Podcast
Questions and Answers
What type of instrument is recommended for detecting furcation involvement?
What type of instrument is recommended for detecting furcation involvement?
- Sickle scaler
- Blunt-ended, curved furcation probe (correct)
- Explorer
- Straight periodontal probe
When assessing horizontal tooth mobility, what serves as a reference point for observing movement?
When assessing horizontal tooth mobility, what serves as a reference point for observing movement?
- Adjacent teeth (correct)
- The opposing arch teeth
- The gingival margin
- The patient's lip line
Which of the following best describes fremitus?
Which of the following best describes fremitus?
- A palpable or visible movement of a tooth when in function (correct)
- The measurement of gingival recession around a tooth.
- The depth of a periodontal pocket as measured with a probe.
- The degree of horizontal tooth mobility when lateral forces are applied.
What does the presence of exudate during probing likely indicate?
What does the presence of exudate during probing likely indicate?
A patient demonstrates the ability to depress a tooth within its socket. What type of mobility is this?
A patient demonstrates the ability to depress a tooth within its socket. What type of mobility is this?
Furcation involvement often signals the need for what type of treatment?
Furcation involvement often signals the need for what type of treatment?
What is the correct method for assessing fremitus?
What is the correct method for assessing fremitus?
You are evaluating a patient and notice that the radiograph shows bone loss between the roots of a mandibular molar. Clinically, what should you assess for?
You are evaluating a patient and notice that the radiograph shows bone loss between the roots of a mandibular molar. Clinically, what should you assess for?
Why is documenting periodontal assessment findings in a patient's chart so important?
Why is documenting periodontal assessment findings in a patient's chart so important?
Which of the following is the PRIMARY objective of a clinical periodontal assessment?
Which of the following is the PRIMARY objective of a clinical periodontal assessment?
A dental hygienist notes a 5mm pocket depth, bleeding on probing, and slight tooth mobility on tooth #8. According to the principles of periodontal assessment, what should be the hygienist's next step?
A dental hygienist notes a 5mm pocket depth, bleeding on probing, and slight tooth mobility on tooth #8. According to the principles of periodontal assessment, what should be the hygienist's next step?
Which of the following is NOT typically recorded as part of a comprehensive periodontal assessment?
Which of the following is NOT typically recorded as part of a comprehensive periodontal assessment?
Why is a periodontal screening examination (PSE) used?
Why is a periodontal screening examination (PSE) used?
A clinician measures 2mm of gingival recession and a 4mm probing depth on the facial aspect of tooth #25. What is the clinical attachment loss (CAL) on this surface?
A clinician measures 2mm of gingival recession and a 4mm probing depth on the facial aspect of tooth #25. What is the clinical attachment loss (CAL) on this surface?
Which of the following is the most accurate way to assess tooth mobility?
Which of the following is the most accurate way to assess tooth mobility?
During a periodontal assessment, a clinician notices the free gingival margin is positioned apical to the cementoenamel junction (CEJ). This finding indicates the presence of which condition?
During a periodontal assessment, a clinician notices the free gingival margin is positioned apical to the cementoenamel junction (CEJ). This finding indicates the presence of which condition?
Which of the following is the correct relationship between the free gingival margin (FGM) and the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) in a healthy periodontium?
Which of the following is the correct relationship between the free gingival margin (FGM) and the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) in a healthy periodontium?
In which Miller classification does gingival recession extend to or beyond the mucogingival line into the mucosa?
In which Miller classification does gingival recession extend to or beyond the mucogingival line into the mucosa?
When assessing the gingiva, which of the following characteristics are important to evaluate to determine its health?
When assessing the gingiva, which of the following characteristics are important to evaluate to determine its health?
What clinical characteristic defines a Miller Class IV gingival defect?
What clinical characteristic defines a Miller Class IV gingival defect?
What clinical sign indicates that the free gingival margin (FGM) is significantly coronal to the cementoenamel junction (CEJ)?
What clinical sign indicates that the free gingival margin (FGM) is significantly coronal to the cementoenamel junction (CEJ)?
What visual characteristic typically distinguishes keratinized gingiva from nonkeratinized mucosa?
What visual characteristic typically distinguishes keratinized gingiva from nonkeratinized mucosa?
Displacement of the gingival soft tissue margin apical to the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) is referred to as:
Displacement of the gingival soft tissue margin apical to the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) is referred to as:
Presence of gingival recession:
Presence of gingival recession:
A probing depth measurement is recorded as 3.5 mm. Following the standard protocol, how should this measurement be documented?
A probing depth measurement is recorded as 3.5 mm. Following the standard protocol, how should this measurement be documented?
What does bleeding on probing (BOP) primarily indicate?
