Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary functional unit of the kidney responsible for urine formation?
What is the primary functional unit of the kidney responsible for urine formation?
Which imaging study is NOT mentioned as a diagnostic tool for renal assessment?
Which imaging study is NOT mentioned as a diagnostic tool for renal assessment?
What symptom is NOT reported by Mr. Jones during his healthcare visit?
What symptom is NOT reported by Mr. Jones during his healthcare visit?
Elevated levels of which substance in Mr. Jones' laboratory values indicate potential issues with renal function?
Elevated levels of which substance in Mr. Jones' laboratory values indicate potential issues with renal function?
Signup and view all the answers
What does the presence of high specific gravity in urine typically indicate?
What does the presence of high specific gravity in urine typically indicate?
Signup and view all the answers
In which physical assessment finding did Mr. Jones present during the examination?
In which physical assessment finding did Mr. Jones present during the examination?
Signup and view all the answers
What condition was Mr. Jones diagnosed with based on his symptoms and assessment?
What condition was Mr. Jones diagnosed with based on his symptoms and assessment?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following components is not part of the urinary system?
Which of the following components is not part of the urinary system?
Signup and view all the answers
What should the nurse implement first for Mr. Jones after receiving the provider's orders?
What should the nurse implement first for Mr. Jones after receiving the provider's orders?
Signup and view all the answers
Which laboratory value should be reported to the provider most urgently for Mr. Jones?
Which laboratory value should be reported to the provider most urgently for Mr. Jones?
Signup and view all the answers
Which priority nursing intervention should the nurse implement for Mr. Jones?
Which priority nursing intervention should the nurse implement for Mr. Jones?
Signup and view all the answers
What priority nursing diagnosis should be included in Mr. Jones's plan of care?
What priority nursing diagnosis should be included in Mr. Jones's plan of care?
Signup and view all the answers
Which statement by Mr. Jones shows effective understanding of discharge teaching?
Which statement by Mr. Jones shows effective understanding of discharge teaching?
Signup and view all the answers
What vital sign indicates a need for further assessment in Mr. Jones?
What vital sign indicates a need for further assessment in Mr. Jones?
Signup and view all the answers
What finding from the lab results suggests a decline in renal function for Mr. Jones?
What finding from the lab results suggests a decline in renal function for Mr. Jones?
Signup and view all the answers
Which symptom reported by Mr. Jones could indicate worsening renal insufficiency?
Which symptom reported by Mr. Jones could indicate worsening renal insufficiency?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a significant physical assessment finding noted in Mr. Jones during his admission?
What is a significant physical assessment finding noted in Mr. Jones during his admission?
Signup and view all the answers
Which nursing diagnosis is most appropriate for Mr. Jones based on his symptoms?
Which nursing diagnosis is most appropriate for Mr. Jones based on his symptoms?
Signup and view all the answers
Which laboratory value indicates a potential need for immediate intervention?
Which laboratory value indicates a potential need for immediate intervention?
Signup and view all the answers
What change in Mr. Jones's diet should be emphasized for his renal health?
What change in Mr. Jones's diet should be emphasized for his renal health?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the expected outcome of daily weight monitoring for Mr. Jones?
What is the expected outcome of daily weight monitoring for Mr. Jones?
Signup and view all the answers
Which nursing intervention will help address Mr. Jones's lethargy and changes in mental status?
Which nursing intervention will help address Mr. Jones's lethargy and changes in mental status?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary reason Mr. Jones is concerned about his health?
What is the primary reason Mr. Jones is concerned about his health?
Signup and view all the answers
Which diagnostic study was ordered to evaluate possible blockages in the urinary tract?
Which diagnostic study was ordered to evaluate possible blockages in the urinary tract?
Signup and view all the answers
What symptom could indicate worsening renal function in Mr. Jones?
What symptom could indicate worsening renal function in Mr. Jones?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following statements indicates Mr. Jones has understood the discharge instructions regarding weight management?
Which of the following statements indicates Mr. Jones has understood the discharge instructions regarding weight management?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a possible consequence of Mr. Jones' uncontrolled hypertension?
