Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is atmospheric pressure?
What is atmospheric pressure?
- The sum of the pressures of all gases in a mixture (correct)
- The contribution of one gas in a mixture
- The force exerted by gravity on a gas
- The pressure exerted by water vapor
What percentage of atmospheric air at sea level is oxygen?
What percentage of atmospheric air at sea level is oxygen?
- 78.6%
- 20.9% (correct)
- 0.04%
- 0.5%
Calculate the partial pressure of oxygen ($PO_2$) at sea level, given that atmospheric pressure is 760 mm Hg and oxygen comprises 20.9% of the atmosphere.
Calculate the partial pressure of oxygen ($PO_2$) at sea level, given that atmospheric pressure is 760 mm Hg and oxygen comprises 20.9% of the atmosphere.
- 159 mm Hg (correct)
- 760 mm Hg
- 300 mm Hg
- 200 mm Hg
What primarily drives gas movement across respiratory surfaces?
What primarily drives gas movement across respiratory surfaces?
Why is supplemental oxygen often used at high altitudes?
Why is supplemental oxygen often used at high altitudes?
What physical state must oxygen be in to enter the tissues and blood?
What physical state must oxygen be in to enter the tissues and blood?
For gases to effectively diffuse into water, what must be true of their partial pressure?
For gases to effectively diffuse into water, what must be true of their partial pressure?
What does the term 'anastomosis' refer to in the context of pulmonary circulation?
What does the term 'anastomosis' refer to in the context of pulmonary circulation?
Why is blood leaving the alveolar capillaries not 100% saturated with oxygen?
Why is blood leaving the alveolar capillaries not 100% saturated with oxygen?
How does increased $PO_2$ in alveolar air affect oxygen uptake by the blood?
How does increased $PO_2$ in alveolar air affect oxygen uptake by the blood?
What is the partial pressure of oxygen ($PO_2$) in deoxygenated blood?
What is the partial pressure of oxygen ($PO_2$) in deoxygenated blood?
What is the primary function of ventilation-perfusion coupling?
What is the primary function of ventilation-perfusion coupling?
How does low $PO_2$ typically affect blood vessels in the lungs?
How does low $PO_2$ typically affect blood vessels in the lungs?
What impact does emphysema have on the alveolar surface area available for gas exchange?
What impact does emphysema have on the alveolar surface area available for gas exchange?
Why is a thin respiratory membrane essential for efficient gas exchange?
Why is a thin respiratory membrane essential for efficient gas exchange?
In the alveoli, what direction does oxygen move?
In the alveoli, what direction does oxygen move?
What is the first step in oxygen diffusion, after it enters the alveoli coming in with inspired air?
What is the first step in oxygen diffusion, after it enters the alveoli coming in with inspired air?
Aerobically metabolizing tissues typically have which characteristics regarding oxygen and carbon dioxide?
Aerobically metabolizing tissues typically have which characteristics regarding oxygen and carbon dioxide?
Compared to blood, alveoli after inspiration typically have which characteristics regarding oxygen and carbon dioxide?
Compared to blood, alveoli after inspiration typically have which characteristics regarding oxygen and carbon dioxide?
After oxygen enters the red blood cells, what does it do?
After oxygen enters the red blood cells, what does it do?
In the equation $CO_2 + H_2O \rightleftharpoons H_2CO_3 \rightleftharpoons H^+ + HCO_3^-$, what does $H_2CO_3$ represent?
In the equation $CO_2 + H_2O \rightleftharpoons H_2CO_3 \rightleftharpoons H^+ + HCO_3^-$, what does $H_2CO_3$ represent?
What enzyme catalyzes the reaction $CO_2 + H_2O \rightleftharpoons H_2CO_3$?
What enzyme catalyzes the reaction $CO_2 + H_2O \rightleftharpoons H_2CO_3$?
What role does the bicarbonate ion ($HCO_3^−$) play in the context of blood pH?
What role does the bicarbonate ion ($HCO_3^−$) play in the context of blood pH?
What is the 'chloride shift'?
What is the 'chloride shift'?
What is the first step of the pulmonary circuit?
What is the first step of the pulmonary circuit?
Through which vessel does blood exit the left ventricle to enter systemic circulation?
Through which vessel does blood exit the left ventricle to enter systemic circulation?
During pulmonary circulation, where does blood go after leaving the pulmonary arteries?
During pulmonary circulation, where does blood go after leaving the pulmonary arteries?
