Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary purpose of value stream mapping?
What is the primary purpose of value stream mapping?
- To create a hierarchical organizational structure
- To analyze the financial aspects of a process
- To identify issues and opportunities for improvement (correct)
- To create a detailed blueprint of the process
What is the recommended approach to collecting data in value stream mapping?
What is the recommended approach to collecting data in value stream mapping?
- Collect data only on the most problematic areas of the process
- Focus on collecting data only on the most critical process steps
- Collect data in random order to get a general sense of the process
- Collect data in sequential order, following the flow of the process (correct)
What type of icon is used to represent inventory in a value stream map?
What type of icon is used to represent inventory in a value stream map?
- Shipment Truck Icon
- Process Step Icon
- Production Control Icon
- Inventory Icon (correct)
When creating a value stream map, what should be the starting point?
When creating a value stream map, what should be the starting point?
What type of data should be collected when creating a value stream map?
What type of data should be collected when creating a value stream map?
What is the primary goal of analyzing a value stream map?
What is the primary goal of analyzing a value stream map?
When should a value stream map be used?
When should a value stream map be used?
What is the purpose of using arrows in a value stream map?
What is the purpose of using arrows in a value stream map?
What is the significance of walking the value stream from start to finish in value stream mapping?
What is the significance of walking the value stream from start to finish in value stream mapping?
What is the purpose of using icons in value stream mapping, and what are some examples of these icons?
What is the purpose of using icons in value stream mapping, and what are some examples of these icons?
How does creating a value stream map from right to left, then left to right, and back up to the customer contribute to the mapping process?
How does creating a value stream map from right to left, then left to right, and back up to the customer contribute to the mapping process?
What types of data should be collected when creating a value stream map, and why are they important?
What types of data should be collected when creating a value stream map, and why are they important?
What is the primary benefit of using a value stream map to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement?
What is the primary benefit of using a value stream map to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement?
How can a value stream map be used to brainstorm and generate ideas for process improvement?
How can a value stream map be used to brainstorm and generate ideas for process improvement?
What is the significance of identifying the root causes of issues when using a value stream map?
What is the significance of identifying the root causes of issues when using a value stream map?
How can a value stream map be used to understand where issues are stemming from in a process?
How can a value stream map be used to understand where issues are stemming from in a process?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
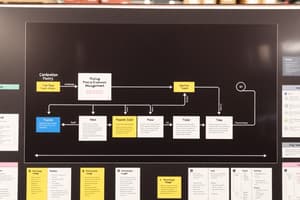
Introduction to Value Stream Mapping
- Value stream mapping is a tool used to improve processes and understand how things truly work from start to finish.
- It's a snapshot of the process, highlighting issues and opportunities for improvement.
Ground Rules for Value Stream Mapping
- Walk the value stream: start at the beginning of the process and follow it through to the end.
- Collect data in sequential order, following the flow of the process.
- It doesn't have to be perfect, just a high-level snapshot.
Icons Used in Value Stream Mapping
- Customer/Supplier Icon
- Shipment Truck Icon
- Process Step Icon
- Production Control Icon
- Inventory Icon
- Arrow Icons:
- Push Arrow
- Shipment Arrow
- Electronic Information Arrow
- Manual Arrow
Creating a Value Stream Map
- Start with the customer and work from right to left, then left to right, and back up to the customer.
- Identify the process steps, process flow, and information flow.
- Collect data on:
- Resource-based data (batch size, people involved)
- Time-based data (set-up time, changeover time, value-added time, total time)
- Quality-based data (completion accuracy percentage)
Analyzing a Value Stream Map
- Identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
- Investigate issues and create projects to improve the process.
- Use the map to understand where to focus efforts for improvement.
When to Use a Value Stream Map
- When there are issues or bottlenecks in the process.
- For continuous improvement and identifying areas for improvement.
- For brainstorming and idea generation, to create a future state value stream map.
- To understand where issues are stemming from and to identify root causes.
Example of Using a Value Stream Map
- A client (Microsoft) orders 200 units of a spark shift book series.
- The process is mapped out, including information flow and process flow.
- Issues are identified, such as:
- Only 25 units in stock.
- Decision to do a revision, which affects the process.
