Podcast
Questions and Answers
What primarily drives the movement of gases from the alveoli into the blood?
What primarily drives the movement of gases from the alveoli into the blood?
- Temperature gradients
- Solubility in blood
- Concentration gradients (correct)
- Electrochemical gradients
Which gas constitutes approximately 21% of the Earth's atmosphere?
Which gas constitutes approximately 21% of the Earth's atmosphere?
- Oxygen (correct)
- Nitrogen
- Hydrogen
- Carbon Dioxide
At sea level, what is the standard atmospheric pressure in mm Hg?
At sea level, what is the standard atmospheric pressure in mm Hg?
- 253 mm Hg
- 760 mm Hg (correct)
- 500 mm Hg
- 600 mm Hg
What is the partial pressure of nitrogen (PN2) in the atmosphere at sea level?
What is the partial pressure of nitrogen (PN2) in the atmosphere at sea level?
During inhalation, what is the first process that affects the inhaled air?
During inhalation, what is the first process that affects the inhaled air?
Which of the following statements is true about the partial pressures of gases at sea level?
Which of the following statements is true about the partial pressures of gases at sea level?
What is the relationship between total atmospheric pressure and the partial pressure of a gas?
What is the relationship between total atmospheric pressure and the partial pressure of a gas?
What happens to gas molecules in terms of pressure during gas exchange?
What happens to gas molecules in terms of pressure during gas exchange?
What is the primary reason carbon dioxide can diffuse across the alveolar capillary despite having a lower driving force compared to oxygen?
What is the primary reason carbon dioxide can diffuse across the alveolar capillary despite having a lower driving force compared to oxygen?
During rest, what is the approximate volume of oxygen that needs to enter the capillary per 100 ml of blood?
During rest, what is the approximate volume of oxygen that needs to enter the capillary per 100 ml of blood?
How much time is required for oxygen equilibration in the capillary under resting conditions?
How much time is required for oxygen equilibration in the capillary under resting conditions?
What happens to the oxygen saturation of blood during strenuous exercise?
What happens to the oxygen saturation of blood during strenuous exercise?
What is the driving force for oxygen diffusion across the alveolar capillary at rest?
What is the driving force for oxygen diffusion across the alveolar capillary at rest?
Which factor contributes most to the enhanced oxygen demand during strenuous exercise?
Which factor contributes most to the enhanced oxygen demand during strenuous exercise?
In the context of gas exchange, which of the following statements is true regarding the safety margin?
In the context of gas exchange, which of the following statements is true regarding the safety margin?
What does the difference in partial pressures (ΔP) for carbon dioxide indicate?
What does the difference in partial pressures (ΔP) for carbon dioxide indicate?
What phenomenon refers to the increased bicarbonate levels and decreased chloride levels in venous blood?
What phenomenon refers to the increased bicarbonate levels and decreased chloride levels in venous blood?
What is the partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) at the arterial end of the pulmonary capillaries?
What is the partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) at the arterial end of the pulmonary capillaries?
What is the primary factor that allows carbon dioxide to diffuse readily from cells into the interstitium?
What is the primary factor that allows carbon dioxide to diffuse readily from cells into the interstitium?
What happens to venous PCO2 levels if carbonic anhydrase is inhibited?
What happens to venous PCO2 levels if carbonic anhydrase is inhibited?
At rest, how much oxygen do the tissues of the body require per minute?
At rest, how much oxygen do the tissues of the body require per minute?
What is the percentage of oxygen saturation of hemoglobin at a partial pressure of oxygen of 40 mm Hg in venous blood?
What is the percentage of oxygen saturation of hemoglobin at a partial pressure of oxygen of 40 mm Hg in venous blood?
What is the venous end partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PCO2) when entering the alveolar capillary?
What is the venous end partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PCO2) when entering the alveolar capillary?
In venous blood, what form does the majority of carbon dioxide take as it is transported to the lungs?
In venous blood, what form does the majority of carbon dioxide take as it is transported to the lungs?
What is the partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) in systemic arterial blood compared to venous blood?
What is the partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) in systemic arterial blood compared to venous blood?
If the partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) is 40 mm Hg, how much oxygen is dissolved in every deciliter of blood?
If the partial pressure of oxygen (PO2) is 40 mm Hg, how much oxygen is dissolved in every deciliter of blood?
What equation would yield the amount of oxygen deliverable if only dissolved oxygen was transported in blood?
What equation would yield the amount of oxygen deliverable if only dissolved oxygen was transported in blood?
What is the concentration of carbon dioxide dissolved in venous blood compared to bicarbonate?
What is the concentration of carbon dioxide dissolved in venous blood compared to bicarbonate?
What is the overall intracellular partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PCO2)?
