Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is considered a primary drive according to drive reduction theory?
What is considered a primary drive according to drive reduction theory?
Which type of need represents psychological or subjective necessities?
Which type of need represents psychological or subjective necessities?
Which hormones are associated with social behaviors as described in the content?
Which hormones are associated with social behaviors as described in the content?
In Maslow's hierarchy of needs, what is the ultimate goal referred to?
In Maslow's hierarchy of needs, what is the ultimate goal referred to?
Signup and view all the answers
Drive reduction theory primarily suggests that human behavior is motivated by what?
Drive reduction theory primarily suggests that human behavior is motivated by what?
Signup and view all the answers
What characterizes secondary drives as opposed to primary drives?
What characterizes secondary drives as opposed to primary drives?
Signup and view all the answers
According to the arousal theory of motivation, individuals are motivated to engage in activities that do what?
According to the arousal theory of motivation, individuals are motivated to engage in activities that do what?
Signup and view all the answers
Which part of the brain is primarily involved in controlling homeostatic systems according to the content?
Which part of the brain is primarily involved in controlling homeostatic systems according to the content?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following best describes the role of effectors in drive reduction?
Which of the following best describes the role of effectors in drive reduction?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of these is a characteristic of primary drives?
Which of these is a characteristic of primary drives?
Signup and view all the answers
What does the 'need for achievement' (nAch) primarily focus on?
What does the 'need for achievement' (nAch) primarily focus on?
Signup and view all the answers
Which need in Maslow's hierarchy represents the basic requirement necessary for survival?
Which need in Maslow's hierarchy represents the basic requirement necessary for survival?
Signup and view all the answers
According to Maslow, which need comes immediately after physiological needs?
According to Maslow, which need comes immediately after physiological needs?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the key focus of the need for power (nP) according to McClelland?
What is the key focus of the need for power (nP) according to McClelland?
Signup and view all the answers
In Maslow's hierarchy, which need is considered the highest level?
In Maslow's hierarchy, which need is considered the highest level?
Signup and view all the answers
How does McClelland's theory differ from Maslow's framework?
How does McClelland's theory differ from Maslow's framework?
Signup and view all the answers
What psychological state results from the inconsistency of incongruence?
What psychological state results from the inconsistency of incongruence?
Signup and view all the answers
Which aspect is emphasized in the need for affiliation (nAf)?
Which aspect is emphasized in the need for affiliation (nAf)?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is NOT one of the five needs identified in Maslow's hierarchy?
Which of the following is NOT one of the five needs identified in Maslow's hierarchy?
Signup and view all the answers
What role do physiological needs play in Maslow's hierarchy?
What role do physiological needs play in Maslow's hierarchy?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the main premise of extrinsic theories regarding human motivation?
What is the main premise of extrinsic theories regarding human motivation?
Signup and view all the answers
How does the hypothalamus influence human behavior according to the content?
How does the hypothalamus influence human behavior according to the content?
Signup and view all the answers
What role does curiosity play in intrinsic motivation?
What role does curiosity play in intrinsic motivation?
Signup and view all the answers
What does the need for achievement (nAch) encompass?
What does the need for achievement (nAch) encompass?
Signup and view all the answers
What does cognitive consistency refer to?
What does cognitive consistency refer to?
Signup and view all the answers
According to the content, what is a limit of integrating extrinsic and intrinsic motivations?
According to the content, what is a limit of integrating extrinsic and intrinsic motivations?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary responsibility of the satiety center in the hypothalamus?
What is the primary responsibility of the satiety center in the hypothalamus?
Signup and view all the answers
What is emphasized in the concept of drive reduction?
What is emphasized in the concept of drive reduction?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the relationship between task difficulty and performance according to Yerkes and Dodson's hypothesis?
What is the relationship between task difficulty and performance according to Yerkes and Dodson's hypothesis?
Signup and view all the answers
What do intrinsic theories of motivation suggest?
What do intrinsic theories of motivation suggest?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
Motivation: Needs and Drives
- Motivation is a key determinant of human behavior, driven by intrinsic needs (physical or psychological).