What is a possible consequence of Mr. Jones' uncontrolled hypertension?
Signup and view all the answers
Which symptom suggests that Mr. Jones may be experiencing fluid retention?
Which symptom suggests that Mr. Jones may be experiencing fluid retention?
Signup and view all the answers
Which lab value indicates a potential issue with Mr. Jones' kidneys?
Which lab value indicates a potential issue with Mr. Jones' kidneys?
Signup and view all the answers
What physical examination finding was noted during Mr. Jones' assessment?
What physical examination finding was noted during Mr. Jones' assessment?
Signup and view all the answers
What role do the kidneys play in maintaining bodily functions?
What role do the kidneys play in maintaining bodily functions?
Signup and view all the answers
Which condition is likely related to Mr. Jones’ symptoms and assessment findings?
Which condition is likely related to Mr. Jones’ symptoms and assessment findings?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
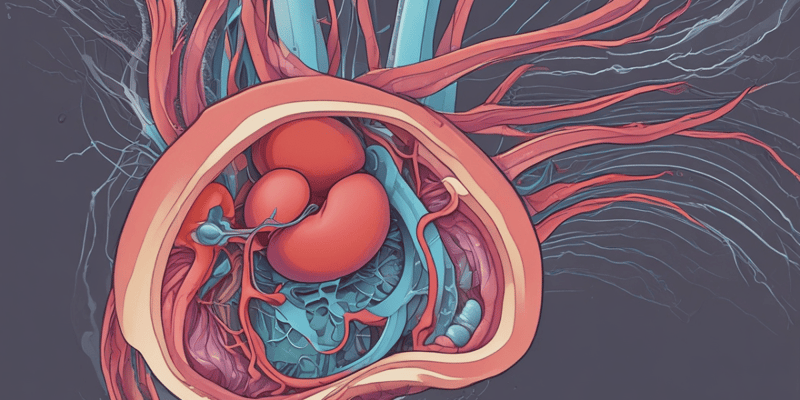
Renal System
- Consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
- Kidneys filter waste and produce urine
- The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney
Urinary System
- Ureters: carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder
- Urinary Bladder: stores urine
- Urethra: transports urine from the bladder to the outside of the body
Renal Anatomy
- The nephron consists of the glomerulus, Bowman's capsule, and a tubular system
Renal Physiology
- The kidneys produce urine through a process of filtration and excretion
- Key functions include:
- Regulation of body fluid volume and electrolyte balance
- Regulation of acid-base balance
- Hormonal functions
Assessment of Renal and Urinary Systems
-
History:
- Demographics and personal data
- Personal and family health history
- Medication use
- Renal and urinary assessment
-
Physical Examination:
- Inspection
- Auscultation
- Palpation
- Percussion
Diagnostic Studies
-
Laboratory Studies:
- Blood tests
- Urine tests
- High specific gravity indicates dehydration
-
Imaging Studies:
- Bedside sonography
- X-ray
- Intravenous urography
- Renal ultrasound
- Computed tomography (CT) Scan
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Cystography and urethrography
- Arteriography
- Renography
- Renal biopsy
- Cystoscopy
Case Study: Reginald Jones
- 72-year-old Black male presents with:
- Recent weight gain
- Swelling in hands and feet
- Voiding only small amounts of urine
- Fatigue
- Has a history of depression and borderline hypertension
- Vital signs:
- Hypertension (blood pressure 188/92 mmHg)
- Heart rate 94 bpm
- Respirations 22
- Temperature 98.2°F (36.8°C)
- O2 saturation 94% on room air
- Laboratory values:
- Elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
- Elevated creatinine
- Elevated potassium
- Elevated phosphorus
- Decreased calcium
- Physical assessment:
- Lethargic
- Pallor (pale skin)
- Peripheral edema (swelling in extremities)
- Ultrasound and CT scan are negative for masses or obstructions
- Diagnosed with renal insufficiency likely related to uncontrolled hypertension
Case Study: Treatment and Nursing Interventions
-
Treatment:
- Hospital admission for monitoring and treatment
- Management of hypertension and renal insufficiency
-
Nurse's Role:
-
Priority Orders:
- Administer furosemide (Lasix) IV daily
- Implement fluid restriction (less than 1,500 mL/24 hr)
- Monitor urine specific gravity
- Instruct patient to follow a low-sodium diet
-
Most Urgent Laboratory Value:
- Potassium 5.7 mEq/L (elevated)
-
Priority Nursing Interventions:
- Strict monitoring of intake and output
- Frequent monitoring of vital signs
- Safety/fall precautions
- Daily weights
-
Priority Nursing Diagnoses:
- Risk for imbalanced fluid volume
- Impaired urinary elimination
-
Effective Discharge Teaching:
- Monitoring weight daily
- Taking blood pressure medications as prescribed
- Avoiding over-the-counter NSAIDs (Motrin)
- Consulting with healthcare provider about potassium intake
-
Priority Orders:
Renal System Overview
- The renal system consists of the kidneys, which filter waste and excess fluid from the blood, and the urinary system which includes ureters, bladder, and urethra.
