Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the typical cadence during walking?
What is the typical cadence during walking?
- 90 steps/min
- 110 steps/min (correct)
- 100 steps/min
- 120 steps/min
The stance phase accounts for 60% of the gait cycle.
The stance phase accounts for 60% of the gait cycle.
True (A)
What is the typical velocity range for walking in meters per minute?
What is the typical velocity range for walking in meters per minute?
70-90 m/min
The typical step length during walking is approximately _____ of a person's height.
The typical step length during walking is approximately _____ of a person's height.
Match the phase of gait with the associated muscle actions:
Match the phase of gait with the associated muscle actions:
During which phase of gait do the knee flexors and ankle plantar flexors stretch?
During which phase of gait do the knee flexors and ankle plantar flexors stretch?
Double support time accounts for 80% of stride time.
Double support time accounts for 80% of stride time.
What is the typical toe-out angle during walking?
What is the typical toe-out angle during walking?
What is one possible underpinning impairment for a lack of dorsi flexion on initial contact during walking?
What is one possible underpinning impairment for a lack of dorsi flexion on initial contact during walking?
Knee hyperextension during the loading response is an adaptive strategy.
Knee hyperextension during the loading response is an adaptive strategy.
What might result in hips being externally rotated bilaterally during the walking cycle?
What might result in hips being externally rotated bilaterally during the walking cycle?
During the stance phase, decreased ________ can lead to the trunk leaning forward.
During the stance phase, decreased ________ can lead to the trunk leaning forward.
Match the missing components with their associated adaptive strategies or compensations:
Match the missing components with their associated adaptive strategies or compensations:
Which of the following could be a consequence of weak dorsiflexors?
Which of the following could be a consequence of weak dorsiflexors?
Uneven base of support often indicates issues with balance and lower limb strength.
Uneven base of support often indicates issues with balance and lower limb strength.
What could decreased passive length of the plantar flexors indicate?
What could decreased passive length of the plantar flexors indicate?
Which of the following is a consequence of decreased knee extension through stance?
Which of the following is a consequence of decreased knee extension through stance?
A lack of plantarflexion at push-off can lead to insufficient hip flexion during swing.
A lack of plantarflexion at push-off can lead to insufficient hip flexion during swing.
What adaptive strategy is commonly seen due to decreased knee flexion during initial swing?
What adaptive strategy is commonly seen due to decreased knee flexion during initial swing?
The condition of having decreased dorsiflexion may be referred to as ______.
The condition of having decreased dorsiflexion may be referred to as ______.
Match the observed movement with its potential underlying impairment:
Match the observed movement with its potential underlying impairment:
What is a potential consequence of weak knee flexion if it is present prior to push-off?
What is a potential consequence of weak knee flexion if it is present prior to push-off?
A long step length is typically associated with weak hip flexors.
A long step length is typically associated with weak hip flexors.
What could indicate insufficient push-off during gait?
What could indicate insufficient push-off during gait?
What is a consequence of impaired clearance mechanisms at the ankle?
What is a consequence of impaired clearance mechanisms at the ankle?
Weak hip contraction can result in optimal knee extension prior to heel strike.
Weak hip contraction can result in optimal knee extension prior to heel strike.
What is one of the primary issues caused by weak quadriceps?
What is one of the primary issues caused by weak quadriceps?
Lack of ______________ results in impaired clearance mechanisms.
Lack of ______________ results in impaired clearance mechanisms.
Match the gait issues with their causes:
Match the gait issues with their causes:
Which of the following can lead to terminal swing issues?
Which of the following can lead to terminal swing issues?
A tight plantar flexor can contribute to poor ankle dorsiflexion.
A tight plantar flexor can contribute to poor ankle dorsiflexion.
What movement is associated with decreased knee extension prior to heel strike?
What movement is associated with decreased knee extension prior to heel strike?
What percentage of the gait cycle is typically represented by the swing phase?
What percentage of the gait cycle is typically represented by the swing phase?
Which muscles are primarily active during the loading response phase of the gait cycle?
Which muscles are primarily active during the loading response phase of the gait cycle?
What is the approximate stride duration during walking?
What is the approximate stride duration during walking?
Which phase of the gait cycle is critical for preparing for the swing phase?