What is the overall intracellular partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PCO2)?
What is the driving pressure forcing oxygen into plasma at the arterial end of a pulmonary capillary?
What is the driving pressure forcing oxygen into plasma at the arterial end of a pulmonary capillary?
What is the difference in the dissolved oxygen amounts at PO2 levels of 95 mm Hg and 40 mm Hg?
What is the difference in the dissolved oxygen amounts at PO2 levels of 95 mm Hg and 40 mm Hg?
What percentage of carbon dioxide is transported in blood as CO2 in solution?
What percentage of carbon dioxide is transported in blood as CO2 in solution?
What percentage of oxygen delivery to tissues occurs in the form of free solution?
What percentage of oxygen delivery to tissues occurs in the form of free solution?
How much oxygen can each gram of hemoglobin bind?
How much oxygen can each gram of hemoglobin bind?
At a partial pressure of 95 mm Hg, what is the saturation percentage of hemoglobin with oxygen?
At a partial pressure of 95 mm Hg, what is the saturation percentage of hemoglobin with oxygen?
What is the total potential oxygen output to circulation each minute at a resting cardiac output of 5 L/min?
What is the total potential oxygen output to circulation each minute at a resting cardiac output of 5 L/min?
What is the amount of oxygen consumed per minute by the tissues at a partial pressure of 40 mm Hg?
What is the amount of oxygen consumed per minute by the tissues at a partial pressure of 40 mm Hg?
What is the relationship between hemoglobin saturation and oxygen partial pressure when the P O2 falls to 40 mm Hg?
What is the relationship between hemoglobin saturation and oxygen partial pressure when the P O2 falls to 40 mm Hg?
What is the calculated amount of oxygen delivered to the tissues at rest?
What is the calculated amount of oxygen delivered to the tissues at rest?
What percentage of oxygen in the blood is contributed by free solution when cardiac output is at rest?
What percentage of oxygen in the blood is contributed by free solution when cardiac output is at rest?
What physiological change occurs to optimize oxygen uptake in the lungs due to the Bohr Effect?
What physiological change occurs to optimize oxygen uptake in the lungs due to the Bohr Effect?
Which factor does NOT contribute to shifting the hemoglobin dissociation curve to the left?
Which factor does NOT contribute to shifting the hemoglobin dissociation curve to the left?
What percentage of carbon dioxide is carried in blood as bicarbonate (HCO3-)?
What percentage of carbon dioxide is carried in blood as bicarbonate (HCO3-)?
Why is fetal hemoglobin more effective than adult hemoglobin in extracting oxygen from maternal circulation?
Why is fetal hemoglobin more effective than adult hemoglobin in extracting oxygen from maternal circulation?
What occurs to the hemoglobin dissociation curve when oxygenated blood reaches systemic capillaries?
What occurs to the hemoglobin dissociation curve when oxygenated blood reaches systemic capillaries?
Which condition would likely cause hypocapnia, affecting the oxygen dissociation curve?
Which condition would likely cause hypocapnia, affecting the oxygen dissociation curve?
How much carbon dioxide must be transported from the tissues to the lungs per 100 ml of blood?
How much carbon dioxide must be transported from the tissues to the lungs per 100 ml of blood?
What is the primary reason fetal hemoglobin does not release its oxygen as readily?
What is the primary reason fetal hemoglobin does not release its oxygen as readily?
Flashcards
Partial Pressure of a Gas
Partial Pressure of a Gas
The pressure exerted by a particular gas in a mixture of gases.
Atmospheric Pressure
Atmospheric Pressure
The pressure exerted by the weight of the atmosphere.
Partial Pressure of Oxygen (PO2)
Partial Pressure of Oxygen (PO2)
The pressure exerted by oxygen in the air or a liquid.
