Questions and Answers
What is the primary treatment for grade I and II medial ligament injuries?
In what scenario is operative management indicated for medial ligament injuries?
Which diagnostic imaging technique is recommended in cases of suspected bony injury?
What complication is commonly observed after surgical intervention on the medial side of the knee?
Signup and view all the answers
Which structure is NOT part of the static components of the posterolateral corner?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the expected healing time for medial ligament injuries managed conservatively?
Signup and view all the answers
How does a fracture of the head of the fibula affect knee stability?
Signup and view all the answers
Which dynamic structure is NOT associated with the posterolateral corner?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary role of the MCL in knee biomechanics?
Signup and view all the answers
Which grade of MCL injury includes opening of the medial joint line without an endpoint?
Signup and view all the answers
During the valgus stress test, which position is recommended to assess MCL injury?
Signup and view all the answers
What imaging technique is most commonly used to diagnose MCL injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the characteristic presentation of a grade I MCL injury?
Signup and view all the answers
Which anatomical part does the medial capsular structure extend from?
Signup and view all the answers
What is commonly observed in a grade II MCL injury during a valgus stress test?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following statements is true regarding the biomechanics of knee stability?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the popliteus tendon during knee movement?
Signup and view all the answers
Which structure does NOT have an attachment with the popliteus tendon?
Signup and view all the answers
In acute injuries, the popliteofibular ligament primarily resists which movement?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of injury mechanism is most associated with stars varus injuries to the popliteus complex?
Signup and view all the answers
Which imaging technique is most effective for assessing injuries to the popliteus tendon?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the recommended management approach for concurrent PLC and PCL injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
Which condition is most commonly associated with popliteus tendon injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
When assessing for nerve or vessel injury related to knee trauma, what should be included in the examination?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the recommended treatment for a posterolateral complex injury?
Signup and view all the answers
Which imaging technique is considered the best after an X-ray for diagnosing knee injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
In examining the knee, which test assesses the control of posterior displacement of the tibia?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of injury is most commonly associated with posterior cruciate ligament injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following statements about the posterior cruciate ligament is true?
Signup and view all the answers
Which ligament injuries are typically managed conservatively rather than surgically?
Signup and view all the answers
What role does the PCL play regarding knee stability?
Signup and view all the answers
Which factor influences the tension of the PCL fibers during knee movement?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary goal of non-operative treatment for older recreational athletes with knee injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
Which statement about post-operative rehabilitation after ACL surgery is true?
Signup and view all the answers
What anatomical feature characterizes the superficial medial collateral ligament (MCL)?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a crucial aspect of the rehabilitation protocol after ACL surgery?
Signup and view all the answers
How does the deep ligament of the medial collateral ligament differ from the superficial ligament?
Signup and view all the answers
What common issue is associated with improper post-operative rehabilitation related to the knee?
Signup and view all the answers
What is typically prioritized in the rehabilitation process from the day of knee injury?
Signup and view all the answers
What role do coppers play in non-operative treatment for older athletes?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary treatment approach for older recreational athletes with knee injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
Which anatomical feature distinguishes the deep medial collateral ligament (MCL) from the superficial MCL?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the earliest goal of rehabilitation following ACL surgery?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a common misconception about the start of post-operative rehabilitation after ACL surgery?
Signup and view all the answers
How does the superficial medial collateral ligament attach within the knee anatomy?
Signup and view all the answers
Which factor plays a critical role in the biological response during the rehabilitation process?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a prevalent issue related to improper post-operative rehabilitation in knee surgeries?
Signup and view all the answers
In evaluating biomechanical stability of the knee, which structure is predominantly involved?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the recommended initial imaging technique for diagnosing injuries to the posterior cruciate ligament?
Signup and view all the answers
Which factor is most likely to influence the healing potential of the posterior cruciate ligament compared to the anterior cruciate ligament?
Signup and view all the answers
In the context of knee biomechanics, what role does the posterior cruciate ligament primarily serve?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary goal when managing medial ligament injuries conservatively?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following assessments is specifically indicated for evaluating the integrity of the posterolateral complex of the knee?
Signup and view all the answers
What surgical approach is favored for treating significant posterolateral complex injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a common misconception regarding the role of the posterior cruciate ligament in knee stability?
