Podcast
Questions and Answers
Who is regarded as the founder of demography?
Who is regarded as the founder of demography?
- Achille Guillard
- John Graunt (correct)
- Mortality Bill
- Life Table Creator
Formal demography includes the study of population size, structure, and migration.
Formal demography includes the study of population size, structure, and migration.
True (A)
What did John Graunt invent that presented mortality in terms of survivorship?
What did John Graunt invent that presented mortality in terms of survivorship?
Life Table
The term 'demography' is derived from the Greek words 'Demo' meaning ____ and 'Graphy' meaning to write or draw.
The term 'demography' is derived from the Greek words 'Demo' meaning ____ and 'Graphy' meaning to write or draw.
Match the key demographic concepts with their descriptions:
Match the key demographic concepts with their descriptions:
Which of the following factors contributes to the high unemployment rate in the Philippines?
Which of the following factors contributes to the high unemployment rate in the Philippines?
The Philippines has the lowest unemployment rate among ASEAN countries.
The Philippines has the lowest unemployment rate among ASEAN countries.
Which of the following is NOT one of the three population processes studied in formal demography?
Which of the following is NOT one of the three population processes studied in formal demography?
What demographic trend is described as having 4,780 babies born daily in the Philippines?
What demographic trend is described as having 4,780 babies born daily in the Philippines?
Formal demography only focuses on the statistical measurement of population size.
Formal demography only focuses on the statistical measurement of population size.
What are the three key population processes in formal demography?
What are the three key population processes in formal demography?
The objective of _______ Demography is to explain demographic phenomena using sociological, economic, or biological data.
The objective of _______ Demography is to explain demographic phenomena using sociological, economic, or biological data.
Match the following terms with their definitions:
Match the following terms with their definitions:
The number of people in a given place is referred to as __________.
The number of people in a given place is referred to as __________.
Match the following items with their definitions:
Match the following items with their definitions:
Which region has the fastest growing population?
Which region has the fastest growing population?
The Philippines has the largest population in Asia.
The Philippines has the largest population in Asia.
What is the term used to describe the physical presence of individuals in a territory at a specific time?
What is the term used to describe the physical presence of individuals in a territory at a specific time?
The population in a given area is evaluated using two methods: ____ and ____.
The population in a given area is evaluated using two methods: ____ and ____.
Match the following population growth indicators with their definitions:
Match the following population growth indicators with their definitions:
What is a characteristic of a population pyramid?
What is a characteristic of a population pyramid?
The de jure population is counted based on a person's physical presence in a location.
The de jure population is counted based on a person's physical presence in a location.
Which country was mentioned as having a population pyramid in 2019?
Which country was mentioned as having a population pyramid in 2019?
Which country is an example of a population with a fast growth rate?
Which country is an example of a population with a fast growth rate?
Germany is an example of a country with a slow growth rate.
Germany is an example of a country with a slow growth rate.
What is the world’s most densely populated city?
What is the world’s most densely populated city?
The percentage of people in a certain area compared to the size of that area is known as ________ density.
The percentage of people in a certain area compared to the size of that area is known as ________ density.
What does the term 'morbidity' refer to in the context of population processes?
What does the term 'morbidity' refer to in the context of population processes?
Match the following terms related to population processes:
Match the following terms related to population processes:
Fertility only has biological significance in population processes.
Fertility only has biological significance in population processes.
What is the primary focus of social demography?
What is the primary focus of social demography?
Flashcards
Demography
Demography
The statistical study of human populations, using data like birth, death, and migration.
John Graunt
John Graunt
Considered the founder of demography. Analyzed Bills of Mortality (London death records) and developed early life tables.
Bills of Mortality
Bills of Mortality
Weekly death records in London, used by John Graunt to study patterns in mortality.
Formal Demography
Formal Demography
Signup and view all the flashcards
Population growth
Population growth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Population Processes
Population Processes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Population Size
Population Size
Signup and view all the flashcards
Population Structure
Population Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Population Change
Population Change
Signup and view all the flashcards
De Facto Population
De Facto Population
Signup and view all the flashcards
De Jure Population
De Jure Population
Signup and view all the flashcards
Population Growth Rate
Population Growth Rate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Positive Growth Rate
Positive Growth Rate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Negative Growth Rate
Negative Growth Rate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Zero Growth Rate
Zero Growth Rate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Population Pyramid
Population Pyramid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fast Growth Rate
Fast Growth Rate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Slow Growth Rate
Slow Growth Rate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Population Density
Population Density
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sparsely Populated
Sparsely Populated
Signup and view all the flashcards
Densely Populated
Densely Populated
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mortality
Mortality
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fertility
Fertility
Signup and view all the flashcards
Migration
Migration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Unemployment in the Philippines
Unemployment in the Philippines
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rapid Population Increase
Rapid Population Increase
Signup and view all the flashcards
OFW Phenomenon
OFW Phenomenon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brain Drain
Brain Drain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Introduction to Demography (Part I)
- Demography is the statistical study of human populations.
