Podcast
Questions and Answers
What does clutch size refer to in population characteristics?
What does clutch size refer to in population characteristics?
- The average lifespan of individuals in a population
- The maximum age of the individuals
- The number of young produced at one time (correct)
- The total population size of an area
What is represented by ecological or realized mortality?
What is represented by ecological or realized mortality?
- Theoretical minimum loss under ideal conditions
- Births that do not lead to viable offspring
- The overall extinction rate of a population
- Actual loss of individuals in a specific environment (correct)
What factors are typically used to measure the carrying capacity of an environment?
What factors are typically used to measure the carrying capacity of an environment?
- Population size and population distribution
- Clutch size and age of first reproduction
- Food, habitat, water, and resources (correct)
- Migration rate and death rate
What does the vital index measure?
What does the vital index measure?
Which of the following is NOT a cause of population change?
Which of the following is NOT a cause of population change?
What is the definition of mortality in a population?
What is the definition of mortality in a population?
What characterizes overpopulation?
What characterizes overpopulation?
What does population density refer to?
What does population density refer to?
What does population density refer to?
What does population density refer to?
What type of population dispersion has individuals spaced apart at equal distances?
What type of population dispersion has individuals spaced apart at equal distances?
Which age pyramid shape suggests a declining population with a low percentage of young individuals?
Which age pyramid shape suggests a declining population with a low percentage of young individuals?
Which term refers to the theoretical maximum production of new individuals under ideal conditions?
Which term refers to the theoretical maximum production of new individuals under ideal conditions?
What is ecological density?
What is ecological density?
In population biology, which aspect does 'natality' specifically refer to?
In population biology, which aspect does 'natality' specifically refer to?
Which type of dispersion describes individuals grouped into patches with few or no individuals in between?
Which type of dispersion describes individuals grouped into patches with few or no individuals in between?
How is 'age structure' typically represented in a population?
How is 'age structure' typically represented in a population?
What is a significant cause of overpopulation related to societal advancements?
What is a significant cause of overpopulation related to societal advancements?
Which of the following is NOT a consequence of overpopulation?
Which of the following is NOT a consequence of overpopulation?
What role does education play in addressing overpopulation?
What role does education play in addressing overpopulation?
Which of the following is a human-mediated cause of biodiversity loss?
Which of the following is a human-mediated cause of biodiversity loss?
What is one way overpopulation contributes to climate change?
What is one way overpopulation contributes to climate change?
What is one of the fatal effects of overpopulation linked to agriculture?
What is one of the fatal effects of overpopulation linked to agriculture?
What common misconception about extinction rates is mentioned?
What common misconception about extinction rates is mentioned?
How does poor contraceptive use relate to overpopulation?
How does poor contraceptive use relate to overpopulation?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Population Characteristics
- Population refers to a group of humans sharing common traits like location, race, ethnicity, or religion.
- In ecology, populations consist of organisms of the same species capable of interbreeding in specific areas.
- Population biology studies population characteristics, sizing, and distribution.
Population Size and Density
- Population size indicates the total number of individuals in a specific area.
- Crude density measures individuals per unit of total area.
- Ecological density considers available habitat space, offering a more accurate reflection of potential occupancy.
Population Dispersion
- Regular dispersion involves individuals spaced evenly apart.
- Random dispersion has no predictable pattern among individuals.
- Clumped dispersion shows individuals gathered in specific patches with sparse distribution elsewhere.
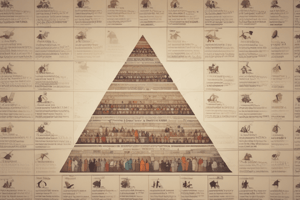
Age Structure and Natality
- Age pyramids visualize age group proportions in populations:
- Broad base indicates a large young population.
- Bell-shaped suggests a stable population.
- Urn-shaped reflects an aging or declining population.
- Natality, or birth rate, encompasses the rate of new individual production, impacted by clutch size, reproductive timing, and age at maturity.
Mortality and Vital Index
- Mortality rates indicate the number of deaths in a population, with two types:
- Minimum mortality is the lowest possible loss under ideal conditions.
- Ecological mortality reflects actual losses under current environmental factors.
- Vital index is calculated as (100 x births/deaths), highlighting the birth-death ratio in a population.
Population Growth and Change
- Population growth results from births (measured per 1,000 individuals/year), deaths (same metric), and migration (movement of individuals in/out).
- Carrying capacity defines the maximum population size an environment can sustainably support with available resources.
Overpopulation
- Overpopulation arises when human numbers exceed Earth's carrying capacity, leading to resource depletion and environmental strain.
- Causes include declining death rates, agricultural advances, medical improvements, child labor, and poor family planning.
Effects of Overpopulation
- Consequences encompass resource depletion, environmental degradation, increased conflicts, unemployment, high living costs, and climate change acceleration.
Solutions to Overpopulation
- Effective solutions include enhanced education, family planning awareness, tax incentives, and improved sex education.
Human Impact on Ecosystems
- Biodiversity signifies the variety of life forms on Earth, encompassing both species and ecosystems.
- Major human-induced threats to biodiversity:
- Land-use changes, pollution, introduction of non-native species, and resource exploitation.
Climate Change and Biodiversity
- Fossil fuels, derived from ancient organic matter, contribute to climate change impacting ecosystems.
- The current extinction rate is alarmingly faster than the natural rate, emphasizing conservation necessity.
Common Misconceptions
- The notion that the extinction rate is 1,000-10,000 times higher than normal highlights biodiversity's fragility.
- Not all aspects of the greenhouse effect are negative, and individual actions can significantly influence biodiversity outcomes.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.