Signup and view all the answers
In terms of rehabilitation, what is a crucial aspect following surgical management of knee injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary reason hinged knee braces are recommended for grade I and II medial ligament injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
Which structure serves as an attachment point for the lateral collateral ligament (LCL)?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a significant complication after surgical intervention on the medial side of the knee?
Signup and view all the answers
During rehabilitation after surgery for a grade III medial ligament tear, patients should be cautious of which common issue?
Signup and view all the answers
Which surgical treatment option is indicated when there is an avulsed bone fragment in a grade III medial ligament injury?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the posterolateral corner structures?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is NOT considered a static structure of the posterolateral corner?
Signup and view all the answers
What diagnostic imaging technique is most appropriate to use alongside X-rays in cases of knee instability?
Signup and view all the answers
What structure does the popliteus tendon NOT attach to?
Signup and view all the answers
Which biomechanical function is primarily resisted by the popliteofibular ligament?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of injury mechanism is associated with the popliteus tendon complex?
Signup and view all the answers
During clinical assessment for a popliteus tendon injury, which symptom is NOT commonly reported?
Signup and view all the answers
In which scenario is it recommended to reconstruct multiple ligaments in one surgical session?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a common diagnosis method that should be part of the overall limb assessment after a knee injury?
Signup and view all the answers
Which anatomical feature does NOT characterize the popliteus tendon complex?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary focus of the rehabilitation protocol following surgical intervention for the popliteus tendon?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the main characteristic of a grade III MCL injury during a valgus stress test?
Signup and view all the answers
Which diagnostic advantage does MRI provide for assessing MCL injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
In performing the valgus stress test, which flexion angle positions the MCL most effectively?
Signup and view all the answers
Which anatomical structures primarily resist valgus stress when the knee is less flexed?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a common misconception about the presentation of a grade I MCL injury?
Signup and view all the answers
What aspect of rehabilitation is critical for recovering from MCL injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
In which situation would grade II MCL injuries typically be classified during assessment?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following parts is NOT associated with the medial capsular component of the knee?
Signup and view all the answers
The superficial medial collateral ligament is shorter and stronger than the deep medial collateral ligament.
Signup and view all the answers
Post-operative rehabilitation for knee surgery should ideally begin after a week to allow for initial healing.
Signup and view all the answers
Maintaining full extension during knee rehabilitation is crucial to prevent flexion deformity.
Signup and view all the answers
The deep ligament of the medial collateral ligament is primarily responsible for lateral stability of the knee.
Signup and view all the answers
The medial collateral ligament consists of a single ligamentous structure without any distinct parts.
Signup and view all the answers
Rehabilitation should be performed without strict supervision to foster independence in recovery.
Signup and view all the answers
The primary goal of non-operative treatment in older recreational athletes involves aggressive surgical intervention.
Signup and view all the answers
A significant delay in initiating rehabilitation can enhance the recovery process after knee surgery.
Signup and view all the answers
The posterolateral complex is known for having a high potential for healing and can be managed conservatively.
Signup and view all the answers
MRI is considered the best imaging modality for diagnosing knee injuries after an X-ray.
Signup and view all the answers
Rehabilitation protocols following ACL surgery prioritize immediate weight-bearing activities to enhance recovery.
Signup and view all the answers
The medial collateral ligament primarily controls varus stresses during knee motion.
Signup and view all the answers
The anatomy of the posterior cruciate ligament shows that it originates from the medial condyle of the femur and attaches to the tibia.
Signup and view all the answers
Post-operative rehabilitation for knee surgeries generally emphasizes repetitive high-impact exercises from the onset.
Signup and view all the answers
Associated injuries with the posterior cruciate ligament can only be diagnosed through physical examination, not imaging techniques.
Signup and view all the answers
The popliteofibular ligament has attachments to the lateral meniscus and the lateral aspect of the lateral condyle of the femur.
Signup and view all the answers
The PCL assists in controlling both posterior drawer and varus stresses of the knee.
Signup and view all the answers
In cases of combined ligament tears in the knee, reconstructing all ligaments in one surgical session is not recommended due to the risk of overstressing other ligaments.
Signup and view all the answers
The cruciate ligaments primarily resist varus stresses in the knee.
Signup and view all the answers
Hyperextension injuries with external tibial rotation are particularly common in contact sports.
Signup and view all the answers
The rehabilitation protocol following ACL surgery prioritizes restoring full range of motion before strength training.
Signup and view all the answers
The biceps tendon inserts at the head of the fibula while the common peroneal nerve runs just proximal to it.