- The kidneys contain nephrons which are the functional units of the kidney responsible for filtering waste and producing urine.
- The nephron consists of the glomerulus (a network of capillaries), Bowman's capsule (surrounds the glomerulus), and a tubular system.
Renal Physiology
- Urine formation is a key function of the kidneys and is regulated by the balance of fluids, electrolytes, and acid-base balance.
- The kidneys also play a role in several hormonal functions.
Renal Assessment
- A comprehensive assessment includes a thorough medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic studies.
Physical Examination
- Includes inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation.
Diagnostic Studies for Renal System
-
Laboratory Studies:
- Analyze blood and urine samples.
- Elevated BUN, creatinine, potassium, and phosphorus are related to kidney disease.
- Decreased calcium also often occurs in renal insufficiency.
- High urine Specific Gravity suggests dehydration
-
Imaging Studies:
- Bedside Sonography, X-Ray, Intravenous Urography, Renal Ultrasound are used for initial screening and visualizing the kidneys, ureters, and bladder.
- CT scan and MRI provide detailed anatomical information.
- Cystography and Urethrography are used to visualize the bladder and urethra.
- Arteriography visualizes the blood vessels.
- Renography assesses kidney function.
- Renal Biopsy provides a tissue sample for microscopic analysis.
- Cystoscopy allows visual inspection of the bladder and urethra.
Case Study: Reginald Jones
- Reginald Jones is a 72-year-old Black male presenting with symptoms of renal insufficiency likely caused by uncontrolled hypertension.
-
Pertinent History:
- History of borderline hypertension (not currently being treated)
- Weight gain, fatigue, changes in mental status, and decreased urine output
-
Physical Exam:
- Lethargic, pallor, bilateral pedal edema
-
Laboratory Results:
- Elevated BUN, creatinine, potassium, phosphorus, and decreased calcium
-
Diagnostic tests:
- Ultrasound and CT scans revealed no masses or obstructions
-
Diagnosis:
- Renal insufficiency likely due to uncontrolled hypertension
Case Study: Nursing Interventions
- Priority Intervention (Answer 1): Administer 40 mg furosemide (Lasix) IV daily. (Lasix is a diuretic that will help to reduce fluid volume and edema)
- Most Urgent Lab Value to Report (Answer 2): Potassium 5.7 mEq/L (Elevated potassium can lead to cardiac arrhythmias)
-
Priority Nursing Interventions (Answers 3-5):
- Strict Intake & Output monitoring
- Frequent vital sign monitoring
- Safety/Fall Precautions (due to altered mental status and potential electrolyte imbalances)
- Daily weights
- Priority Nursing Diagnoses:
- Risk for Imbalanced Fluid Volume
- Impaired Urinary Elimination
Discharge Teaching
- Effective Teaching (Answer 5): " I should carefully monitor and record my weight each day" (Monitoring weight indicates changes in fluid status, a key indicator of renal function).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
This quiz covers key aspects of the renal and urinary system, including anatomy, physiology, and assessment methods. You will learn about the structure and function of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. Test your understanding of how these systems work together to maintain homeostasis and health.