Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is a primary function of epithelial tissue?
What is a primary function of epithelial tissue?
Which characteristic is distinctive of epithelial cells?
Which characteristic is distinctive of epithelial cells?
What defines the apical surface of an epithelial cell?
What defines the apical surface of an epithelial cell?
Which of the following correctly describes keratinised epithelial tissue?
Which of the following correctly describes keratinised epithelial tissue?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary role of tight junctions in epithelial cells?
What is the primary role of tight junctions in epithelial cells?
Signup and view all the answers
Which part of the kidney is primarily involved in the absorption and filtration of blood?
Which part of the kidney is primarily involved in the absorption and filtration of blood?
Signup and view all the answers
In the context of homeostasis, what is primarily maintained by epithelial tissues?
In the context of homeostasis, what is primarily maintained by epithelial tissues?
Signup and view all the answers
How does the structure of epithelial tissue contribute to its functions?
How does the structure of epithelial tissue contribute to its functions?
Signup and view all the answers
Which feature of epithelial membranes helps them define boundaries between body compartments?
Which feature of epithelial membranes helps them define boundaries between body compartments?
Signup and view all the answers
What does the concept of water balance refer to in physiology?
What does the concept of water balance refer to in physiology?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary role of exocrine glands?
What is the primary role of exocrine glands?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following pairs of glands functions primarily in hormone secretion?
Which of the following pairs of glands functions primarily in hormone secretion?
Signup and view all the answers
Which statement describes the concept of 'inside' as related to body fluids?
Which statement describes the concept of 'inside' as related to body fluids?
Signup and view all the answers
What could be a reason for significant water loss during exercise?
What could be a reason for significant water loss during exercise?
Signup and view all the answers
Which component of body water composition is most affected by dehydration from alcohol consumption?
Which component of body water composition is most affected by dehydration from alcohol consumption?
Signup and view all the answers
How much total body water would you expect in a typical 70 kg adult human?
How much total body water would you expect in a typical 70 kg adult human?
Signup and view all the answers
What effect does salty food, like popcorn, have on the body's hydration status?
What effect does salty food, like popcorn, have on the body's hydration status?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following could be classified as an endocrine gland?
Which of the following could be classified as an endocrine gland?
Signup and view all the answers
What is required for maintaining water balance in the body?
What is required for maintaining water balance in the body?
Signup and view all the answers
Which gland secretes testosterone as part of its endocrine function?
Which gland secretes testosterone as part of its endocrine function?
Signup and view all the answers
What percentage of total body water is considered intracellular fluid (ICF)?
What percentage of total body water is considered intracellular fluid (ICF)?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the total volume of extracellular fluid (ECF) in a 70 kg human?
What is the total volume of extracellular fluid (ECF) in a 70 kg human?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following fluids is classified as interstitial fluid?
Which of the following fluids is classified as interstitial fluid?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary solute concentration difference between plasma and muscle cells?
What is the primary solute concentration difference between plasma and muscle cells?
Signup and view all the answers
How much water must be consumed daily to avoid dehydration?
How much water must be consumed daily to avoid dehydration?
Signup and view all the answers
Which component accounts for the majority of extracellular fluid volume?
Which component accounts for the majority of extracellular fluid volume?
Signup and view all the answers
What leads to a state of acute dehydration despite adequate water retention?
What leads to a state of acute dehydration despite adequate water retention?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the total volume of intracellular fluid (ICF) in a typical 70 kg human?
What is the total volume of intracellular fluid (ICF) in a typical 70 kg human?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the impact of exercise on daily water balance?
What is the impact of exercise on daily water balance?
Signup and view all the answers
What does the osmolarity indicate about the balance of fluid between ICF and ECF?
What does the osmolarity indicate about the balance of fluid between ICF and ECF?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary method by which H2O is absorbed in the body?
What is the primary method by which H2O is absorbed in the body?
Signup and view all the answers
What role do transport proteins play in the movement of water across epithelia?
What role do transport proteins play in the movement of water across epithelia?
Signup and view all the answers
Which mechanism does NOT typically contribute to the loss of water from the body?
Which mechanism does NOT typically contribute to the loss of water from the body?
Signup and view all the answers
How does water primarily leave the body?
How does water primarily leave the body?
Signup and view all the answers
What causes water to cross epithelial cells if not through lipid bilayers?