After traveling through the lungs, where does blood go next in the pulmonary circulation pathway?
After traveling through the lungs, where does blood go next in the pulmonary circulation pathway?
In a scenario where a person is suffering from severe pneumonia and the alveoli in a significant portion of their lungs are filled with fluid and cellular debris, but they are also simultaneously at very high altitude, what is the MOST likely immediate physiological consequence?
In a scenario where a person is suffering from severe pneumonia and the alveoli in a significant portion of their lungs are filled with fluid and cellular debris, but they are also simultaneously at very high altitude, what is the MOST likely immediate physiological consequence?
According to Dalton's Law, what determines the total pressure of a gas mixture?
According to Dalton's Law, what determines the total pressure of a gas mixture?
What happens to atmospheric pressure as altitude increases?
What happens to atmospheric pressure as altitude increases?
What is the first fluid that alveolar air encounters as it moves towards the bloodstream?
What is the first fluid that alveolar air encounters as it moves towards the bloodstream?
Compared to alveolar air, what is the relative partial pressure of carbon dioxide ($PCO_2$) in the blood arriving at the alveoli?
Compared to alveolar air, what is the relative partial pressure of carbon dioxide ($PCO_2$) in the blood arriving at the alveoli?
What is the typical partial pressure of oxygen ($PO_2$) in alveolar air?
What is the typical partial pressure of oxygen ($PO_2$) in alveolar air?
What is the typical partial pressure of carbon dioxide ($PCO_2$) in expired air?
What is the typical partial pressure of carbon dioxide ($PCO_2$) in expired air?
What is the typical partial pressure of oxygen ($PO_2$) in deoxygenated blood?
What is the typical partial pressure of oxygen ($PO_2$) in deoxygenated blood?
Besides pressure gradients, what is another major factor influencing the efficiency of gas exchange?
Besides pressure gradients, what is another major factor influencing the efficiency of gas exchange?
How does the solubility of carbon dioxide ($CO_2$) compare to that of oxygen ($O_2$) in water?
How does the solubility of carbon dioxide ($CO_2$) compare to that of oxygen ($O_2$) in water?
What effect does increased ventilation have on $PO_2$, and how does this affect blood vessels?
What effect does increased ventilation have on $PO_2$, and how does this affect blood vessels?
Approximately how much respiratory membrane surface area is available for gas exchange in healthy lungs?
Approximately how much respiratory membrane surface area is available for gas exchange in healthy lungs?
Approximately how much blood is contained within the alveolar capillaries at any given time?
Approximately how much blood is contained within the alveolar capillaries at any given time?
What type of cells primarily compose the alveoli, facilitating gas exchange?
What type of cells primarily compose the alveoli, facilitating gas exchange?
During inspiration, how do the oxygen and carbon dioxide concentrations in the alveoli compare to those in the deoxygenated blood returning from the body?
During inspiration, how do the oxygen and carbon dioxide concentrations in the alveoli compare to those in the deoxygenated blood returning from the body?
In aerobically metabolizing tissues, what are the relative concentrations of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood?
In aerobically metabolizing tissues, what are the relative concentrations of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood?
Under what conditions does oxygen unbind from hemoglobin and diffuse into tissue cells?
Under what conditions does oxygen unbind from hemoglobin and diffuse into tissue cells?
What happens to carbon dioxide after it diffuses out of tissue cells and enters the blood?
What happens to carbon dioxide after it diffuses out of tissue cells and enters the blood?
In red blood cells, what is the intermediate product formed from $CO_2$ and $H_2O$ before dissociating into ions?
In red blood cells, what is the intermediate product formed from $CO_2$ and $H_2O$ before dissociating into ions?
What is the ultimate fate of carbon dioxide in the lungs?
What is the ultimate fate of carbon dioxide in the lungs?
How frequently does the cycle of gas exchange in the lungs happen?
How frequently does the cycle of gas exchange in the lungs happen?
Which of the following accurately describes the movement of gases during alveolar gas exchange?
Which of the following accurately describes the movement of gases during alveolar gas exchange?
What is the primary reason for the decrease in atmospheric pressure with increasing altitude?
What is the primary reason for the decrease in atmospheric pressure with increasing altitude?
How does the thin layer of water on the alveolar epithelium contribute to gas exchange?
How does the thin layer of water on the alveolar epithelium contribute to gas exchange?
If the partial pressure of oxygen ($PO_2$) in the alveoli suddenly increased significantly, what immediate effect would this have on pulmonary blood vessels?