- Low accuracy rate with the supplier (70%).
- Long wait times between process steps.
- Projects are created to investigate and improve these areas.
Introduction to Value Stream Mapping
- Value stream mapping is a tool used to improve processes and understand how things truly work from start to finish.
- It's a snapshot of the process, highlighting issues and opportunities for improvement.
Ground Rules for Value Stream Mapping
- Start by walking the value stream, following the process from beginning to end.
- Collect data in sequential order, following the flow of the process.
- A high-level snapshot is sufficient, perfection is not required.
Icons Used in Value Stream Mapping
- Customer/Supplier Icon: represents customers and suppliers.
- Shipment Truck Icon: represents transportation.
- Process Step Icon: represents a process step.
- Production Control Icon: represents production control.
- Inventory Icon: represents inventory.
- Arrow Icons:
- Push Arrow: represents push-type flow.
- Shipment Arrow: represents shipment.
- Electronic Information Arrow: represents electronic information flow.
- Manual Arrow: represents manual information flow.
Creating a Value Stream Map
- Start with the customer and work from right to left, then left to right, and back up to the customer.
- Identify process steps, process flow, and information flow.
- Collect data on resource-based, time-based, and quality-based metrics.
Data Collection for Value Stream Mapping
- Resource-based data: batch size, people involved.
- Time-based data: set-up time, changeover time, value-added time, total time.
- Quality-based data: completion accuracy percentage.
Analyzing a Value Stream Map
- Identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
- Investigate issues and create projects to improve the process.
- Use the map to understand where to focus efforts for improvement.
When to Use a Value Stream Map
- When there are issues or bottlenecks in the process.
- For continuous improvement and identifying areas for improvement.
- For brainstorming and idea generation, to create a future state value stream map.
- To understand where issues are stemming from and to identify root causes.
Example of Using a Value Stream Map
- A client orders 200 units of a spark shift book series.
- The process is mapped out, including information flow and process flow.
- Issues are identified, such as:
- Only 25 units in stock.
- Decision to do a revision, which affects the process.
- Low accuracy rate with the supplier (70%).
- Long wait times between process steps.
- Projects are created to investigate and improve these areas.
Introduction to Value Stream Mapping
- Value stream mapping is a tool used to improve processes and understand how things truly work from start to finish.
- It's a snapshot of the process, highlighting issues and opportunities for improvement.
Ground Rules for Value Stream Mapping
- Start by walking the value stream, following the process from beginning to end.
- Collect data in sequential order, following the flow of the process.
- A high-level snapshot is sufficient, perfection is not required.
Icons Used in Value Stream Mapping
- Customer/Supplier Icon: represents customers and suppliers.
- Shipment Truck Icon: represents transportation.
- Process Step Icon: represents a process step.
- Production Control Icon: represents production control.
- Inventory Icon: represents inventory.
- Arrow Icons:
- Push Arrow: represents push-type flow.
- Shipment Arrow: represents shipment.
- Electronic Information Arrow: represents electronic information flow.
- Manual Arrow: represents manual information flow.
Creating a Value Stream Map
- Start with the customer and work from right to left, then left to right, and back up to the customer.
- Identify process steps, process flow, and information flow.
- Collect data on resource-based, time-based, and quality-based metrics.
Data Collection for Value Stream Mapping
- Resource-based data: batch size, people involved.
- Time-based data: set-up time, changeover time, value-added time, total time.
- Quality-based data: completion accuracy percentage.
Analyzing a Value Stream Map
- Identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement.
- Investigate issues and create projects to improve the process.
- Use the map to understand where to focus efforts for improvement.
When to Use a Value Stream Map
- When there are issues or bottlenecks in the process.
- For continuous improvement and identifying areas for improvement.
- For brainstorming and idea generation, to create a future state value stream map.
- To understand where issues are stemming from and to identify root causes.
Example of Using a Value Stream Map
- A client orders 200 units of a spark shift book series.
- The process is mapped out, including information flow and process flow.
- Issues are identified, such as:
- Only 25 units in stock.
- Decision to do a revision, which affects the process.
- Low accuracy rate with the supplier (70%).
- Long wait times between process steps.
- Projects are created to investigate and improve these areas.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.