Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the purpose of performing a walking stroke while probing the gingival sulcus?
What is the purpose of performing a walking stroke while probing the gingival sulcus?
- To record multiple readings at the same site
- To cover wider areas with fewer strokes
- To minimize patient discomfort
- To ensure no pockets are missed (correct)
How should the deepest reading be recorded for the buccal surface during probing?
How should the deepest reading be recorded for the buccal surface during probing?
- By noting the highest measurement obtained (correct)
- By recording the first reading encountered
- By averaging the readings from multiple sites
- By summing all readings for that site
What does a positive measurement indicate when determining the level of the free gingival margin?
What does a positive measurement indicate when determining the level of the free gingival margin?
- Gingival recession beyond the CEJ
- Bone loss is significant
- Gingival margin covering the CEJ (correct)
- Overgrown gingiva present
What does a negative number indicate about the distance between the gingival margin and the CEJ?
What does a negative number indicate about the distance between the gingival margin and the CEJ?
Which of the following is not a limitation of probing mentioned?
Which of the following is not a limitation of probing mentioned?
What is a crucial factor that distinguishes between gingivitis and periodontitis?
What is a crucial factor that distinguishes between gingivitis and periodontitis?
What is the correct approach when measuring for recession?
What is the correct approach when measuring for recession?
How is Clinical Attachment Level (CAL) measured?
How is Clinical Attachment Level (CAL) measured?
What characterizes inflammation without clinical attachment loss?
What characterizes inflammation without clinical attachment loss?
What does a positive measurement indicate regarding the gingival margin's positioning relative to the CEJ?
What does a positive measurement indicate regarding the gingival margin's positioning relative to the CEJ?
What is the clinical attachment loss (CAL) when the gingival margin is at the natural location with a probing depth of 6mm?
What is the clinical attachment loss (CAL) when the gingival margin is at the natural location with a probing depth of 6mm?
How is the clinical attachment loss calculated when recession is present?
How is the clinical attachment loss calculated when recession is present?
When the gingival margin covers the CEJ and the probing depth is 9mm with a gingival margin level of -3mm, what is the clinical attachment loss?
When the gingival margin covers the CEJ and the probing depth is 9mm with a gingival margin level of -3mm, what is the clinical attachment loss?
In the case of a gingival margin apical to the CEJ with a probing depth of 4mm and a gingival margin level of +2mm, what is the resulting clinical attachment loss?
In the case of a gingival margin apical to the CEJ with a probing depth of 4mm and a gingival margin level of +2mm, what is the resulting clinical attachment loss?
What does a positive gingival margin level indicate when calculating clinical attachment loss?
What does a positive gingival margin level indicate when calculating clinical attachment loss?
What does probing depth measure in periodontal assessments?
What does probing depth measure in periodontal assessments?
What is the significance of a probing depth greater than 4mm?
What is the significance of a probing depth greater than 4mm?
Which component is NOT part of the periodontal probing process?
Which component is NOT part of the periodontal probing process?
How many points are typically evaluated in a six-point pocket chart?
How many points are typically evaluated in a six-point pocket chart?
What clinical aspect does the clinical attachment level relate to?
What clinical aspect does the clinical attachment level relate to?
Why is the diameter of the probe important in periodontal assessments?
Why is the diameter of the probe important in periodontal assessments?
When conducting a periodontal assessment, what is the primary purpose of measuring free gingival margin?
When conducting a periodontal assessment, what is the primary purpose of measuring free gingival margin?
What is one limitation associated with periodontal probing?
What is one limitation associated with periodontal probing?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
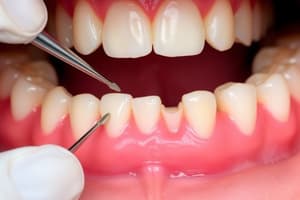
Probing Depth
- The probing depth is the distance from the gingival margin to the bottom of the pocket.
- It is measured using a periodontal probe with a standardized tip diameter (0.4mm–0.5mm).
- A probing depth of 4mm or more indicates a periodontal pocket.
Limitations of Periodontal Probing
- The probe needs to be walked across the sulcus to ensure no pockets are missed.
- Bone levels vary in a small space, which can affect probing readings.
- Probing depth alone does not accurately reflect the loss of periodontal support.
6 Point Pocket Chart
- The six points refer to the buccal and lingual surfaces of a tooth, divided into six sections.
- The probing depth is recorded for each of the six points on a tooth.
- The walking stroke technique is used to ensure that all pockets are documented.
Free Gingival Margin
- The free gingival margin is the edge of the gingiva that surrounds the tooth.
- The location of the free gingival margin relative to the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) is important for periodontal assessment.
- A negative number indicates that the gingival margin covers the CEJ; a positive number indicates recession.
Clinical Attachment Levels
- The clinical attachment level (CAL) is a measurement of the true periodontal support around a tooth.
- It is calculated by adding the probing depth to the location of the gingival margin relative to the CEJ.
- CAL helps distinguish between gingivitis (inflammation without attachment loss) and periodontitis (inflammation with attachment loss).
Calculating CAL
- To calculate CAL, you need the probing depth and the level of the gingival margin.
- If the gingival margin is at the natural level, the CAL is equal to the probing depth.
- If there is recession, add the level of the gingival margin to the probing depth.
- If the gingival margin covers the CEJ, subtract the level of the gingival margin from the probing depth.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.