If the partial pressure of oxygen ($PO_2$) in the alveoli suddenly increased significantly, what immediate effect would this have on pulmonary blood vessels?
Flashcards
Atmospheric Pressure
Atmospheric Pressure
The sum of the pressures exerted by each gas in a gaseous mixture.
Partial pressure
Partial pressure
The contribution of a single gas to the total atmospheric pressure.
Pressure Gradient
Pressure Gradient
Gases move from areas of higher pressure to lower pressure.
Water Film in Lungs
Water Film in Lungs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxygen Dissolution
Oxygen Dissolution
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveolar Air Movement
Alveolar Air Movement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveolar Gas Exchange
Alveolar Gas Exchange
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anastomosis
Anastomosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulmonary Vein Anastomose
Pulmonary Vein Anastomose
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Saturation
Blood Saturation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ventilation-Perfusion Coupling
Ventilation-Perfusion Coupling
Signup and view all the flashcards
Low PO₂ Response
Low PO₂ Response
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveoli Cell Type
Alveoli Cell Type
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveoli and Blood Vessels
Alveoli and Blood Vessels
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oxygen Movement
Oxygen Movement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carbonic Acid Equation
Carbonic Acid Equation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulmonary Circulation Start
Pulmonary Circulation Start
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aorta Function
Aorta Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Partial Pressure?
What is Partial Pressure?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Dalton's Law?
What is Dalton's Law?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Altitude and Atmospheric Pressure Relationship
Altitude and Atmospheric Pressure Relationship
Signup and view all the flashcards
Water Film in Alveoli
Water Film in Alveoli
Signup and view all the flashcards
CO₂ Diffusion in Alveoli
CO₂ Diffusion in Alveoli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blood Gas Partial Pressures
Blood Gas Partial Pressures
Signup and view all the flashcards
CO₂ Solubility
CO₂ Solubility
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ventilation and Vasodilation
Ventilation and Vasodilation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alveoli Cell Structure
Alveoli Cell Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tissue Metabolism
Tissue Metabolism
Signup and view all the flashcards
O₂ Release Factors
O₂ Release Factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
CO₂ Diffusion at Tissues
CO₂ Diffusion at Tissues
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carbon Dioxide Conversion
Carbon Dioxide Conversion
Signup and view all the flashcards
CO₂ Reformation
CO₂ Reformation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gas Exchange Frequency
Gas Exchange Frequency
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Partial Pressure
- Atmospheric pressure is the sum of the pressure of all gases in a mixture, according to Dalton's Law.
- Partial pressure is the contribution of one gas to the total pressure.
- At sea level, atmospheric pressure measures 760 mm Hg.
- Oxygen constitutes 20.9% of the atmosphere.
- The partial pressure of oxygen (PO₂) is 159 mm Hg, representing 20.9% of atmospheric pressure.
- Gases move from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure.
- Atmospheric pressure decreases with altitude due to less air weight pressing down.
- Lower partial pressure of oxygen at high altitudes can cause breathing difficulties; supplemental oxygen helps.
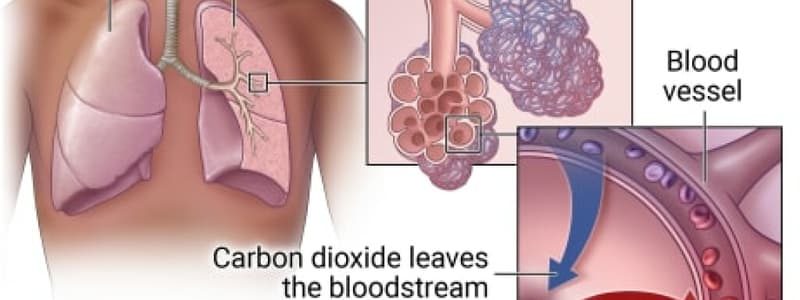
Alveolar Gas Exchange
- The epithelium lining the lumen is coated with a water film.
- Gases must dissolve in water to enter tissues and blood.
- Alveolar air enters the water film before reaching the respiratory membrane, which separates air from the bloodstream.
- Gases diffuse into water if their partial pressure is greater than that of the water.
- Higher PO₂ in alveolar air results in increased O₂ uptake by the blood.
- Blood arriving at the alveolus has a higher PCO₂ than the air, causing it to release CO₂ into the alveolar air.