Which phase of the gait cycle is critical for preparing for the swing phase?
What is the typical base of support (BOS) distance between heels during walking?
What is the typical base of support (BOS) distance between heels during walking?
During which phase of gait are the hip flexors and dorsiflexors mainly active to clear the foot?
During which phase of gait are the hip flexors and dorsiflexors mainly active to clear the foot?
What is the approximate angle of toe-out during walking?
What is the approximate angle of toe-out during walking?
What is a likely consequence of insufficient push-off during gait?
What is a likely consequence of insufficient push-off during gait?
Which muscle group is primarily involved during the mid-stance phase of the gait cycle?
Which muscle group is primarily involved during the mid-stance phase of the gait cycle?
Which issue may arise from a lack of proper knee flexion prior to push-off?
Which issue may arise from a lack of proper knee flexion prior to push-off?
What could be an underlying impairment resulting from decreased dorsiflexion length?
What could be an underlying impairment resulting from decreased dorsiflexion length?
Which adaptive strategy might be seen with decreased knee flexion during initial swing?
Which adaptive strategy might be seen with decreased knee flexion during initial swing?
What is a possible consequence of decreased hip extension at the end of stance?
What is a possible consequence of decreased hip extension at the end of stance?
What can shorter hip flexors indicate during the swing phase?
What can shorter hip flexors indicate during the swing phase?
Which underlying impairment might be related to excessive hip flexion during swing?
Which underlying impairment might be related to excessive hip flexion during swing?
What condition may result from decreased plantarflexion during push-off?
What condition may result from decreased plantarflexion during push-off?
What could be a result of decreased ankle dorsiflexion at initial contact during walking?
What could be a result of decreased ankle dorsiflexion at initial contact during walking?
Which of the following may occur due to weak dorsiflexors during the stance phase?
Which of the following may occur due to weak dorsiflexors during the stance phase?
What compensatory strategy might a person use if they experience a lack of knee flexion on loading response?
What compensatory strategy might a person use if they experience a lack of knee flexion on loading response?
What underlying impairment could result in hips being externally rotated during the walking cycle?
What underlying impairment could result in hips being externally rotated during the walking cycle?
Which potential impairment is indicated by a forward trunk lean during the stance phase?
Which potential impairment is indicated by a forward trunk lean during the stance phase?
What might a decreased base of support in a walking cycle indicate?
What might a decreased base of support in a walking cycle indicate?
How does a lack of dorsiflexion through the stance phase likely affect the gait cycle?
How does a lack of dorsiflexion through the stance phase likely affect the gait cycle?
What could result from excessive hip flexion during gait?
What could result from excessive hip flexion during gait?
What is a probable consequence of weak relative lower limb during the walking cycle?
What is a probable consequence of weak relative lower limb during the walking cycle?
What might cause impaired clearance mechanisms at the ankle?
What might cause impaired clearance mechanisms at the ankle?
A lack of dorsiflexion prior to heel strike can lead to which of the following?
A lack of dorsiflexion prior to heel strike can lead to which of the following?
What is a likely consequence of weak quadriceps during the gait cycle?
What is a likely consequence of weak quadriceps during the gait cycle?
Which factor is associated with a lack of control of hip flexion during gait?
Which factor is associated with a lack of control of hip flexion during gait?
What might excessive tightness of the plantar flexors affect during gait?
What might excessive tightness of the plantar flexors affect during gait?
What movement may indicate a lack of knee control during the gait cycle?
What movement may indicate a lack of knee control during the gait cycle?
Which of the following could be a consequence of weak ankle dorsiflexors during gait?
Which of the following could be a consequence of weak ankle dorsiflexors during gait?
Flashcards
Stride duration
Stride duration
The time it takes to complete one stride (approximately 1.1 seconds).
Stance/swing time
Stance/swing time
The proportions of the gait cycle dedicated to the stance and swing phases, approximately 60% stance and 40% swing.
Double/single support time
Double/single support time
The portion of the stride time during which both feet are in contact with the ground (double support) versus only one foot (single support).