Signup and view all the answers
Injury to the posterolateral corner usually occurs independently of other ligament or meniscal injuries.
Signup and view all the answers
Eccymosis along the lateral or posterolateral aspects of the knee is a common symptom of a popliteus complex injury.
Signup and view all the answers
The medial ligament has little potential for healing due to its narrow structure and complete tears in most cases.
Signup and view all the answers
X-rays are the recommended imaging technique in cases of suspected fibular head fractures affecting posterolateral corner stability.
Signup and view all the answers
Hinged knee braces provide protection from varus valgus stress while allowing motion in the normal arc during conservative treatment of grade I and II medial ligament injuries.
Signup and view all the answers
Rehabilitation following surgery for grade III medial ligament injuries is typically shorter and less complex compared to conservative treatment management.
Signup and view all the answers
Static components of the posterolateral corner include structures like the lateral collateral ligament and the popliteal tendon.
Signup and view all the answers
The expected healing time for the medial ligament managed conservatively is generally shorter than 4 weeks.
Signup and view all the answers
An avulsed bone fragment from the knee can be repaired using open techniques that involve sutures.
Signup and view all the answers
The head of the fibula has no significant attachment to any ligament that contributes to posterolateral corner stability.
Signup and view all the answers
The primary restraint to valgus stress in knee biomechanics is the lateral collateral ligament.
Signup and view all the answers
Grade III MCL injuries are indicated by immediate and continuous opening of the medial joint line during the valgus stress test.
Signup and view all the answers
MRI is the least recommended imaging technique for diagnosing medial ligament injuries.
Signup and view all the answers
In rehabilitation protocols for MCL injuries, maximum knee flexion is contraindicated to prevent further instability.
Signup and view all the answers
The posterior oblique ligament is a component of the medial ligament complex that contributes to knee stability.
Signup and view all the answers
Increased flexion range during knee movement generally puts the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) at a higher risk of injury.
Signup and view all the answers
The meniscofemoral and meniscotibial parts are essential components of the lateral collateral ligament complex.
Signup and view all the answers
Posteromedial capsular structures are primarily responsible for restraining valgus stress at higher degrees of knee flexion.
Signup and view all the answers
The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is generally treated surgically rather than conservatively.
Signup and view all the answers
X-rays are the best initial imaging technique for diagnosing knee injuries related to the posterior cruciate ligament.
Signup and view all the answers
Rehabilitation protocols for knee injuries prioritize early mobilization of the joint.
Signup and view all the answers
The posterolateral corner is primarily responsible for controlling varus stresses in the knee.
Signup and view all the answers
The thickness of the posterior cruciate ligament is less than that of the anterior cruciate ligament.
Signup and view all the answers
Meniscal damage is often associated with injuries to the posterior cruciate ligament.
Signup and view all the answers
The posterior drawer test assesses the control of anterior displacement of the tibia.
Signup and view all the answers
The potential for healing in the posterolateral complex is generally high.
Signup and view all the answers
The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is not a primary restraint to valgus stress at any degree of flexion.
Signup and view all the answers
MRI is not considered a diagnostic tool for medial ligament injuries and typically does not show irregularity at the medial side of the knee.
Signup and view all the answers
A grade II MCL injury is characterized by an end point on the valgus stress test.
Signup and view all the answers
The posterior oblique ligament contributes significantly to the stability of the knee under valgus stress.
Signup and view all the answers
Using a valgus stress test at 30 degrees of flexion is ineffective for assessing MCL injuries.
Signup and view all the answers
Increasing the flexion range of the knee reduces the risk of injury to the ACL.
Signup and view all the answers
Minimal swelling is often seen in grade III MCL injuries, indicating a less severe injury.
Signup and view all the answers
The anterior fibers of the MCL work independently from the posterior fibers depending on the angle of flexion.
Signup and view all the answers
The popliteus tendon complex is primarily responsible for resisting varus and external rotation of the knee.
Signup and view all the answers
The popliteofibular ligament is not a component of the popliteus tendon complex.
Signup and view all the answers
Immediate post-operative rehabilitation following knee surgeries should focus on aggressive strengthening exercises.
Signup and view all the answers
In cases of combined ligament tears, reconstructing all ligaments in one surgical session is recommended to prevent overstressing.
Signup and view all the answers
The lateral meniscus is directly attached to the popliteus tendon.
Signup and view all the answers
Clinical assessment for knee injuries should only include checking for injuries to the collateral ligaments.