What causes water to cross epithelial cells if not through lipid bilayers?
Signup and view all the answers
Which process greatly influences water reabsorption in the kidneys?
Which process greatly influences water reabsorption in the kidneys?
Signup and view all the answers
Which is NOT a way water can leave the body?
Which is NOT a way water can leave the body?
Signup and view all the answers
What happens to water during the filtration process in the kidneys?
What happens to water during the filtration process in the kidneys?
Signup and view all the answers
Why is water absorption in kidneys considered essential?
Why is water absorption in kidneys considered essential?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a consequence of lack of absorption in the gut?
What is a consequence of lack of absorption in the gut?
Signup and view all the answers
Which characteristic of epithelial cells significantly contributes to their ability to protect underlying tissues?
Which characteristic of epithelial cells significantly contributes to their ability to protect underlying tissues?
Signup and view all the answers
What role does the basolateral surface of an epithelial cell serve in fluid balance?
What role does the basolateral surface of an epithelial cell serve in fluid balance?
Signup and view all the answers
Which feature of stratified epithelial tissue supports its function in areas subject to abrasion?
Which feature of stratified epithelial tissue supports its function in areas subject to abrasion?
Signup and view all the answers
How do keratinized epithelial cells primarily adapt to environmental conditions?
How do keratinized epithelial cells primarily adapt to environmental conditions?
Signup and view all the answers
What main physiological concept is crucial for understanding the function of kidneys in relation to body water?
What main physiological concept is crucial for understanding the function of kidneys in relation to body water?
Signup and view all the answers
What distinguishes the apical surface from the basolateral surface in epithelial cells?
What distinguishes the apical surface from the basolateral surface in epithelial cells?
Signup and view all the answers
In the context of epithelial tissue, what does a lack of blood vessels signify?
In the context of epithelial tissue, what does a lack of blood vessels signify?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following best explains the role of epithelial tissues in maintaining water balance in the body?
Which of the following best explains the role of epithelial tissues in maintaining water balance in the body?
Signup and view all the answers
What primarily influences the absorption of nutrients in the gut epithelium?
What primarily influences the absorption of nutrients in the gut epithelium?
Signup and view all the answers
What distinguishes exocrine glands from endocrine glands?
What distinguishes exocrine glands from endocrine glands?
Signup and view all the answers
Which organ's endocrine function primarily involves the secretion of insulin?
Which organ's endocrine function primarily involves the secretion of insulin?
Signup and view all the answers
Which statement accurately describes the role of the pineal gland?
Which statement accurately describes the role of the pineal gland?
Signup and view all the answers
In the context of fluid classification, what does 'outside' refer to?
In the context of fluid classification, what does 'outside' refer to?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the total body water volume in a 70 kg human generally considered to be?
What is the total body water volume in a 70 kg human generally considered to be?
Signup and view all the answers
Why does the body lose water during exercise?
Why does the body lose water during exercise?
Signup and view all the answers
What primarily influences water reabsorption in the kidneys?
What primarily influences water reabsorption in the kidneys?
Signup and view all the answers
What effect does alcohol consumption have on hydration status?
What effect does alcohol consumption have on hydration status?
Signup and view all the answers
What is primarily maintained by the concept of homeostasis?
What is primarily maintained by the concept of homeostasis?
Signup and view all the answers
What primary process is responsible for the secretion of substances by glands?
What primary process is responsible for the secretion of substances by glands?
Signup and view all the answers
What percentage of total body water is classified as extracellular fluid (ECF)?
What percentage of total body water is classified as extracellular fluid (ECF)?
Signup and view all the answers
Which component of the extracellular fluid (ECF) has the highest volume?
Which component of the extracellular fluid (ECF) has the highest volume?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the total volume of intracellular fluid (ICF) in a typical 70 kg human?
What is the total volume of intracellular fluid (ICF) in a typical 70 kg human?
Signup and view all the answers
Which solute is present in a higher concentration in muscle cells compared to plasma?
Which solute is present in a higher concentration in muscle cells compared to plasma?
Signup and view all the answers
How much water does a typical human lose daily through urine?
How much water does a typical human lose daily through urine?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary component of interstitial fluid?
What is the primary component of interstitial fluid?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the osmolarity of both intracellular fluid (ICF) and extracellular fluid (ECF) in a healthy individual?