Cadence
Cadence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Walking velocity
Walking velocity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Step length
Step length
Signup and view all the flashcards
Base of Support (BOS)
Base of Support (BOS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Toe Out
Toe Out
Signup and view all the flashcards
Initial Contact
Initial Contact
Signup and view all the flashcards
Loading Response
Loading Response
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mid-Stance
Mid-Stance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Terminal Stance
Terminal Stance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pre-Swing
Pre-Swing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Initial Swing
Initial Swing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mid Swing
Mid Swing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Terminal Swing
Terminal Swing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heel Strike
Heel Strike
Signup and view all the flashcards
Initial Alignment
Initial Alignment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Missing R ankle dorsiflexion
Missing R ankle dorsiflexion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lack of dorsiflexion during initial contact
Lack of dorsiflexion during initial contact
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip Neutral Rotation
Hip Neutral Rotation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip External Rotation
Hip External Rotation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decreased knee flexion on loading response
Decreased knee flexion on loading response
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lack of knee flexion on loading response
Lack of knee flexion on loading response
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decreased dorsiflexion through stance
Decreased dorsiflexion through stance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reduced Knee Extension (Stance)
Reduced Knee Extension (Stance)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trunk Inclination (Stance)
Trunk Inclination (Stance)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decreased Dorsiflexion (Stance)
Decreased Dorsiflexion (Stance)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Short Step Length
Short Step Length
Signup and view all the flashcards
Weak Knee Flexion (Initial Swing)
Weak Knee Flexion (Initial Swing)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Insufficient Push-off PF (Swing)
Insufficient Push-off PF (Swing)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Excessive Hip Flexion (Swing)
Excessive Hip Flexion (Swing)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Insufficient Dorsiflexion (Swing)
Insufficient Dorsiflexion (Swing)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Short Hip Flexor (Swing)
Short Hip Flexor (Swing)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Appropriate hip flexion
Appropriate hip flexion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Impaired hip flexion
Impaired hip flexion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Weak ankle dorsiflexors
Weak ankle dorsiflexors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decreased knee extension
Decreased knee extension
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lack of ankle dorsiflexion
Lack of ankle dorsiflexion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Weak knee extensors
Weak knee extensors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Poor hip flexion control during gait
Poor hip flexion control during gait
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip flexion weakness
Hip flexion weakness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Knee flexion weakness
Knee flexion weakness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decreased hip abduction
Decreased hip abduction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Weak knee extensors prior to heel strike
Weak knee extensors prior to heel strike
Signup and view all the flashcards
Shortened hip flexors
Shortened hip flexors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stride Duration
Stride Duration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stance/Swing Time
Stance/Swing Time
Signup and view all the flashcards
Double/Single Support
Double/Single Support
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cadence
Cadence
Signup and view all the flashcards
Walking Velocity
Walking Velocity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Step Length
Step Length
Signup and view all the flashcards
Base of Support (BOS)
Base of Support (BOS)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Toe Out
Toe Out
Signup and view all the flashcards
Initial Contact
Initial Contact
Signup and view all the flashcards
Loading Response
Loading Response
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mid-Stance
Mid-Stance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Terminal Stance
Terminal Stance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pre-Swing
Pre-Swing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Initial Swing
Initial Swing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Terminal Swing
Terminal Swing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heel Strike
Heel Strike
Signup and view all the flashcards
Initial Alignment
Initial Alignment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Missing R ankle dorsiflexion (Initial Alignment)
Missing R ankle dorsiflexion (Initial Alignment)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hips NOT neutral rotation (Initial Alignment)
Hips NOT neutral rotation (Initial Alignment)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lack of dorsiflexion during initial contact
Lack of dorsiflexion during initial contact
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lack of knee flexion on loading response
