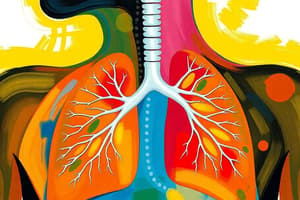
Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary purpose of gas exchange in organisms?
What is the primary purpose of gas exchange in organisms?
To support cellular respiration by taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide.
List the three adaptations that facilitate gas exchange in animals.
List the three adaptations that facilitate gas exchange in animals.
Respiratory surfaces remain moist, are very thin, and have a large surface area.
How does diffusion support gas exchange?
How does diffusion support gas exchange?
Diffusion allows molecules to move from high to low concentration areas, facilitating gas exchange.
What are the two main parts of the human respiratory system?
What are the two main parts of the human respiratory system?
Why must respiratory surfaces remain moist?
Why must respiratory surfaces remain moist?
What role does the respiratory system play in cellular respiration?
What role does the respiratory system play in cellular respiration?
Explain the importance of having thin respiratory surfaces.
Explain the importance of having thin respiratory surfaces.
What is the relationship between concentration gradients and gas exchange?
What is the relationship between concentration gradients and gas exchange?
What role does the epiglottis play during normal breathing?
What role does the epiglottis play during normal breathing?
How are vocal sounds produced in the larynx?
How are vocal sounds produced in the larynx?
Describe the pathway air follows as it enters the respiratory system.
Describe the pathway air follows as it enters the respiratory system.
What happens to the epiglottis during swallowing?
What happens to the epiglottis during swallowing?
What is the function of the trachea in the respiratory system?
What is the function of the trachea in the respiratory system?
Explain the branching process that occurs within the lungs.
Explain the branching process that occurs within the lungs.
Identify the main components of the conducting portion of the respiratory system.
Identify the main components of the conducting portion of the respiratory system.
What are the vocal cords and what is their significance?
What are the vocal cords and what is their significance?
What role do alveoli play in gas exchange?
What role do alveoli play in gas exchange?
How does the presence of surfactant in the alveoli assist the gas exchange process?
How does the presence of surfactant in the alveoli assist the gas exchange process?
Describe the composition of the respiratory membrane.
Describe the composition of the respiratory membrane.
What is the significance of having approximately 300 million alveoli in an adult's lungs?
What is the significance of having approximately 300 million alveoli in an adult's lungs?
Explain how gases diffuse in the lungs.
Explain how gases diffuse in the lungs.
What role do capillaries play in the gas exchange process?
What role do capillaries play in the gas exchange process?
Why is it important for the alveolar walls to be thin?
Why is it important for the alveolar walls to be thin?
Discuss how the moist environment of the alveoli aids in gas exchange.
Discuss how the moist environment of the alveoli aids in gas exchange.
How does hemoglobin contribute to oxygen transport in the blood?
How does hemoglobin contribute to oxygen transport in the blood?
Describe the process of carbon dioxide transport in the bloodstream.
Describe the process of carbon dioxide transport in the bloodstream.
What role do diffusion gradients play in gas exchange in the lungs and body tissues?
What role do diffusion gradients play in gas exchange in the lungs and body tissues?
What structural change occurs in hemoglobin when oxygen binds to it?
What structural change occurs in hemoglobin when oxygen binds to it?
Explain the significance of bicarbonate ions in carbon dioxide transport.
Explain the significance of bicarbonate ions in carbon dioxide transport.
How does the diaphragm contribute to the process of inhalation?
How does the diaphragm contribute to the process of inhalation?
What happens to the diaphragm and rib muscles during exhalation?
What happens to the diaphragm and rib muscles during exhalation?
What role does the respiratory center in the brain play in breathing?
What role does the respiratory center in the brain play in breathing?
How does the body ensure constant CO2 levels during respiration?
How does the body ensure constant CO2 levels during respiration?
In what way is inhalation considered an active process?
In what way is inhalation considered an active process?
What triggers the contraction of the diaphragm and rib muscles?
What triggers the contraction of the diaphragm and rib muscles?
Describe the process of passive exhalation.
Describe the process of passive exhalation.
What is the significance of the diaphragm's dome shape when relaxed?
What is the significance of the diaphragm's dome shape when relaxed?
Flashcards
Inhalation
Inhalation
The process of breathing that draws air into the lungs.
Exhalation
Exhalation
The process of breathing that pushes air out of the lungs.
