Podcast Beta
Questions and Answers
Match the following terms with their correct definitions:
Sensation = The process of detecting stimuli from the environment Perception = How the brain organizes and interprets sensory information Sensory transduction = Converting physical stimuli into neuronal signals Sensory receptors = Specialized neurons that detect external stimuli
Match the parts of the human eye to their functions:
Cornea = Transparent outer layer where light enters Iris = Controls the size of the pupil Lens = Focuses light onto the retina Optic nerve = Transmits signals from the retina to the brain
Match the types of photoreceptors with their characteristics:
Cones = Concentrated in the fovea Rods = Do not detect color
Match the visual cues with their descriptions:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the components of the visual system to their roles:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the examples with the processes they illustrate:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the definitions with the corresponding processes in vision:
Signup and view all the answers
Match each stage of visual processing with the correct description:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the features of the eye with their respective locations:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the type of reinforcement with its definition:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the type of memory with its description:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the type of interference with its effect:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the reinforcement schedule with its characteristic:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the type of memory with its associated case study:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the term with its description related to memory:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the type of conditioning with its definition:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the stage of memory with its function:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the wavelength characteristics with their corresponding color:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following terms with their definitions:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following types of memory to their characteristics:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following concepts to their descriptions:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following key figures with their contributions:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following statements with their applicable area of study:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following memory systems with their features:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following visual perception concepts with their descriptions:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following Gestalt principles with their explanations:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following perceptual constancies with their definitions:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following terms related to learning and memory with their descriptions:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following classical conditioning terms with their definitions:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following components of classical conditioning with their examples:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following concepts from Gestalt psychology with their effects:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following types of constancies with their applications:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following principles of perception with their characteristics:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following components of the auditory system to their functions:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following terms related to psychophysics with their definitions:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the different types of reinforcement schedules in operant conditioning:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following sensory receptors to their corresponding sensations:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following terms with their related concepts in classical conditioning:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following aspects of the somatosensory system to their features:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following classical conditioning phenomena with their descriptions:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following components of cognitive learning to their characteristics:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following types of psychophysical principles to their characteristics:
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following sounds characteristics with their descriptions:
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
Sensation and Perception
- Sensation is the process of detecting stimuli from the environment using sensory receptors and the nervous system.
- Perception is the brain's interpretation of sensory information, making it meaningful and allowing us to recognize objects, events, and patterns.
- Sensory receptors are specialized neurons that detect external stimuli.
- Sensory transduction is the conversion of physical stimuli into chemical energy (neural signals), the first step in sensation.
- Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation, with wavelengths between 380 nm and 760 nm being visible to humans.
-
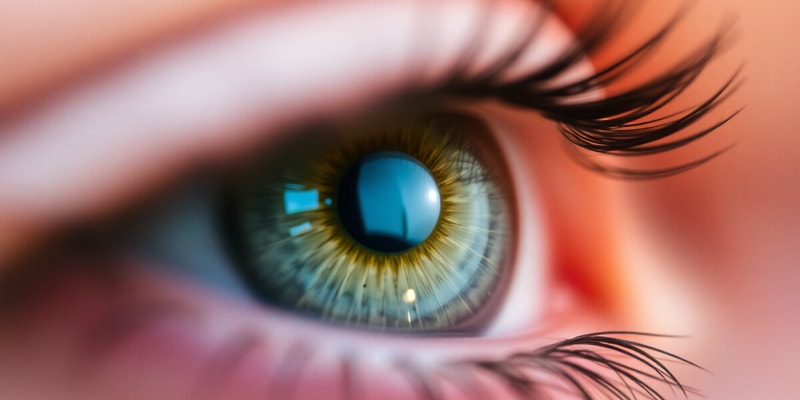
The human eye has several key parts:
- Cornea: Transparent outer layer where light enters.
- Iris: Muscular ring controlling pupil size.
- Pupil: Hole where light enters.
- Lens: Focuses light onto the retina.
- Retina: Contains photoreceptors (rods and cones) responsible for detecting light.
- Optic nerve: Transmits signals from the retina to the brain.
- Cones: Photoreceptors responsible for detailed, color vision, best in daylight, concentrated in the fovea, the area with the highest visual acuity.
- Rods: More numerous, responsible for vision in low-light conditions, located peripherally, do not detect color.
- Binocular depth cues: Relies on retinal disparity (slightly different views from both eyes) and convergence (eyes moving inward when focusing on close objects).
- Monocular depth cues: Useful for distant objects, including cues like relative size (closer objects appear larger) and linear perspective (parallel lines converging as they get farther away).
- Gestalt psychology emphasizes perceiving whole objects rather than individual parts.
-
Gestalt principles:
- Closure: Filling in gaps to create a complete object.
- Similarity: Grouping similar objects together.