What is the osmolarity of both intracellular fluid (ICF) and extracellular fluid (ECF) in a healthy individual?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the total daily loss of water, excluding urine, in liters?
What is the total daily loss of water, excluding urine, in liters?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the role of osmolarity in the context of ICF and ECF?
What is the role of osmolarity in the context of ICF and ECF?
Signup and view all the answers
What could happen if daily water intake does not match daily water loss?
What could happen if daily water intake does not match daily water loss?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary mechanism through which H2O is absorbed in the gut?
What is the primary mechanism through which H2O is absorbed in the gut?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following pathways describes how H2O exits the body via the skin?
Which of the following pathways describes how H2O exits the body via the skin?
Signup and view all the answers
Which statement correctly describes a condition that leads to water loss in the gut?
Which statement correctly describes a condition that leads to water loss in the gut?
Signup and view all the answers
What role do transport proteins play in the movement of water across epithelial cells?
What role do transport proteins play in the movement of water across epithelial cells?
Signup and view all the answers
Which mechanism does NOT typically contribute to water entering the kidneys?
Which mechanism does NOT typically contribute to water entering the kidneys?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a primary function of filtration in the kidneys regarding water?
What is a primary function of filtration in the kidneys regarding water?
Signup and view all the answers
How does water primarily leave the body in the respiratory system?
How does water primarily leave the body in the respiratory system?
Signup and view all the answers
Which factor does NOT influence water reabsorption in the kidneys?
Which factor does NOT influence water reabsorption in the kidneys?
Signup and view all the answers
Which is a consequence of lack of water reabsorption in the kidneys?
Which is a consequence of lack of water reabsorption in the kidneys?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary driver for the movement of water out of the renal tubules?
What is the primary driver for the movement of water out of the renal tubules?
Signup and view all the answers
Epithelial tissue has a high density of blood vessels.
Epithelial tissue has a high density of blood vessels.
Signup and view all the answers
Stratified epithelial cells are typically found in areas subject to abrasion.
Stratified epithelial cells are typically found in areas subject to abrasion.
Signup and view all the answers
The apical surface of an epithelial cell faces the basement membrane.
The apical surface of an epithelial cell faces the basement membrane.
Signup and view all the answers
Keratinized epithelial cells are alive and moist.
Keratinized epithelial cells are alive and moist.
Signup and view all the answers
Tight junctions in epithelial cells prevent the passage of substances between cells.
Tight junctions in epithelial cells prevent the passage of substances between cells.
Signup and view all the answers
Epithelial membranes only absorb and filter substances.
Epithelial membranes only absorb and filter substances.
Signup and view all the answers
Kidneys are primarily involved in the excretion of water and solutes.
Kidneys are primarily involved in the excretion of water and solutes.
Signup and view all the answers
The concept of homeostasis is not essential for understanding physiology.
The concept of homeostasis is not essential for understanding physiology.
Signup and view all the answers
Epithelial cells can reproduce readily, enabling tissue repair.
Epithelial cells can reproduce readily, enabling tissue repair.
Signup and view all the answers
Epithelial tissue does not play any role in gas exchange.
Epithelial tissue does not play any role in gas exchange.
Signup and view all the answers
Exocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream.
Exocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream.
Signup and view all the answers
Total body water composition is approximately 60% by mass in a 70 kg human.
Total body water composition is approximately 60% by mass in a 70 kg human.
Signup and view all the answers
The pancreas serves exclusively as an endocrine gland.
The pancreas serves exclusively as an endocrine gland.
Signup and view all the answers
Melatonin is secreted by the adrenal glands.
Melatonin is secreted by the adrenal glands.
Signup and view all the answers
Kidneys regulate water balance by secreting renin, which contributes to homeostasis.
Kidneys regulate water balance by secreting renin, which contributes to homeostasis.
Signup and view all the answers
Salty foods like popcorn reduce thirst by retaining body water.
Salty foods like popcorn reduce thirst by retaining body water.
Signup and view all the answers
Hydration from drinking alcohol leads to increased body water.
Hydration from drinking alcohol leads to increased body water.
Signup and view all the answers
The outer skin layer is classified as 'inside' based on body fluid definitions.
The outer skin layer is classified as 'inside' based on body fluid definitions.
Signup and view all the answers
Endocrine tissues are mainly involved in filtration and absorption processes.