Signup and view all the answers
Biomechanically, the cruciate ligaments do not provide significant support against varus stresses in the knee.
Signup and view all the answers
Eccymosis is typically associated with injuries to the posterior lateral aspects of the knee.
Signup and view all the answers
The superficial medial collateral ligament is the shortest and weakest component of the knee.
Signup and view all the answers
Starting rehabilitation right after the day of ACL surgery is essential for proper recovery.
Signup and view all the answers
The deep medial collateral ligament is located on the lateral side of the knee joint.
Signup and view all the answers
Full extension of the knee is prioritized immediately after ACL surgery to prevent complications.
Signup and view all the answers
Knee ligaments injuries are commonly managed through an extensive rehabilitation period lasting approximately 12 months.
Signup and view all the answers
Diagnostic imaging techniques are unnecessary for assessing MCL injuries due to their clear clinical presentation.
Signup and view all the answers
ACL surgery may not always require subsequent rehabilitation if healing occurs naturally.
Signup and view all the answers
Proprioception is a goal of the rehabilitation process following knee ligament surgery.
Signup and view all the answers
The medial ligament has low potential for healing due to being narrow and completely torn in many cases.
Signup and view all the answers
For grade I and II medial ligament injuries, hinged knee braces provide support while allowing motion.
Signup and view all the answers
Operative management for grade III medial ligament tears is generally not recommended.
Signup and view all the answers
The posterolateral corner is primarily composed of dynamic structures rather than static ones.
Signup and view all the answers
Local measures and physical therapy should be initiated immediately after a knee injury to limit side-to-side movement.
Signup and view all the answers
Rehabilitation following surgery for medial ligament injuries is typically shorter than for conservative management.
Signup and view all the answers
A fracture of the head of the fibula has no significant impact on posterolateral corner stability.
Signup and view all the answers
X-rays are the only imaging technique used for diagnosing bony injuries in knee evaluations.
Signup and view all the answers
What is a common clinical feature of a posterior dislocation of the hip?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a recommended initial treatment for a posterior dislocation of the hip?
Signup and view all the answers
Which imaging finding is typical in posterior dislocation of the hip?
Signup and view all the answers
What serious complication can result from delayed reduction of a hip dislocation?
Signup and view all the answers
What should be avoided during the treatment of a posterior dislocation of the hip?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a common clinical feature of intertrochanteric fractures?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of fracture is known for good healing due to stable contact between bony surfaces?
Signup and view all the answers
Which imaging technique is crucial for identifying intertrochanteric fractures?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary goal of surgical treatment for intertrochanteric fractures?
Signup and view all the answers
Which complication might arise from conservative treatment of intertrochanteric fractures?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a significant clinical feature associated with subtrochanteric fractures?
Signup and view all the answers
What treatment option is typically suggested for non-union in femoral neck fractures?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is NOT a type of hip dislocation?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a common complication after surgical intervention for fractures?
Signup and view all the answers
What complication is primarily associated with prolonged bed recumbency after conservative treatment?
Signup and view all the answers
Which clinical feature is characteristic of anterior dislocation of the hip?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a common complication associated with both anterior and central hip dislocations?
Signup and view all the answers
Which diagnostic imaging technique is used to determine the position of the femoral head in dislocated hips?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the recommended initial treatment method for anterior dislocation of the hip?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following best describes the mechanism of injury leading to central dislocation of the hip?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the duration of skeletal traction maintained for central dislocation of the hip?
Signup and view all the answers
What clinical feature would you NOT expect to see in anterior dislocation of the hip?
Signup and view all the answers
Which complication is specifically associated with central dislocation of the hip?
Signup and view all the answers
Posterior dislocation of the hip often requires closed manipulation for reduction.
Signup and view all the answers
The lesser trochanter is clearly visible in X-rays of a posterior dislocation of the hip.
Signup and view all the answers
Avascular necrosis can occur as a complication of delayed reduction of a hip dislocation.
Signup and view all the answers
Anterior dislocation of the hip is more common than posterior dislocation.
Signup and view all the answers
Traction is applied for one week following the reduction of a dislocated hip.
Signup and view all the answers
Severe pain and deformity are common clinical features of an intertrochanteric fracture.
Signup and view all the answers
A subtrochanteric fracture typically heals faster than an intertrochanteric fracture.
Signup and view all the answers
X-rays are not useful for identifying fractures and assessing stability.