- Achieving 100% blood saturation is nearly impossible, despite blood leaving alveolar capillaries being highly saturated.
- Anastomosis is the convergence or joining of two structures.
- Pulmonary veins anastomose with bronchial veins, mixing oxygen-rich pulmonary blood with oxygen-poor systemic blood.
Changes in Partial Pressures & the Pulmonary Circuit
- Inspired air contains a PO₂ of 159 mm Hg and a PCO₂ of 0.3 mm Hg.
- Alveolar air contains a PO₂ of 104 mm Hg and a PCO₂ of 40 mm Hg.
- Expired air contains a PO₂ of 116 mm Hg and a PCO₂ of 32 mm Hg.
- Deoxygenated blood has a PO₂ of 40 mm Hg and a PCO₂ of 46 mm Hg.
- Oxygenated blood has a PO₂ of 95 mm Hg and a PCO₂ of 40 mm Hg.
Gas Exchange Efficiency
- Key factors influencing efficiency include pressure gradients, gas solubility, membrane thickness and area, and ventilation-perfusion coupling.
- CO₂ is 20 times more soluble in water than O₂.
- Solubility refers to the ability of a substance to dissolve in water.
- The membrane is approximately 0.5mm thick, which prevents little obstacle to diffusion
- Ventilation-perfusion coupling ensures blood flow is matched to oxygen supply.
- Poor ventilation leads to low PO₂, causing vasoconstriction, while increased ventilation leads to high PO₂, causing vasodilation.
- A healthy lung has about 70m² of respiratory membrane for gas exchange.
- Alveolar capillaries contain only about 100ml of blood at any given time, spreading the blood thinly.
- Certain pulmonary diseases reduce the alveolar surface area, leading to low blood PO₂.
- Emphysema and lung cancer are examples of diseases that reduce the alveolar surface area for gas exchange.
Gas Exchange
- Alveoli are composed of thin simple squamous cells, which facilitate gas exchange.
- Blood vessels surround alveoli, allowing efficient O₂ and CO₂ transfer.
- During inspiration, alveoli have high O₂ and low CO₂ concentrations compared to deoxygenated blood returning from the body.
- The concentration difference drives O₂ diffusion from alveoli into the blood and CO₂ from the blood into alveoli.
- Oxygen moves from the air, across the water film lining the alveoli, through the alveolar epithelium, and into the blood.
- Oxygen binds to hemoglobin within RBCs and is transported to body tissues.
- At the tissues, high oxygen concentration in blood contrasts with the tissues undergoing aerobic metabolism (using O₂ to produce CO₂ + H₂O).
- Blood possesses a high O₂ and low CO₂ concentration, while tissues have low O₂ and high CO₂ concentrations.
- Oxygen unbinds from hemoglobin and diffuses into tissue cells when pH is low and CO₂ is high.
- CO₂ diffuses out of tissue cells and enters the blood.
- CO₂ binds to hemoglobin inside RBCs.
- Within RBCs, CO₂ + H₂O ⇄ H₂CO₃ ⇄ H⁺ + HCO₃⁻ occurs, converting carbon dioxide and water into carbonic acid, then bicarbonate and hydrogen ions.
- Carbonic anhydrase assists in the conversion of carbonic acid to bicarbonate.
- HCO₃⁻ leaves RBCs to buffer against low pH.
- Cl⁻ enters RBCs to maintain electrical balance (Chloride shift).
- Back in the lungs where temperatures are colder.
- Alveoli have high O₂ and blood has low O₂.
- Alveoli have low CO₂ and blood has high CO₂.
- HCO₃⁻ enters RBCs, and Cl⁻ exits (reverse Chloride shift).
- The equation reverses to regenerate CO₂ + H₂O: CO₂ + H₂O ⇄ H₂CO₃ ⇄ H⁺ + HCO₃⁻.
- CO₂ diffuses out of RBCs and into alveoli.
- Oxygen diffuses from alveoli into the blood.
- This cycle repeats roughly three times per minute.
Pulmonary Circulation
- Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium of the heart from the superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, and coronary sinus.
- Atrial contraction pushes blood into the right ventricle.
- Ventricular contraction sends blood through the pulmonary trunk to the pulmonary arteries and the lungs.
- The blood travels from the lungs to the pulmonary veins, which lead to the left atrium.
- Contraction of the left atrium moves blood to the left ventricle and then to the aorta.
- The aorta delivers blood to systemic and coronary circulation.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.