Endocrine tissues are mainly involved in filtration and absorption processes.
Signup and view all the answers
The concept of water balance is solely dependent on dietary water intake.
The concept of water balance is solely dependent on dietary water intake.
Signup and view all the answers
Water can cross a lipid bilayer due to transport proteins forming pores in the membrane.
Water can cross a lipid bilayer due to transport proteins forming pores in the membrane.
Signup and view all the answers
The only way water leaves the body is through secretion and evaporation.
The only way water leaves the body is through secretion and evaporation.
Signup and view all the answers
Filtration in the kidneys is responsible for filtering out all solutes except for water.
Filtration in the kidneys is responsible for filtering out all solutes except for water.
Signup and view all the answers
Secretion in the gut can lead to water loss, which is a major factor in diarrhea.
Secretion in the gut can lead to water loss, which is a major factor in diarrhea.
Signup and view all the answers
Reabsorption of water in the kidneys is governed solely by the presence of transport proteins.
Reabsorption of water in the kidneys is governed solely by the presence of transport proteins.
Signup and view all the answers
The filtration process in kidneys occurs through gaps between cells in the glomerulus.
The filtration process in kidneys occurs through gaps between cells in the glomerulus.
Signup and view all the answers
Evaporation from the skin is a minor route compared to renal filtration for water loss in the body.
Evaporation from the skin is a minor route compared to renal filtration for water loss in the body.
Signup and view all the answers
Water is primarily absorbed in the stomach before it reaches the intestines.
Water is primarily absorbed in the stomach before it reaches the intestines.
Signup and view all the answers
Health conditions affecting renal filtration can significantly alter water balance in the body.
Health conditions affecting renal filtration can significantly alter water balance in the body.
Signup and view all the answers
The process of water secretion in the lungs is a significant contributor to hydration levels.
The process of water secretion in the lungs is a significant contributor to hydration levels.
Signup and view all the answers
Total body water in a 70 kg human is 34 L.
Total body water in a 70 kg human is 34 L.
Signup and view all the answers
Intracellular fluid constitutes 67% of the total water in the body.
Intracellular fluid constitutes 67% of the total water in the body.
Signup and view all the answers
The extracellular fluid is exclusively composed of plasma.
The extracellular fluid is exclusively composed of plasma.
Signup and view all the answers
There are 50 million million cells in the human body.
There are 50 million million cells in the human body.
Signup and view all the answers
The daily loss of water through urine amounts to 2.5 L.
The daily loss of water through urine amounts to 2.5 L.
Signup and view all the answers
Interstitial fluid makes up 11 L of the total extracellular fluid.
Interstitial fluid makes up 11 L of the total extracellular fluid.
Signup and view all the answers
Osmolarity is different in intracellular and extracellular fluids.
Osmolarity is different in intracellular and extracellular fluids.
Signup and view all the answers
A human can survive nearly 17 days without water intake.
A human can survive nearly 17 days without water intake.
Signup and view all the answers
The composition of solutes in muscle cells shows higher potassium concentration compared to plasma.
The composition of solutes in muscle cells shows higher potassium concentration compared to plasma.
Signup and view all the answers
The skin accounts for 0.6 L of water loss daily.
The skin accounts for 0.6 L of water loss daily.
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
Understanding Systems & Integrated Physiology
- Module objective: To lay the foundation for understanding systems & integrated physiology, the relationship between normal physiological processes and disease, in the context of homeostasis.
Epithelial Tissue & Body Water
- Epithelial tissue protects, secretes, absorbs and excretes.
- Epithelial tissue covers body surfaces (inside and out) and glands.
- Epithelial tissue has no blood vessels, is reproduced readily and consists of tightly packed cells.
- Epithelial tissue defines the boundary of body compartments.
Exploring Epithelial Tissue
- Epithelial tissue examples include skin, sweat glands, mouth, lips, lungs, gut, kidneys, and blood vessels.
- Epithelial tissue forms membranes, which define boundaries between body compartments.
- Epithelial membranes include stratified layers or monolayers.
- Monolayers have an apical surface, basolateral surface, and a basement membrane.
- The apical surface is exposed to outside or internal open space.
- The basolateral surface links to connective tissue via the basement membrane
- Epithelial cells are held together by tight junctions.
- Monolayers can be keratinised (dead & dry) like outer skin or non-keratinised (alive & moist) like the inside of the mouth and lungs.