What does bleeding on probing (BOP) primarily indicate?
In the Miller Classification, what is a key characteristic of a Class I gingival recession defect?
In the Miller Classification, what is a key characteristic of a Class I gingival recession defect?
When assessing overt clinical signs of gingival inflammation, contour changes are observed. What specific contour change would suggest inflammation?
When assessing overt clinical signs of gingival inflammation, contour changes are observed. What specific contour change would suggest inflammation?
What is the primary composition of exudate found in a periodontal pocket?
What is the primary composition of exudate found in a periodontal pocket?
How is the presence of exudate typically detected in a periodontal pocket?
How is the presence of exudate typically detected in a periodontal pocket?
A patient presents with gingival recession that is isolated to the facial surface, not extending to the mucogingival junction, and the interdental papillae remain intact, filling the interdental spaces. According to the Miller Classification, which class does this represent?
A patient presents with gingival recession that is isolated to the facial surface, not extending to the mucogingival junction, and the interdental papillae remain intact, filling the interdental spaces. According to the Miller Classification, which class does this represent?
During a periodontal examination, a delayed bleeding response is observed after probing. What does this suggest?
During a periodontal examination, a delayed bleeding response is observed after probing. What does this suggest?
Why is direct visual examination important when assessing for calculus deposits?
Why is direct visual examination important when assessing for calculus deposits?
What is the most important purpose of plaque scores in periodontal assessment?
What is the most important purpose of plaque scores in periodontal assessment?
Why is identifying local contributing factors crucial during a periodontal assessment?
Why is identifying local contributing factors crucial during a periodontal assessment?
What does radiographic evidence of bone loss primarily contribute to in a clinical periodontal assessment?
What does radiographic evidence of bone loss primarily contribute to in a clinical periodontal assessment?
In attached gingiva calculation, if the total width of gingiva is 3mm and the probing depth is 2mm, what is the width of the attached gingiva?
In attached gingiva calculation, if the total width of gingiva is 3mm and the probing depth is 2mm, what is the width of the attached gingiva?
When the gingival margin is slightly coronal to the cementoenamel junction (CEJ), how is the clinical attachment level (CAL) determined?
When the gingival margin is slightly coronal to the cementoenamel junction (CEJ), how is the clinical attachment level (CAL) determined?
A patient presents with a 5mm total width of gingiva and a 3mm probing depth. What is the width of the attached gingiva, and what does this indicate?
A patient presents with a 5mm total width of gingiva and a 3mm probing depth. What is the width of the attached gingiva, and what does this indicate?
A radiograph reveals bone loss in the furcation area of a mandibular molar. What does this finding suggest about the periodontal status of the tooth?
A radiograph reveals bone loss in the furcation area of a mandibular molar. What does this finding suggest about the periodontal status of the tooth?
Flashcards
Clinical Periodontal Assessment
Clinical Periodontal Assessment
A systematic process to gather comprehensive data about a patient's periodontal health.
Purpose of Assessment Data
Purpose of Assessment Data
Used to make a periodontal diagnosis and create an individualized treatment plan.
Objectives of Assessment
Objectives of Assessment
Detecting inflammation, identifying damage, assigning diagnosis, documenting features for long-term monitoring.
Standard of Care
Standard of Care
Signup and view all the flashcards
Baseline Data
Baseline Data
Signup and view all the flashcards
Periodontal Screening Examination
Periodontal Screening Examination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Comprehensive Periodontal Assessment
Comprehensive Periodontal Assessment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Assessment Components
Assessment Components
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gingival Health Evaluation
Gingival Health Evaluation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gingival Inflammation Signs
Gingival Inflammation Signs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Free Gingival Margin (FGM) Levels
Free Gingival Margin (FGM) Levels
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gingival Recession
Gingival Recession
Signup and view all the flashcards
Recession Result
Recession Result
Signup and view all the flashcards
Recession and Age
Recession and Age
Signup and view all the flashcards
Miller Class I Defect
Miller Class I Defect
Signup and view all the flashcards
Miller Class II Defect
Miller Class II Defect
Signup and view all the flashcards
Horizontal Tooth Mobility
Horizontal Tooth Mobility
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vertical Tooth Mobility
Vertical Tooth Mobility
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fremitus
Fremitus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Furcation Involvement
Furcation Involvement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Horizontal Mobility Assessment
Horizontal Mobility Assessment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vertical Mobility Assessment
Vertical Mobility Assessment
Signup and view all the flashcards
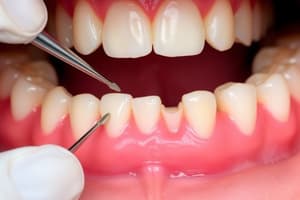
Furcation Probes
Furcation Probes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Furcation Involvement Significance
Furcation Involvement Significance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mucogingival Junction
Mucogingival Junction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Probing Depth
Probing Depth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bleeding on Probing
Bleeding on Probing
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exudate
Exudate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Keratinized gingiva
Keratinized gingiva
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nonkeratinized mucosa:
Nonkeratinized mucosa:
Signup and view all the flashcards
Calculus Deposits
Calculus Deposits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Plaque Biofilm
Plaque Biofilm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Local Contributing Factors
Local Contributing Factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radiographic Bone Loss
Radiographic Bone Loss
Signup and view all the flashcards
Attached Gingiva Width
Attached Gingiva Width
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clinical Attachment Level (CAL)
Clinical Attachment Level (CAL)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Furcation Involvement Scale
Furcation Involvement Scale
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Clinical periodontal assessment is designed to provide a comprehensive view of a patient's periodontal health.