Signup and view all the answers
Osteoporosis is a risk factor for intertrochanteric fractures, particularly in women.
Signup and view all the answers
Total hip replacement is a common treatment for nonunion in femoral neck fractures.
Signup and view all the answers
Complications from surgical intervention for intertrochanteric fractures can include non-union.
Signup and view all the answers
The initial treatment for a subtrochanteric fracture is typically conservative, involving traction.
Signup and view all the answers
Inadequate fixation can lead to nonunion of a femoral neck fracture.
Signup and view all the answers
Surgical fixation for intertrochanteric fractures guarantees complete recovery without complications.
Signup and view all the answers
Dislocation of the hip occurs when there is complete loss of contact between opposing articular surfaces.
Signup and view all the answers
The leg in anterior dislocation of the hip lies in external rotation, abduction, and slight flexion.
Signup and view all the answers
Avascular necrosis is a complication associated only with central dislocation of the hip.
Signup and view all the answers
X-rays are used to show the position of the femoral head in dislocation cases.
Signup and view all the answers
The treatment for anterior dislocation includes gentle internal rotation after traction.
Signup and view all the answers
Skeletal traction through the tibia is used in treating complications of hip dislocation.
Signup and view all the answers
Severe pain is a common clinical feature observed in hip dislocation cases.
Signup and view all the answers
Loss of movement is not associated with anterior dislocation of the hip.
Signup and view all the answers
Complications of hip dislocation can include osteoarthritis of the hip.
Signup and view all the answers
The superficial medial collateral ligament is the largest medial structure, measuring 10-12cm long and 1.5cm wide.
Signup and view all the answers
Grade I MCL injuries involve complete tearing of the ligament.
Signup and view all the answers
Valgus stress testing is used to assess injuries to the medial collateral ligament.
Signup and view all the answers
Non-operative treatment for older recreational athletes includes complete avoidance of sports.
Signup and view all the answers
Post-operative rehabilitation for ACL surgery should ideally begin the day of surgery.
Signup and view all the answers
Rehabilitation after knee ligament surgery generally lasts for 3 months.
Signup and view all the answers
The deep medial collateral ligament is a longer and weaker structure than the superficial ligament.
Signup and view all the answers
The primary goal of rehabilitation after ACL surgery is to regain full range of motion, proprioception, and strength.
Signup and view all the answers
The medial ligament has a low potential for healing due to its narrow structure.
Signup and view all the answers
Grade III tear of the MCL typically requires operative management.
Signup and view all the answers
Hinged knee braces restrict motion to aid in the healing of grade I and II ligament injuries.
Signup and view all the answers
Rehabilitation following surgery for knee ligament injuries is usually short and uncomplicated.
Signup and view all the answers
Valgus stress testing is used to assess the integrity of the medial ligament in the knee.
Signup and view all the answers
Conservative management is the first approach for grade I and II MCL injuries.
Signup and view all the answers
The posterolateral corner of the knee is simple and well-understood in anatomy.
Signup and view all the answers
A fracture of the head of the fibula does not affect posterolateral corner stability.
Signup and view all the answers
The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is typically managed surgically.
Signup and view all the answers
Grade I MCL injuries involve a complete tear of the ligament.
Signup and view all the answers
Valgus stress testing is performed to assess the integrity of the MCL.
Signup and view all the answers
Surgical exploration and primary repair are advised for all knee ligament injuries.
Signup and view all the answers
The healing potential of the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is better than that of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL).
Signup and view all the answers
Rehabilitation after knee ligament surgery should begin immediately after the surgery.
Signup and view all the answers
A gentle valgus stress test is performed with the knee in 90 degrees of flexion.
Signup and view all the answers
It is unnecessary to compare ligament test findings with the normal side.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the MCL in knee stability?
Signup and view all the answers
Which grade classification includes a complete tear of the MCL?
Signup and view all the answers
During a valgus stress test, what is the proper position for evaluating MCL injury?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the recommended treatment for a medial collateral ligament injury?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a key goal during the rehabilitation process after ACL surgery?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the most common management approach for ascertaining knee stability post-injury?
Signup and view all the answers
What aspect is critical in the rehabilitation protocol after a knee ligament surgery?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary goal of non-operative treatment for ligament injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary purpose of hinged knee braces in the management of grade I and II medial ligament injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
Which grade of medial ligament injury is best suited for conservative management?
Signup and view all the answers
During a valgus stress test for assessing medial ligament injuries, what is primarily tested?