- Epithelial tissue forms glands which secrete into or out of the body.
- Glands can be endocrine (secreting hormones into the blood) or exocrine (secreting substances via ducts).
- Endocrine glands examples: pancreas, testes, ovaries.
- Exocrine gland examples: pancreas, testes, ovaries, tear glands, sweat glands, salivary glands, gastric glands.
Inside vs. Outside Bodies
- "Inside" refers to the blood or lymph system.
- "Outside" refers to the skin, lung, kidney tubules, or digestive tract.
Body Water Overview
- Total body water in a 70 kg human is 42 L (55-60% by mass).
- Daily water loss occurs via kidneys (urine), lungs, skin/sweat, faeces.
- Intake must match loss to avoid dehydration.
- Exercise, external temperature, coffee/alcohol/salt intake, and/or disease can affect the rate of water loss dramatically.
Body Water Composition
- 67% of body water is intracellular fluid (ICF).
- 33% of body water is extracellular fluid (ECF).
- ECF includes 3 L of plasma (liquid component of blood) and 11 L of interstitial fluid (solution bathing cells).
ICF vs. ECF
- ICF and ECF differ in solute concentration but have the same osmolarity, preventing net water movement.
Water Transport Across Epithelia
- Water is absorbed in the gut and reabsorbed in the kidney.
- Water is secreted and evaporated from the lungs and skin.
- Water is secreted and/or not absorbed in the gut during diarrhoea (Micro/Path).
- Water is filtered/secreted and/or not reabsorbed in the kidney.
- Water cannot cross a lipid bilayer but can cross epithelia via filtration or transport proteins.
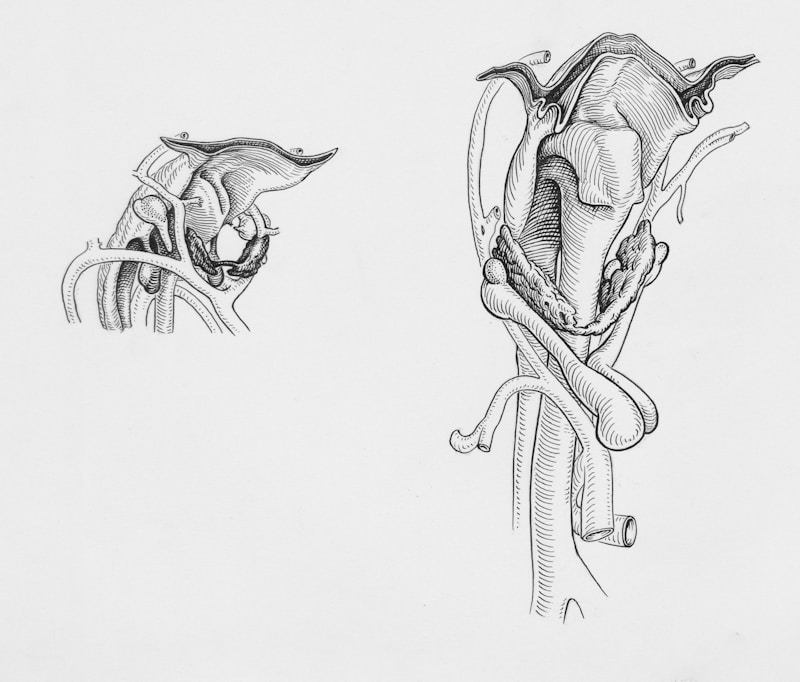
Kidneys & Water Filtration
- Kidneys filter plasma continually.
- All water and small solutes are filtered through the gaps between cells in the glomerulus.
Mechanisms for Water Balance
- Water enters the body via drinking and absorption in the gut.
- Water leaves the body via secretion and evaporation from the lungs and skin, secretion and lack of absorption in the gut (diarrhoea), filtration and secretion/lack of reabsorption in the kidney.
- Water balance is maintained by intake and excretion.
- Intake must match loss to avoid dehydration.
- Homeostasis is the fundamental principle of physiology, and water balance is a key example of homeostasis.