Gas Movement
Gas Movement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Calculating Partial Pressure
Calculating Partial Pressure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas Exchange (Lungs)
Gas Exchange (Lungs)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Humidification
Humidification
Signup and view all the flashcards
Partial Pressure of Nitrogen (PN2)
Partial Pressure of Nitrogen (PN2)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chloride Shift
Chloride Shift
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carbon Dioxide Transport
Carbon Dioxide Transport
Signup and view all the flashcards
Venous Blood PCO2
Venous Blood PCO2
Signup and view all the flashcards
Venous Oxygen Saturation
Venous Oxygen Saturation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxygen Partial Pressure in Venous Blood
Oxygen Partial Pressure in Venous Blood
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulmonary Capillary Gas Exchange
Pulmonary Capillary Gas Exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibition
Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxygen in Venous Blood
Oxygen in Venous Blood
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveolar-Capillary Equilibration
Alveolar-Capillary Equilibration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Safety Factor in Gas Exchange
Safety Factor in Gas Exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diffusion Coefficient
Diffusion Coefficient
Signup and view all the flashcards
Driving Force for Gas Diffusion
Driving Force for Gas Diffusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carbon Dioxide Diffusion
Carbon Dioxide Diffusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exercise and Gas Exchange
Exercise and Gas Exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxygen Saturation
Oxygen Saturation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cardiac Output
Cardiac Output
Signup and view all the flashcards
Systemic Venous PO2
Systemic Venous PO2
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveolar PO2
Alveolar PO2
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mitochondrial CO2 Production
Mitochondrial CO2 Production
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interstitial CO2
Interstitial CO2
Signup and view all the flashcards
Systemic Venous PCO2
Systemic Venous PCO2
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveolar PCO2
Alveolar PCO2
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxygen Transport in Blood
Oxygen Transport in Blood
Signup and view all the flashcards
Resting Oxygen Demand
Resting Oxygen Demand
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hemoglobin saturation
Hemoglobin saturation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hemoglobin dissociation curve
Hemoglobin dissociation curve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Allosteric binding of oxygen
Allosteric binding of oxygen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxygen offloading at tissues
Oxygen offloading at tissues
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxygen delivery at rest
Oxygen delivery at rest
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxygen delivery during exercise
Oxygen delivery during exercise
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxygen contribution of free solution
Oxygen contribution of free solution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bohr Effect
Bohr Effect
Signup and view all the flashcards
Left Shift in Dissociation Curve
Left Shift in Dissociation Curve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Right Shift in Dissociation Curve
Right Shift in Dissociation Curve
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fetal Hemoglobin
Fetal Hemoglobin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bicarbonate (HCO3-)
Bicarbonate (HCO3-)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carbaminohemoglobin
Carbaminohemoglobin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carbon Dioxide Excretion
Carbon Dioxide Excretion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
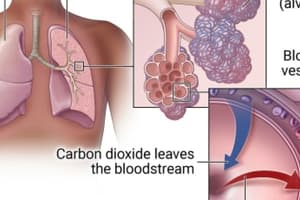
Pulmonary Gas Exchange
- Gas exchange occurs between blood and alveoli.
- Oxygen moves from alveoli to blood.
- Carbon dioxide moves from blood to alveoli.
Gas Partial Pressures
- Gases move from high pressure to low pressure.
- Partial pressure is used to compare gas concentration between compartments.
- Atmospheric pressure is the weight of the air column above us.
- Partial pressure of nitrogen in atmosphere = 600 mm Hg
- Partial pressure of oxygen in atmosphere = 160 mm Hg
Humidification of Inhaled Air
- Inhaling humidifies air.
- Atmospheric pressure stays constant (760 mm Hg)
- Water vapor partial pressure = 47 mm Hg.
- This reduces partial pressure of oxygen and nitrogen.
- Inhaled Air P02 = 150 mm Hg
- Inhaled Air PN2 = 563 mm Hg
Tidal Volume and Alveolar Air
- Tidal volume is the air inhaled in one breath.
- Only a portion of tidal volume reaches alveoli.
- Air in alveoli mixes with air from previous breath.
- Partial pressures of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water vapor differ in various locations.
Gas Exchange in Pulmonary Capillaries
- At beginning of capillary, P02 is 40 mm Hg and PCO2 is 46 mm Hg.
- 1/3rd the length of a capillary is for oxygen equilibration.
- P02 = 104 mm Hg; PCO2 = 40 mm Hg.
Factors that cause fast oxygen and CO2 exchange
- Oxygen equilibrates quicker.
- CO2 has faster diffusion coefficient than oxygen.
- Therefore there is a 20-fold greater diffusion coefficient for carbon dioxide.
Oxygen Transport in the Blood
- 97% of oxygen transported bound to hemoglobin
- At rest, tissues require 250 ml of oxygen/min
- Dissolved oxygen is insufficient.
- Hemoglobin carries the rest of the oxygen needed.
Factors that shift the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve to the right.
- Increased blood acidity (lower pH)
- Increased blood PCO2
- Increased blood 2,3-DPG
- Increased body temperature
Factors that shift the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve to the left
- Decreased blood acidity (higher pH)
- Decreased blood PCO2
Carbon Dioxide Transport in the Blood
- 70% of carbon dioxide is bicarbonate (HCO3−)
- 23% bound to hemoglobin (carbaminohemoglobin)
- 7% in free solution
- 4 ml CO2/100 ml of blood must be removed
Haldane Effect
- Increased oxygen binding decreases haemoglobin affinity for carbon dioxide.
Bohr Effect
- Low pH and high PCO2 cause a right shift in the oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.