Signup and view all the answers
What treatment option is indicated for grade III medial ligament tears?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the expected duration for rehabilitation after surgical intervention on the medial side of the knee?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following structures is considered a static component of the posterolateral corner?
Signup and view all the answers
What complication is commonly associated with knee surgeries on the medial side?
Signup and view all the answers
Which statement best describes the healing potential of the medial ligament?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the medial collateral ligament?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following describes the superficial medial collateral ligament?
Signup and view all the answers
Which grade classification is assigned to an MCL injury with a complete tear?
Signup and view all the answers
During the valgus stress test, what position is most effective for assessing MCL injury?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a common misconception about the post-operative rehabilitation process after ACL surgery?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary goal of rehabilitation following ACL surgery?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the recommended approach for managing knee ligaments injuries in older recreational athletes?
Signup and view all the answers
After an ACL surgery, what should the rehabilitation process aim to maintain as a priority?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary method of treatment for anterior dislocation of the hip?
Signup and view all the answers
Which complication is commonly associated with central dislocation of the hip?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the recommended duration for skeletal traction treatment for central dislocation of the hip?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a key characteristic feature of the leg in anterior dislocation of the hip?
Signup and view all the answers
Which symptom is NOT typically associated with anterior dislocation of the hip?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary treatment goal for elderly patients with femoral neck fractures?
Signup and view all the answers
In patients with Garden III and IV femoral neck fractures, what surgical method is typically recommended?
Signup and view all the answers
What complication can arise due to avascular necrosis of the femoral head?
Signup and view all the answers
Which surgical fixation technique is commonly used for young individuals with femoral neck fractures?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary approach for managing a femoral neck fracture?
Signup and view all the answers
Which factor is critical to consider when determining the treatment for a neck of femur fracture?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is a risk factor for femoral neck fractures?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a common outcome of nonunion in fractures?
Signup and view all the answers
What role does the periosteum play in the healing of neck of femur fractures?
Signup and view all the answers
What complication may arise from a femoral neck fracture if not properly managed?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the effect of an intracapsular hematoma on the femoral head?
Signup and view all the answers
Which classification is used to categorize femoral neck fractures?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of femoral neck fracture is categorized as stable?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a common mechanism of injury for a femoral neck fracture in elderly individuals?
Signup and view all the answers
What nonunion complication can arise from femoral neck fractures if surgical fixation is not successful?
Signup and view all the answers
Which surgical fixation technique is most appropriate for unstable femoral neck fractures?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of femoral neck fracture is described as completely displaced?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following factors does NOT contribute to the risk of developing a femoral neck fracture?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary treatment for nonunion following a femoral neck fracture?
Signup and view all the answers
Which complication is least likely to occur following surgical treatment of an intertrochanteric fracture?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is a potential complication due to prolonged bed recumbency after a conservative treatment of an intertrochanteric fracture?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the technique used for surgical fixation of intertrochanteric fractures?
Signup and view all the answers
What does NOT contribute to nonunion in displaced fractures?
Signup and view all the answers
What mechanism of injury is most associated with intertrochanteric fractures?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a common risk factor for intertrochanteric fractures in the elderly?
Signup and view all the answers
Which statement is true regarding complications following surgical treatment of intertrochanteric fractures?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of fracture is characterized by a complete loss of contact between opposing surfaces?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a primary goal during the early management of an intertrochanteric fracture?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary approach to treating a posterior dislocation of the hip?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is a potential complication related to untreated posterior dislocation of the hip?
Signup and view all the answers
What treatment option is taken for acutely reducing a dislocated hip?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the recommended duration of traction after the reduction of a dislocated hip?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following conditions is associated with a delay in hip dislocation reduction?
Signup and view all the answers
What specific injury can occur due to improper treatment of a hip dislocation?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of hip dislocation is less common?
Signup and view all the answers
What anatomical feature is affected in a posterior dislocation of the hip as observed on X-ray?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is a treatment consideration for managing complications of dislocated hips?
Signup and view all the answers
Which nerve injury is a known complication of hip dislocation?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following structures is primarily associated with the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a common mechanism of injury for the posterior cruciate ligament?
Signup and view all the answers
Which management option is considered effective for treating posterior cruciate ligament injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
Which diagnostic technique is considered most effective for assessing posterior cruciate ligament injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
Which sport is commonly associated with injuries to the posterior cruciate ligament?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the most common cause of chronic low back pain in athletes?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of femoroacetabular impingement leads to labral tears due to abnormal acetabular morphology?