Introductory Physiology - Lectures 1-8
- The body is organized into systems, composed of tissues, cells, and genes
- Human body is 55-60% water by mass, approximately 42 liters
- The body's water is divided into intracellular fluid (ICF) and extracellular fluid (ECF)
- ICF is within cells, approximately 28 liters (67% of total water)
- ECF is outside cells, approximately 14 liters (33% of total water)
- ECF includes plasma (3 liters) and interstitial fluid (11 liters)
- Typical daily water loss is approximately 2.5 liters
- Water loss occurs through urine (1.5 L), lungs (0.3 L), skin/sweat (0.6 L), and feces (0.1 L).
- Dehydration can occur if intake does not match loss
- Epithelial tissues protect, secrete, absorb, and excrete
- Found covering body surfaces (inside and out) and glands
- No blood vessels, readily reproduced, tightly packed cells
- Epithelial cells form membranes that define boundaries between body compartments
- Apical surface faces the outside or internal open space
- Basolateral surface connects to connective tissue via the basement membrane
- Cells are held together by tight junctions
- Can be keratinized (dead, dry, like skin) or non-keratinized (alive, moist, like the inside of the mouth)
- Epithelial cells form glands
- Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream
- Exocrine glands secrete substances through ducts, like sweat glands, salivary glands, and digestive glands
- Water cannot cross a lipid bilayer directly, requiring specialized transport mechanisms across epithelia
- Filtration occurs in the kidneys, where plasma is filtered through gaps in the glomerulus
- (Re)absorption and secretion occur in other epithelial cells via transport proteins that form pores in the membrane
- The concentration of solutes varies between ICF and ECF, however, osmolarity is the same
- This balance prevents net water movement between the compartments
- Osmosis and passive transport through epithelial cell membranes play a key role in water movement
- Water balance is regulated by intake, filtration and reabsorption in the kidneys
- Maintaining water balance is vital & essential for homeostasis
Body organization and function
- The body is organized into systems, tissues, cells.
- Normal physiological function is linked to disease
- Homeostasis is the fundamental principle of physiology
Epithelial Tissue
- Covers body surfaces both inside and out, as well as glands.
- Epithelial tissue has no blood vessels, but it can be readily reproduced.
- The cells are densely packed together.
Epithelial Tissue: Location
- Epithelial tissue is found in skin, sweat glands, mouth, lips, lungs, gut, kidneys, and blood vessels.
Epithelial Tissue: Functions
- Protects, secretes, absorbs, and excretes.
- Defines boundaries between body compartments.
Epithelial Tissue: Characteristics
- Tightly packed cells
- Cells are connected by tight junctions
- Epithelial cells can be keratinised (dead/dry) or non-keratinised (alive/moist).
Epithelial Tissue: Glands
- Epithelial cells can form glands that secrete into or out of the body.
- Endocrine glands secrete substances inside the body, for example, the pancreas secretes insulin into blood and the kidneys secrete renin.
- Exocrine glands secrete substances outside the body, for example, the pancreas secretes digestive enzymes into the gastrointestinal tract, tears glands secrete tears, sweat glands secrete sweat, and salivary glands secrete saliva.
Outside vs Inside
- "Outside" refers to skin, lung, kidney tubules, or digestive tract.
- "Inside" refers to blood or lymph systems.
Body Water
- The body water content of a 70 kg human is 42 L.
- Body water represents 55-60% of body mass.
- Most of the water in a body is found inside cells (intracellular fluid).
- The extracellular fluid is made up of plasma (blood) and interstitial fluid (around cells).
Body Water Composition
- The composition of intracellular fluid (ICF) and extracellular fluid (ECF) differs.
- Osmolarity is the same in both compartments, so there is no net water movement.
Water Balance
- The intake of water must match the loss of water to avoid dehydration.
- A normal daily loss of water ranges from 2.5L.
- Causes for increased water loss include exercise, external temperature, coffee/alcohol/salt intake, or disease.
Water Transport
- Water can cross epithelia, but not a lipid bilayer.
- Water transport is achieved through:
- Filtration of blood via gaps between cells in the glomerulus.
- (Re)absorption/secretion via transport proteins that form pores in cell membranes.
Kidney function
- Kidneys filter plasma continuously.
- This process is achieved by filtering water and small solutes through the kidneys.
- This filtration process is a key function of how the body maintains water balance.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
This quiz explores the key concepts of epithelial tissue and its role in integrated physiology. You'll learn about the structure, functions, and examples of epithelial tissues throughout the body, as well as their significance in maintaining homeostasis. Prepare to test your knowledge on how this crucial tissue type interacts with other physiological processes.