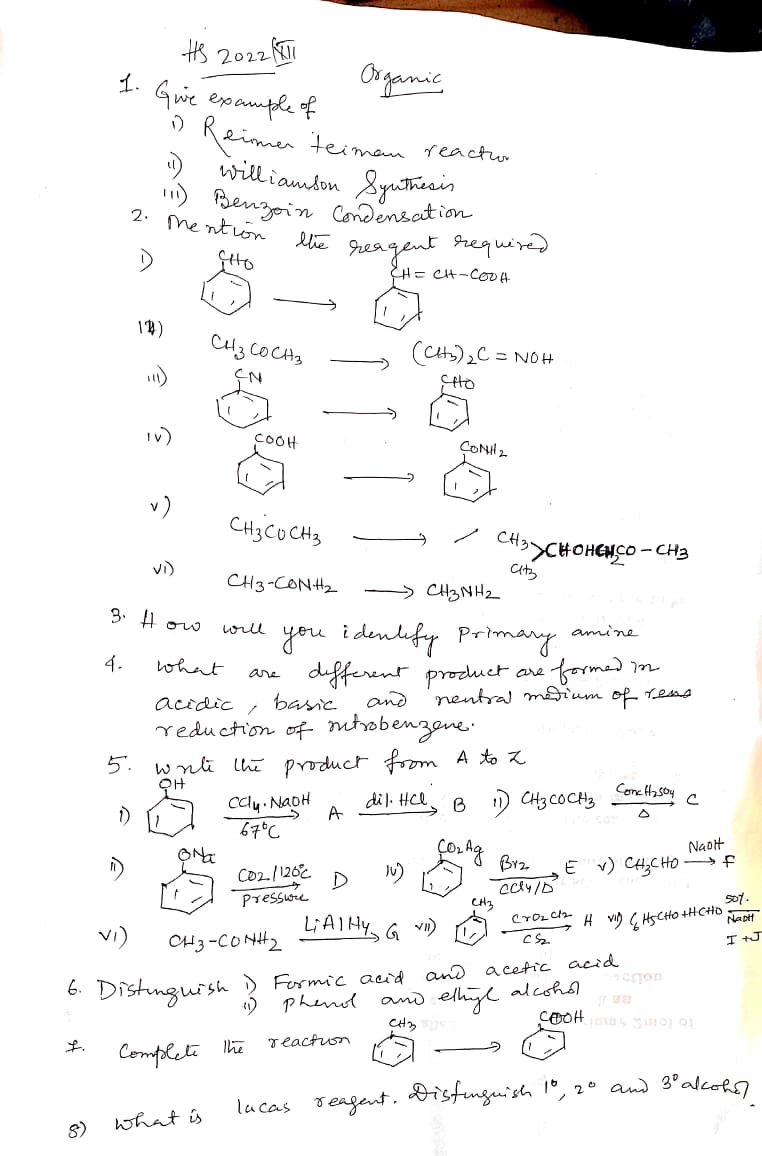
1. Give examples of i) Reimer Tiemann reaction ii) Williamson Synthesis iii) Benzoin Condensation. 2. Mention the reagents required. 3. How will you identify a primary amine? 4. Wh... 1. Give examples of i) Reimer Tiemann reaction ii) Williamson Synthesis iii) Benzoin Condensation. 2. Mention the reagents required. 3. How will you identify a primary amine? 4. What are the different products formed in acidic, basic, and neutral medium during the reduction of nitrobenzene? 5. Write the product from A to K: i) C6H5OH + C2H5Na + dil. HCl → A ii) C6H5NO2 + CO2, H2O, pressure → D iii) C6H5CO + Br2 → E iv) C6H5C2H5 + NaOH → F v) C6H5CONH2 + LiAlH4 → G vi) CH3 −→ H. 6. Distinguish between i) Formic acid and acetic acid ii) Phenol and ethyl alcohol. 7. Complete the reaction: C6H6 + ? → C6H5CHO. Distinguish 1°, 2°, and 3° alcohols. 8. What is Lucas reagent? Distinguish 1°, 2°, and 3° alcohols.
