Podcast
Questions and Answers
During the heel-strike phase, which muscles keep the ankle dorsi flexed?
During the heel-strike phase, which muscles keep the ankle dorsi flexed?
- Gluteus maximus and quadriceps
- Inverters and everters
- Gluteus medius and minimus
- Muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg (correct)
What is the primary function of the gluteus maximus during the heel-strike phase?
What is the primary function of the gluteus maximus during the heel-strike phase?
- To tilt the pelvis down
- To maintain the extended position of the knee
- To keep the ankle dorsi flexed
- To decelerate the flexion of the hip (correct)
What percentage of the walking cycle does the swing phase occupy?
What percentage of the walking cycle does the swing phase occupy?
- 60%
- 30%
- 40% (correct)
- 50%
During the support phase, which muscles maintain the extended position of the knee?
During the support phase, which muscles maintain the extended position of the knee?
What is the primary function of the gluteus medius and minimus during the support phase?
What is the primary function of the gluteus medius and minimus during the support phase?
What is the primary function of the hamstring muscles in the gait cycle?
What is the primary function of the hamstring muscles in the gait cycle?
Which nerve is responsible for innervating the muscles that dorsi flex the foot during the swing phase?
Which nerve is responsible for innervating the muscles that dorsi flex the foot during the swing phase?
What is the characteristic gait pattern seen in patients with myopathies, such as muscular dystrophy?
What is the characteristic gait pattern seen in patients with myopathies, such as muscular dystrophy?
What is the term for the phenomenon where the pelvis drops on the raised limb during walking?
What is the term for the phenomenon where the pelvis drops on the raised limb during walking?
During which phase of the gait cycle is the ankle dorsiflexed?
During which phase of the gait cycle is the ankle dorsiflexed?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
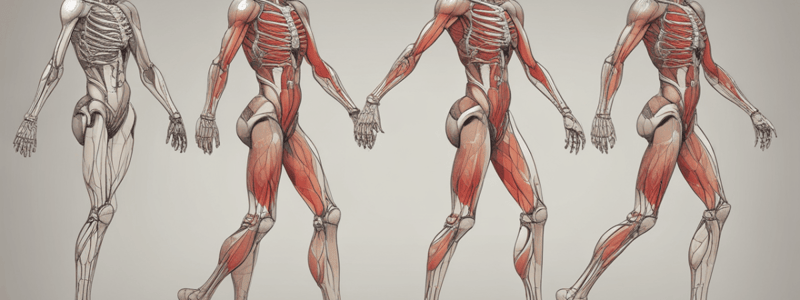
Gait Cycle
- Normal gait is a series of rhythmical, alternating movements of the trunk and limbs that result in the forward progression of the center of gravity.
- It can be described as a series of 'controlled falls'.
Phases of Walking
- There are five stages to walking: heel-strike, support, toe-off, leg lift, and swing.
- Heel-strike: the gluteus maximus, quadriceps, and muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg work together to decelerate flexion, maintain the extended position of the knee, and keep the ankle dorsi flexed.
- Support: the quadriceps maintains the extended position of the knee, and the ankle is kept stable by the balanced contraction of the inverters and everters.
- Toe-off: the hamstring muscles flex the knee, and the ankle is plantar flexed by the muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg.
- Leg lift: the iliopsoas and rectus femoris flex the lower limb at the hip, the knee is flexed by the hamstrings, and the ankle is dorsi flexed by the muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg.
- Swing: the iliopsoas and rectus femoris keep the hip flexed, the knee is extended by the quadriceps, and the ankle is still dorsi flexed by the muscles in the anterior compartment of the leg.
Common Gait Abnormalities
- Antalgic gait: pain-relieving gait.
- Lateral trunk bending: Trendelenburg gait.
- Functional leg-length discrepancy: a difference in leg length that affects gait.
- Increased walking base: ataxia, a lack of coordination and balance.
- Inadequate dorsiflexion control: foot drop, caused by damage to the deep fibular nerve.
- Trendelenburg sign: the pelvis drops on the raised limb, indicating weakness or paralysis of the abductor muscles.
- Waddling gait: seen in patients with myopathies, such as muscular dystrophy, due to bilateral weakness of the abductor muscles.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.