- John Graunt is considered the founder of demography despite Achille Guillard coining the term in 1855.
- Demography is derived from two Greek words: "demo" (people) and "graphy" (to write or draw).
- Demography is divided into formal demography and social demography.
History of Demography
- John Graunt (April 24, 1620—April 18, 1674)
- Founded demography.
- Analyzed mortality (weekly recording of deaths in London).
- Created "Bills of Mortality" which recorded weekly mortality statistics from 1592 - 1595 and continuously from 1603.
- Graunt's Analysis:
- Classified death rates by cause, including overpopulation.
- Noted Urban death rates exceeded rural rates.
- Observed male birth rate exceeding the female rate, but offset by higher male mortality rates, resulting in nearly equal population distribution by sex.
- Invented the life table.
- Predicted percentage of survivors to each successive age, with life expectancy.
Mortality Example
- Figure 7 - Statistics on the Number of Maternal Deaths by Region, Philippines; 2016
Fertility Example
- Total Fertility Rate per Woman in Southeast Asia (2018)
- Includes the total fertility rate for countries in Southeast Asia.
Migration Example
- Figure 4 - Distribution of OFWs (Overseas Filipino Workers) by Place of Work, 2016
- Illustrates the distribution of OFWs with destinations in various countries.
Formal Demography
- Concerned with precise mathematical and statistical measurement and recording of population processes.
- Mortality
- Fertility
- Migration
- Formal demography aims to explain population processes by using demographic data.
- Formal Demography studies population change and its consequences, and investigates factors influencing change.
- Population size
- Population structure
- Population growth and decline.
- Population distribution
- Population characteristics/composition
- Population processes
Population Size
- The number of people in a given place
- World Population (2020) = 7.8 Billion
- Highest population = Asia
- Lowest population = Oceania
- Slowest population growth = Europe
- Philippines population (2020) = 109,581,078 Million
- Metro Manila population = 15 million by day, 12 million by night
De Facto and De Jure Population
- De Facto population - Physical presence in a territory at a given moment. -De Jure population - Based on permanent residence.
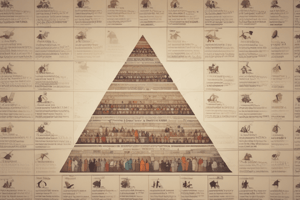
Population Structure
- Distribution of males and females in each age group.
- Depicted graphically in population pyramids (age-sex structure/pyramid).
Population Growth and Decline
- How the population changes over time.
- Positive growth rate: Increasing population
- Negative growth rate: Decreasing population
- Zero growth rate: Same individuals at the start and end of a measured period.
- Fast growth rate: Characterized by a young population.
- Slow growth rate: Characterized by an older population with low birth rates
Population Distribution
- Pattern of human locations.
- Sparsely populated areas contain few people.
- Densely populated areas contain many people
- Examples: Metro Manila, densely populated.
Population Density
- Measurement of people per area (e.g. per square kilometer).
- Examples: Map showcasing density variations across regions.
Factors Affecting Population Density
- Physical: Relief, resources, climate.
- Human: Political stability, social factors, economic opportunities.
Population Characteristics/Composition
- Characteristics of people in a given area
- Variables include: education, income, occupation, family relationships, immigrant/refugee status etc.
Population Processes
- Levels and trends in mortality, fertility, and migration.
- Key moments: Hatching, Matching, and Dispatching.
- Mortality: Death and morbidity (I: Death, II: Morbidity/Health)
- Fertility: Birth (I: Biological aspect, II: Economic aspect, III: Socio-cultural aspect)
- Migration: Mobility
Social Demography
- Explains demographic phenomena through sociological, economic, and biological perspectives.
- Focuses on why certain demographic occurrences happen.
Examples of Population Statistics (various countries and regions)
- Data on unemployment rates in ASEAN nations.
- HIV cases by region in the Philippines.
- Measles cases from 2016-2019.
- COVID-19 cases as of July 14th, 2020, across Southeast Asia.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.