Lack of knee flexion on loading response
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decreased dorsiflexion through stance
Decreased dorsiflexion through stance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decreased hip extension (end stance)
Decreased hip extension (end stance)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lack of knee flexion prior to push-off
Lack of knee flexion prior to push-off
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lack of plantar flexion (PF) at push-off
Lack of plantar flexion (PF) at push-off
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decreased knee flexion (initial swing)
Decreased knee flexion (initial swing)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Excessive hip flexion (swing)
Excessive hip flexion (swing)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Insufficient push-off PF (swing)
Insufficient push-off PF (swing)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Short step length
Short step length
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trunk inclination (stance)
Trunk inclination (stance)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decreased dorsiflexion (stance)
Decreased dorsiflexion (stance)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Weak knee flexion (initial swing)
Weak knee flexion (initial swing)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Appropriate hip flexion
Appropriate hip flexion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Impaired hip flexion
Impaired hip flexion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Weak ankle dorsiflexors
Weak ankle dorsiflexors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decreased knee extension
Decreased knee extension
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lack of ankle dorsiflexion
Lack of ankle dorsiflexion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Weak knee extensors
Weak knee extensors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Poor hip flexion control during gait
Poor hip flexion control during gait
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip flexion weakness
Hip flexion weakness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Knee flexion weakness
Knee flexion weakness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Decreased hip abduction
Decreased hip abduction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Weak knee extensors prior to heel strike
Weak knee extensors prior to heel strike
Signup and view all the flashcards
Shortened hip flexors
Shortened hip flexors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lack of dorsiflexion during heel strike
Lack of dorsiflexion during heel strike
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
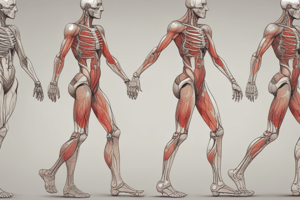
Walking Gait Cycle Phases
- Normative values for walking include stride duration (~1.1 seconds/stride), stance/swing time (60%/40% of gait cycle), double/single support time (20%/80% of stride time), cadence (~110 steps/minute), velocity (70-90 meters/minute or 4.2-5.4 km/hour), step length (~1/3 of height, 60-65 cm), and toe out (~7 degrees).
Gait Phases and Muscle Actions
- Initial Contact: Hip extensors, knee flexors/extensors, and ankle dorsiflexors are active.
- Loading Response: Knee extensors work eccentrically, controlling dorsiflexors.
- Mid-Stance: Ankle plantar flexors work eccentrically, and knee flexors are active.
- Terminal Stance: Hip flexors and dorsiflexors assist in clearing the foot.
- Pre-swing: Hip flexors and dorsiflexors are mainly active.
- Initial Swing: Hip extensors, dorsiflexors, and knee flexors work eccentrically to slow the foot.
- Mid Swing: Hip extensors, dorsiflexors, and knee flexors work eccentrically to slow the foot.
- Terminal Swing: Heel strike triggers ankle dorsiflexors, knee extensors/flexors, and hip extensors.
Initial Alignment and Possible Impairments
- Missing components: Decreased ankle dorsiflexion, hips not neutrally rotated.
- Adaptive strategies: Hip externally rotated, increased base of support (BOS).
- Possible underlying impairments: Decreased plantarflexor length (contracture/spasticity), weak hip internal rotation/hip adduction/short external rotation/hip abduction/balance/sensory issues, uneven BOS (weight).
Stance Phase Impairments
- Missing components: Lack of dorsiflexion on initial contact, lack of knee flexion on loading response, decreased dorsiflexion throughout stance, lack of appropriate knee extension/flexion during stance, decreased hip extension during terminal stance, lack of knee flexion prior to push-off, lack of plantarflexors at push-off.
- Adaptive strategies: Hyperextension, trunk included forward during stance (hip flexion), trunk incline forward (hip flexion). Increased time in double support/quick step, short step length, circumduction, increased hip flexion in swing to clear leg.
- Possible underlying impairments: Weak dorsiflexion (eccentric control) plantarflexor contracture, weak dorsiflexion decreased dorsiflexion plantarflexor length (contracture/spasticity), short hip flexor/short plantarflexor, weak knee flexion.
Swing Phase Impairments
- Missing components: Decreased knee flexion (initial swing), appropriate hip flexion (excessive), decreased knee extensions prior to heel strike, lack of ankle dorsiflexion prior to heel strike.
- Adaptive strategies: Excessive hip flexion, elevation of pelvis, and abduction of leg.
- Possible underlying impairments: Insufficient push-off due to weak/short plantarflexors, short hip flexors, impaired clearance mechanisms at the ankle due to weak ankle dorsiflexors/short plantarflexors, weak hip flexion and or knee flexion/dorsiflexion, and lack of control of hip flexion/knee flexion/knee extension, and Co-contraction.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.