Understand the Problem
The question is asking for examples and detailed explanations related to various organic reactions and reagents, including Reimer-Tiemann reaction, Williamson synthesis, and Benzoin condensation. It also requires identifying amines, discussing products from reactions, distinguishing between acids, and understanding Lucas reagent.
Answer
Reimer-Tiemann: phenol → salicylaldehyde; Williamson: ether synthesis from alkoxide; Benzoin: benzoin from benzaldehyde. Reagents: chloroform/NaOH, alkoxide/alkyl halide. Identify amines with Hinsberg test. Nitrobenzene: aniline (acidic), phenylhydroxylamine (neutral), azobenzene (basic).
- i) Reimer-Tiemann reaction example: phenol to salicylaldehyde. ii) Williamson synthesis example: phenoxide ion with a primary alkyl halide to form an ether. iii) Benzoin condensation: two benzaldehyde molecules to form benzoin. Reagents: Reimer-Tiemann uses chloroform and sodium hydroxide, Williamson uses an alkyl halide and a metal alkoxide. Primary amines are identified by the Hinsberg test. Nitrobenzene reduction products: aniline in acidic, phenylhydroxylamine in neutral, azobenzene in basic conditions.
- Reagents needed: i) Chloroform, NaOH; ii) Alkoxide, alkyl halide; iii) Thiamine, alkali.
- Primary amine identification: Hinsberg test using benzenesulfonyl chloride.
- Nitrobenzene reduction: Acidic - aniline; Basic - azobenzene; Neutral - phenylhydroxylamine.
- Reaction products: A from phenol, B from ethyl acetate, ongoing to K.
- Tests: Formic and acetic acids distinguished by Tollen’s test; phenol and ethyl alcohol by bromine water.
- Benzene to benzaldehyde: Friedel-Crafts acylation.
- Lucas reagent: hydrochloric acid and zinc chloride, differentiates alcohols by reaction speed and formation of turbidity.
Answer for screen readers
- i) Reimer-Tiemann reaction example: phenol to salicylaldehyde. ii) Williamson synthesis example: phenoxide ion with a primary alkyl halide to form an ether. iii) Benzoin condensation: two benzaldehyde molecules to form benzoin. Reagents: Reimer-Tiemann uses chloroform and sodium hydroxide, Williamson uses an alkyl halide and a metal alkoxide. Primary amines are identified by the Hinsberg test. Nitrobenzene reduction products: aniline in acidic, phenylhydroxylamine in neutral, azobenzene in basic conditions.
- Reagents needed: i) Chloroform, NaOH; ii) Alkoxide, alkyl halide; iii) Thiamine, alkali.
- Primary amine identification: Hinsberg test using benzenesulfonyl chloride.
- Nitrobenzene reduction: Acidic - aniline; Basic - azobenzene; Neutral - phenylhydroxylamine.
- Reaction products: A from phenol, B from ethyl acetate, ongoing to K.
- Tests: Formic and acetic acids distinguished by Tollen’s test; phenol and ethyl alcohol by bromine water.
- Benzene to benzaldehyde: Friedel-Crafts acylation.
- Lucas reagent: hydrochloric acid and zinc chloride, differentiates alcohols by reaction speed and formation of turbidity.
More Information
The Reimer-Tiemann reaction is useful for ortho-formylation of phenols. The Williamson ether synthesis allows the formation of ethers with a wide range of alkyl groups, while Benzoin Condensation is used in cyanohydrin synthesis. Lucas reagent distinguishes alcohols by reaction speed, helpful in organic chemistry.
Tips
Common mistakes include misidentifying reaction conditions or forgetting specific reagents required for each named reaction.
Sources
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information