- Periodontal assessment is a critical function performed by clinicians as it facilitates:
- Periodontal diagnosis
- Individualized treatment plans
Objectives of Assessment
- Detect clinical signs of inflammation in the periodontium.
- Identify damage caused by disease or trauma.
- Provide data to assign periodontal diagnosis.
- Document features for long-term monitoring of periodontal disease activity.
- A legal responsibility exists for dentists and hygienists to complete thorough periodontal assessments for every patient.
- Periodontal assessment is incomplete until all gathered information is recorded on the patient chart.
- Documentation measures both treatment outcomes and periodontal health status over time.
- Findings from the initial assessment act as baseline data for long-term monitoring of periodontal health.
- There are two types of Periodontal Assessments:
- Periodontal Screening Examination is a quick process to check if a comprehensive assessment is needed.
- Comprehensive Periodontal Assessment involves an intensive and in-depth information-gathering process.
Periodontal Assessment Components
- Gingival inflammation
- Level of free gingival margin
- Gingival recession
- Level of mucogingival junction
- Probing depth measurements
- Bleeding on probing
- Presence of exudate
- Tooth mobility
- Furcation involvement
- Calculus deposits on teeth
- Dental plaque biofilm
Assessing Gingiva
- Evaluate tissue color, contour, consistency, and texture.
- Assess for overt clinical signs of gingival inflammation like Erythema, Edema, Gingival color and Contour.
Level of Free Gingival Margin
- Possible relationships of free gingival margin (FGM) to cementoenamel junction (CEJ) include:
- FGM slightly coronal to the CEJ equals normal position
- FGM significantly coronal to the CEJ equals gingival enlargement
- FGM apical to the CEJ equals recession of gingival margin
Gingival Recession
- Refers to displacement of the gingival soft tissue margin apical to the CEJ, resulting in root exposure
- Presence increases with age, but can occur even in patients with good oral hygiene
Miller Classification for Gingival Recession
Refer to the following Classifications when charting:
- Class I: Recession isolated to the facial surface, interdental papillae fill adjacent interdental spaces, and recession does not extend to mucogingival line.
- Class II: Recession isolated to the facial surface, interdental papillae remain intact and fill interdental spaces, and recession extends or goes beyond mucogingival line into the mucosa.
- Class III: Recession is broad, interdental papillae is missing due to damage from disease, and recession stretches to or beyond the mucogingival line in to the mucosa.
- Class IV: Recession extends to or beyond the mucogingival junction with severe loss of interproximal alveolar bone resulting in open interdental areas.
Level of Mucogingival Junction
- It is the junction between the keratinized gingiva and the nonkeratinized mucosa.
- Keratinized tissue is pale pink, while nonkeratinized tissue is thinner and more vascular.
Probing Depths
- Measurements from the free gingival margin to the base of the pocket.
- Recorded to the nearest millimeter, with half measurements rounded up.
- Depths are recorded at six sites per tooth.
Bleeding on Probing
- It represents bleeding from the ulcerated soft tissue wall of the periodontal pocket.
- Bleeding on probing can occur either immediately or be delayed.
- But also, excessive force could also cause bleeding.
Presence of Exudate
- Exudate, also called suppuration or pus is dead white blood cells and only occurs in infection.
- A pale yellow material oozes from the orifice of a pocket and is easiest to detect by tissue manipulation.
Tooth Mobility
- Horizontal tooth mobility is the movement of a tooth from facial to lingual direction, adjacent tooth is observed as a point of reference.
- Vertical tooth mobility is the movement of a tooth up and down in the socket.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Test your periodontal knowledge with this quiz! Questions cover detecting furcation involvement, assessing tooth mobility, recognizing fremitus, and interpreting clinical signs like exudate. Understand the importance of documentation and treatment planning.