- Needs, like water and food (physical) or self-esteem (psychological), influence behavior.
- Abraham Maslow categorized needs hierarchically, from basic to self-actualization.
- Internal drives motivate us to fulfill needs.
- Hunger motivates us to cook or buy food.
Drive-Reduction Theory
- Drive-reduction theory suggests behavior aims to reduce arousal from physiological needs (hunger, thirst, warmth).
- Primary drives (essential for survival) are controlled by the hypothalamus.
- Sensors detect changes and effectors make adjustments to maintain homeostasis.
- Examples include hunger, thirst, and feeling cold.
- Secondary drives are learned (social approval, recognition, love), not essential for survival.
- Secondary drives are influenced by social and cultural factors.
Arousal Theory
- Arousal theory proposes that people seek activities to maintain or increase arousal levels.
- Increased activity in the dopaminergic mesolimbic system relates to increased arousal.
- The Yerkes-Dodson law describes an inverted-U relationship between task difficulty and performance, optimal arousal leads to peak performance.
Extrinsic Theories
- Extrinsic theories suggest individuals are motivated by external rewards or avoiding punishment (drive reduction).
- Homeostasis is a key concept, explaining the need for equilibrium.
- Examples include working for a wage or completing work for monetary rewards.
- Extrinsic factors can motivate behavior via operant conditioning and incentive theory.
Hypothalamic Systems and Satiety
- The hypothalamus is the coordination center, maintaining homeostasis.
- The satiety center signals fullness or satisfaction, influencing body processes like temperature regulation.
- Hormones play a crucial role in these processes.
Intrinsic Theories
- Intrinsic motivation is driven by internal factors, curiosity, and learning without external incentives.
- Curiosity drives exploration and new information discovery.
- Intrinsic motivation emphasizes autonomy, purpose, and mastery.
- Intrinsic motivators include pursuing basic biological needs like food and sex.
Limitations and Integration of Motivational Approaches
- Motivation is complex and necessitates understanding both intrinsic and extrinsic factors.
- Integrating different approaches is challenging due to the subjectivity of mental processes.
- Behavioral integration is linked to psychological growth and overcoming past behaviors.
Cognitive Consistency and Need for Achievement
- The need for achievement involves pursuing mastery, control, and accomplishments.
- This can be influenced by internal or external factors (social pressures).
- Cognitive consistency suggests thoughts and behaviors should align without conflict.
- Inconsistencies lead to tension and unpleasantness.
- McClelland's theory suggests three social needs: achievement (nAch), affiliation (nAf), and power (nP).
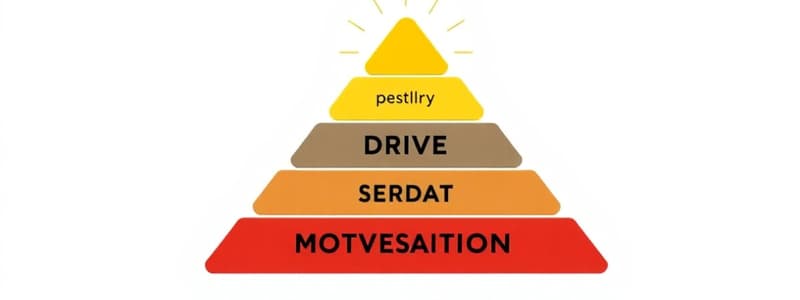
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
- Maslow's hierarchy prioritizes needs from basic (physiological) to higher-level needs (self-actualization).
- Physiological needs(food, water) are foundational, before safety and then love, esteem, and finally self-actualization can be pursued.
- Needs are ranked hierarchically, lower-level needs must be met before higher-level needs become important.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Explore the fundamental concepts of motivation, needs, and drives in psychology. This quiz covers various theories, including Maslow's hierarchy and drive-reduction theory, while discussing the roles of internal and external factors in motivating behavior. Test your understanding of how physical and psychological needs influence our actions.