- Proximity: Perceiving objects near each other as related.
- Good continuation: Perceiving smooth, continuous lines.
- Size constancy: Perceiving objects as the same size despite changes in retinal image size due to distance.
- Shape constancy: Perceiving objects as maintaining their shape even when viewed from different angles.
- Color constancy: The brain adjusts for lighting changes so we perceive colors consistently.
Learning and Memory
- Learning is a lasting change in behavior due to experience.
- Memory is the encoding, storing, and retrieving information as a result of learning.
-
Classical conditioning: A type of learning where a neutral stimulus becomes associated with an unconditioned stimulus, eventually eliciting a conditioned response.
- Unconditioned stimulus (UCS): Naturally produces a response (e.g., food).
- Unconditioned response (UCR): The natural response to the UCS (e.g., salivation).
- Conditioned stimulus (CS): Previously neutral stimulus that elicits a conditioned response after pairing with the UCS (e.g., a bell).
- Conditioned response (CR): The learned response to the CS (e.g., salivation at the sound of the bell).
-
Operant conditioning: Learning through rewards and punishments, where behaviors are influenced by their consequences.
-
Reinforcement: Increases behavior.
- Positive reinforcement: Adding something pleasant (e.g., a treat).
- Negative reinforcement: Removing something unpleasant (e.g., ending a chore).
-
Punishment: Decreases behavior.
- Positive punishment: Adding something unpleasant (e.g., scolding).
- Negative punishment: Removing something pleasant (e.g., taking away TV privileges).
- Continuous reinforcement: Behavior is reinforced every time.
- Intermittent reinforcement: Reinforcement is given at varying intervals or ratios, making behavior more resistant to extinction.
-
Reinforcement: Increases behavior.
-
Explicit memory: Consciously recalled memories.
- Episodic memory: Memory of personal experiences.
- Semantic memory: Facts and general knowledge.
-
Implicit memory: Unconsciously recalled memories.
- Procedural memory: Skills and tasks (e.g., riding a bike).
- Associative memory: Classical conditioning responses.
- H.M.'s case: H.M. lost the ability to form new explicit memories after surgery for epilepsy, highlighting the role of the hippocampus in memory consolidation.
- Forgetting curve: Rapid forgetting occurs initially after learning, but the remaining information tends to be retained over time.
- Proactive interference: Old memories interfering with new memories.
- Retroactive interference: New memories interfering with recalling old memories.
- Flashbulb memories: Strong memories formed under intense emotional experiences, though they may not be accurate.
Additional Notes on Sensation and Perception
- Light as a Stimulus: Wavelength determines color (short = blue/violet, long = red).
- The Auditory System: Structure of the ear: outer ear (pinna), middle ear (tympanic membrane & ossicles), inner ear (cochlea).
- Transduction of Sound: Vibrations move basilar membrane, shearing hair cells and converting it to neural signals.
- Somatosensory System: Detects touch, pressure, vibration, pain, temperature.
- The Homunculus & Somatosensory Cortex: Sensory input is mapped in the brain, with areas with more sensory input represented larger (e.g., hands, lips).
-
Psychophysics: Studies the relationship between stimuli and perception.
- Absolute threshold: Minimum stimulus intensity detectable 50% of the time.
- Subliminal perception: Processing stimuli below conscious detection.
-
The Gestalt School & Grouping Principles:
- Similarity, proximity, continuity, closure help us perceive whole objects.
Additional Notes on Learning and Memory
- Real-World Classical Conditioning: Explains preferences, aversions, emotional reactions.
- Extinction in Classical Conditioning: The CS no longer paired with UCS, leading to CR disappearance.
-
Operant Conditioning: Skinner's Reinforcement Schedules:
- Fixed ratio, Variable ratio, Fixed interval, Variable interval.
- Cognitive Learning (Edward Tolman): Latent learning - learning occurs without immediate reinforcement, cognitive maps (e.g., rats navigating a maze).
-
Memory Encoding, Storage, and Retrieval:
- Encoding - converting input to memory.
- Storage - retaining information.
- Retrieval - accessing stored information.
-
Short-Term vs.Long-Term Memory:
- Short-term - temporary, limited capacity (7±2 items).
- Long-term - stable, lasting years; consolidated in the hippocampus.
- The Case of H.M.& Memory Systems: H.M. could not form new explicit memories but retained implicit memories.
- Forgetting and Memory Interference: Proactive and retroactive interference.
- Context-dependent memory: Better recall when context matches the learning environment.
- Eyewitness Memory & Misinformation Effect: Eyewitness testimony is unreliable; memory can be altered by misleading information.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Explore the intricate processes of sensation and perception in this quiz. Learn how sensory receptors detect stimuli and how our brains interpret this information to understand the world around us. Test your knowledge on the anatomy of the human eye and the principles of sensory transduction.