Diaphragm
Diaphragm
The muscle that forms the lower boundary of the chest cavity. It contracts and moves down during inhalation, and relaxes and domes upward during exhalation.
Rib Muscles
Rib Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiratory Center
Respiratory Center
Signup and view all the flashcards
CO2 Receptors
CO2 Receptors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Breathing Rate
Breathing Rate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Breathing Volume
Breathing Volume
Signup and view all the flashcards
Conducting Portion of the Respiratory System
Conducting Portion of the Respiratory System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pharynx
Pharynx
Signup and view all the flashcards
Larynx
Larynx
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epiglottis
Epiglottis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vocal Cords
Vocal Cords
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trachea
Trachea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bronchi
Bronchi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveoli
Alveoli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Respiration
Respiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cellular respiration
Cellular respiration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diffusion
Diffusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Concentration gradients
Concentration gradients
Signup and view all the flashcards
Conducting portion
Conducting portion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas-exchange portion
Gas-exchange portion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas Exchange
Gas Exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Requirements for gas exchange
Requirements for gas exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
Human respiratory system
Human respiratory system
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxygenation of Hemoglobin
Oxygenation of Hemoglobin
Signup and view all the flashcards
CO2 Transport
CO2 Transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bicarbonate Formation
Bicarbonate Formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are alveoli?
What are alveoli?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is surfactant?
What is surfactant?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does gas exchange occur?
How does gas exchange occur?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the respiratory membrane?
What is the respiratory membrane?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is gas exchange?
What is gas exchange?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are capillaries?
What are capillaries?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are epithelial cells?
What are epithelial cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How many alveoli are in the average adult's lungs?
How many alveoli are in the average adult's lungs?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Respiration in BIOL160 Chapter 34
- Gas exchange is fundamental to cellular respiration, supplying organisms with oxygen and removing carbon dioxide.
- Respiration is the process by which organisms exchange gases with the environment
- Cellular respiration converts nutrients into ATP (energy), requiring oxygen and producing carbon dioxide as waste.
- Gas exchange in all organisms relies on diffusion.
Requirements for Gas Exchange
- For diffusion to occur effectively, respiratory surfaces must be moist.
- To minimize diffusion distances, respiratory surfaces must be thin.
- Respiratory surfaces need a large surface area to meet organismal needs.
Human Respiratory System: Structure and Function
- The human respiratory system is divided into two parts: conducting portion and gas-exchange portion.
- The conducting portion consists of passageways that carry air to and from the gas-exchange portion.
- The gas-exchange portion, located in the lungs, is where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged with the blood.
Conducting Portion of the System
-
Air enters through the nose or mouth, entering the nasal or oral cavity, and passing into the pharynx.
-
It then travels to the larynx ("voice box") where sound is produced.
-
The epiglottis, a flap of tissue, covers the larynx during swallowing, preventing food and liquids from entering the respiratory tract
-
The trachea (windpipe) is a flexible tube, reinforced with cartilage, conducting air to the lungs.
-
The trachea branches into two bronchi, one leading to each lung.
-
Bronchi branch into smaller bronchioles, which lead to microscopic alveoli.
-
Breathing is an active process for inhalation and passive for exhalation.
-
Inhalation involves diaphragm contraction and rib muscle contraction to expand the chest cavity.
-
Exhalation is when the diaphragm relaxes and the chest cavity decreases in size, forcing air out.
-
The respiratory system is controlled by a respiratory center within the brain's medulla. This center adjusts breathing rate and volume based on changing body needs.
Gas Exchange in Alveoli
- Gas exchange in humans occurs in the alveoli, tiny air sacs in the lungs.
- The alveoli provide a large surface area for gas exchange.
- Alveolar walls are extremely thin to minimize diffusion distances.
- Surfactant, a detergent-like substance, prevents alveolar collapse during exhalation.
- A network of capillaries surrounds alveoli, facilitating gas exchange between air and blood.
Gas Transport in Blood
- Oxygen (O2) binds to hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells, for transport
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) is transported in the blood through several mechanisms, including dissolution in plasma, binding with hemoglobin, and conversion to bicarbonate ions.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Explore the essential concepts of gas exchange and cellular respiration covered in BIOL160 Chapter 34. Understand the structure and function of the human respiratory system and the requirements for effective gas exchange. This quiz will enhance your knowledge of how organisms, including humans, perform respiration.