Podcast
Questions and Answers
What does a positive number indicate when determining the level of the free gingival margin?
What does a positive number indicate when determining the level of the free gingival margin?
How is clinical attachment level (CAL) primarily distinguished between gingivitis and periodontitis?
How is clinical attachment level (CAL) primarily distinguished between gingivitis and periodontitis?
When measuring recession from the CEJ to the gingival margin, how should the probe be positioned?
When measuring recession from the CEJ to the gingival margin, how should the probe be positioned?
What measurement provides an estimate of true periodontal stability and loss of support for a tooth?
What measurement provides an estimate of true periodontal stability and loss of support for a tooth?
Signup and view all the answers
What is indicated by a negative number when measuring the free gingival margin?
What is indicated by a negative number when measuring the free gingival margin?
Signup and view all the answers
What aspect is critical in the predictive assessment of periodontal status?
What aspect is critical in the predictive assessment of periodontal status?
Signup and view all the answers
What does a zero (0) measurement indicate in the context of free gingival margin assessment?
What does a zero (0) measurement indicate in the context of free gingival margin assessment?
Signup and view all the answers
In the context of periodontal disease, what characterizes gingivitis?
In the context of periodontal disease, what characterizes gingivitis?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is a critical factor when evaluating periodontal health?
Which of the following is a critical factor when evaluating periodontal health?
Signup and view all the answers
What is necessary for calculating clinical attachment level (CAL)?
What is necessary for calculating clinical attachment level (CAL)?
Signup and view all the answers
What does a positive number recorded during pocket charting typically indicate?
What does a positive number recorded during pocket charting typically indicate?
Signup and view all the answers
What is false pocketing primarily caused by?
What is false pocketing primarily caused by?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following conditions can lead to drug-induced gingival overgrowth?
Which of the following conditions can lead to drug-induced gingival overgrowth?
Signup and view all the answers
In normal conditions, how should the free gingival margin relate to the CEJ?
In normal conditions, how should the free gingival margin relate to the CEJ?
Signup and view all the answers
What could be an indication of overgrown gingivae on a clinical chart?
What could be an indication of overgrown gingivae on a clinical chart?
Signup and view all the answers
What does it mean when gingival marking has moved apically from the CEJ?
What does it mean when gingival marking has moved apically from the CEJ?
Signup and view all the answers
How is the natural position of the CEJ to the gingival margin recorded in cases of recession?
How is the natural position of the CEJ to the gingival margin recorded in cases of recession?
Signup and view all the answers
What is indicated by a measurement that indicates an increase in pocket depths?
What is indicated by a measurement that indicates an increase in pocket depths?
Signup and view all the answers
What might contribute to increased numbers on the placket chart in a patient?
What might contribute to increased numbers on the placket chart in a patient?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the definition of 'free gingiva' in periodontal examination?
What is the definition of 'free gingiva' in periodontal examination?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the clinical attachment loss (CAL) when the probing depth is 6mm and the gingival margin is at its normal level?
What is the clinical attachment loss (CAL) when the probing depth is 6mm and the gingival margin is at its normal level?
Signup and view all the answers
If the probing depth is 4mm and the gingival margin is 2mm apical to the CEJ, what is the clinical attachment loss?
If the probing depth is 4mm and the gingival margin is 2mm apical to the CEJ, what is the clinical attachment loss?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the difference in clinical attachment loss when the gingival margin covers the CEJ with a probing depth of 9mm and a gingival margin level of -3mm?
What is the difference in clinical attachment loss when the gingival margin covers the CEJ with a probing depth of 9mm and a gingival margin level of -3mm?
Signup and view all the answers
When calculating CAL with a recession present and a probing depth of 4mm, how is the gingival margin level expressed?
When calculating CAL with a recession present and a probing depth of 4mm, how is the gingival margin level expressed?
Signup and view all the answers
What would be the clinical attachment loss if the probing depth is 9mm and the gingival margin is at -3mm?
What would be the clinical attachment loss if the probing depth is 9mm and the gingival margin is at -3mm?
Signup and view all the answers
When the gingival margin is at its normal level, what is the correlation between probing depth and clinical attachment loss?
When the gingival margin is at its normal level, what is the correlation between probing depth and clinical attachment loss?
Signup and view all the answers
If the probing depth is 6mm and CAL is 3mm, what could be the position of the gingival margin?
If the probing depth is 6mm and CAL is 3mm, what could be the position of the gingival margin?
Signup and view all the answers
In the absence of any recession with a probing depth of 5mm, what is the expected clinical attachment loss?
In the absence of any recession with a probing depth of 5mm, what is the expected clinical attachment loss?
Signup and view all the answers
A patient has a probing depth of 7mm and a gingival margin at -4mm. What is their clinical attachment loss?
A patient has a probing depth of 7mm and a gingival margin at -4mm. What is their clinical attachment loss?
Signup and view all the answers
What is meant by probing depth in periodontal assessments?
What is meant by probing depth in periodontal assessments?
Signup and view all the answers
Which probing depth indicates an unhealthy gingival sulcus?
Which probing depth indicates an unhealthy gingival sulcus?
Signup and view all the answers
What tools are used to measure probing depth?
What tools are used to measure probing depth?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the significance of Clinical Attachment Level in periodontal assessment?
What is the significance of Clinical Attachment Level in periodontal assessment?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is NOT a component of periodontal probing?
Which of the following is NOT a component of periodontal probing?
Signup and view all the answers
How is a six-point pocket chart organized during probing?
How is a six-point pocket chart organized during probing?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a common limitation of periodontal probing?
What is a common limitation of periodontal probing?
Signup and view all the answers
Which feature is important for achieving accurate periodontal probing results?
Which feature is important for achieving accurate periodontal probing results?
Signup and view all the answers
Which location is NOT included in the six-point pocket chart?
Which location is NOT included in the six-point pocket chart?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary purpose of conducting a basic periodontal examination?
What is the primary purpose of conducting a basic periodontal examination?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
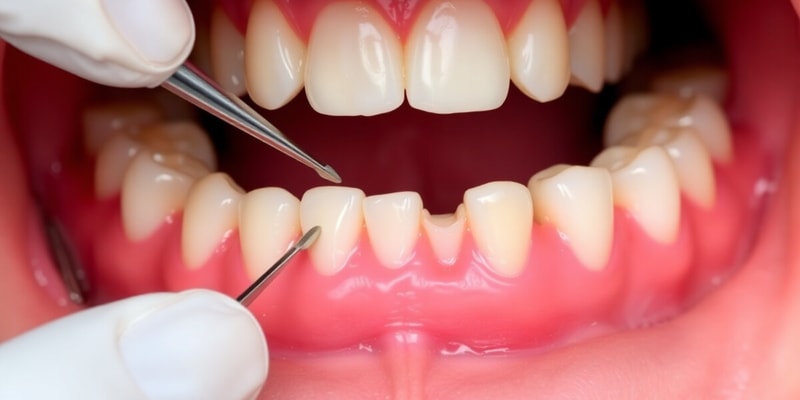
Probing Depth
- Probing depth is the distance from the gingival margin to the bottom of the pocket.
- Measured with a periodontal probe with a standardised tip diameter (0.4mm-0.5mm).
- Healthy sulcus is 1–3mm, unhealthy is 4mm+.
Six Point Pocket Chart
- Assesses periodontal health pre-treatment.
- Used to calculate probing depth around the tooth at six points.
- Points include: Distobuccal, Buccal, Mesiobuccal, Distolingual, Lingual, Mesiolingual.
- Deepest reading recorded for each site.
Limitations of Probing
- Can be affected by factors like inflammation, recession, and bleeding.
- Six point charting can overestimate pocket depth due to false pocketing.
Free Gingival Margin
- The level of the free gingival margin can be:
- Normal: slightly coronal to CEJ (0).
- Overgrown: significantly covers CEJ (-).
- Recession: apical to CEJ (+).
- Overgrowth can be caused by medication, leading to false pocketing.
Clinical Attachment Levels (CAL)
- Measure of true periodontal support around a tooth.
- Provides an estimate of periodontal stability and loss of support for a tooth.
- Calculated using probing depth and gingival margin level.
- Critical for distinguishing between gingivitis and periodontitis.
- Inflammation with no attachment loss - gingivitis.
- Inflammation with attachment loss - periodontitis.
Calculating CAL
- Normal level: CAL = Probing depth + Gingival margin level (0).
- Recession: CAL = Probing Depth - Gingival margin level (+).
- Overgrowth: CAL = Probing depth + Gingival margin level (-).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
This quiz evaluates knowledge on probing depth and periodontal assessments. It covers the methods of measurement, the significance of the six-point pocket chart, and limitations encountered during probing. Additionally, it discusses the free gingival margin and clinical attachment levels.