Signup and view all the answers
What key aspect is crucial for managing acute spine injuries in athletes?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a primary characteristic of the Cam type of femoroacetabular impingement?
Signup and view all the answers
Which management approach is recommended for chronic low back pain in athletes?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of spinal injury is most likely associated with indirect trauma during vigorous sports?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of hip injuries are commonly caused by FAI?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary consequence of improper handling of an acutely injured spine?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of injury is most prevalent in diving and motorized sports?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of tissue is crucial for recovery from chronic muscular strains?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the most critical aspect to focus on before returning to sports following an ankle injury?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the first line of treatment for chronic ankle instability after conservative measures fail?
Signup and view all the answers
How long should an intense rehabilitation protocol for sports ankle injuries be attempted before re-evaluation?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of injury is the deltoid ligament predominantly associated with?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a common treatment to support the healing of a ruptured deltoid ligament?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a common consequence of prolonged cast immobilization for ankle injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of graft is most commonly used for surgical reconstruction of ankle ligaments?
Signup and view all the answers
What does chronic ankle instability often require after conservative management fails?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is a characteristic of either type of ligament injury in ankle sprains?
Signup and view all the answers
Which factor contributes to the need for surgical intervention in top-level athletes with ankle instability?
Signup and view all the answers
Which structure should be palpated first when assessing an ankle injury?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary goal of the PRICE method in the first week following an ankle injury?
Signup and view all the answers
Which imaging technique provides high sensitivity for viewing ligaments in cases of ankle injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is NOT an appropriate treatment modality for grade III ankle injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
What is an important reason for not needing an X-ray after an ankle injury?
Signup and view all the answers
Which phase of rehabilitation focuses on reacquiring strength and mobility after acute symptoms subside?
Signup and view all the answers
In the acute phase of ankle injury treatment, what is a recommended way to immobilize the injury?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the most common mechanism of injury for the posterior cruciate ligament?
Signup and view all the answers
In treating an ankle injury, which method follows after the reduction of acute symptoms?
Signup and view all the answers
What diagnostic technique is most effective in evaluating posterior cruciate ligament injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
In cases of isolated posterior cruciate ligament injuries, what is the recommended management approach?
Signup and view all the answers
What percentage of posterior cruciate ligament injuries are sports-related?
Signup and view all the answers
Which physical exam test is typically performed to assess posterior cruciate ligament stability?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a common associated injury with posterior cruciate ligament tears?
Signup and view all the answers
Which treatment option is typically used for combined posterior cruciate ligament injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
What specific type of graft is commonly used in surgical reconstruction of the posterior cruciate ligament?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of these sports is most frequently associated with posterior cruciate ligament injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary benefit of using an MRI for diagnosing posterior cruciate ligament injuries?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
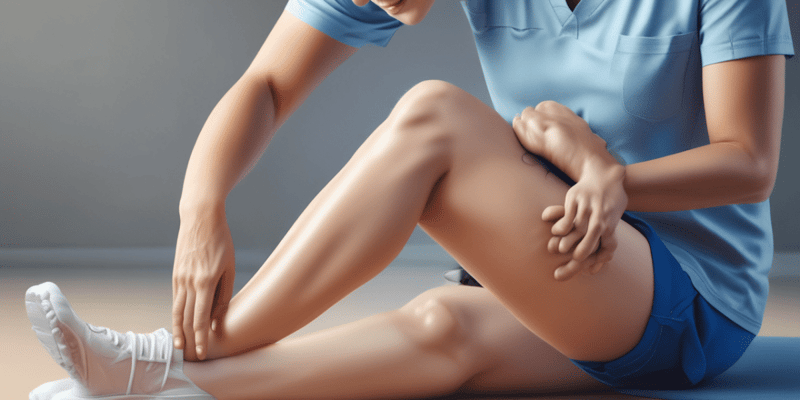
Knee Ligament Assessment
- Conduct variable tests: gentle varus stress test at 0 and 30 degrees of flexion, dial test, external rotation assessment, and posterior drawer test.
- Always compare findings with the contralateral knee.
Radiological Assessment
- X-rays used to identify avulsion fractures.
- MRI essential to evaluate soft tissue injuries like PCL, meniscal, or chondral damage.
- MRI is the best modality following X-ray for soft tissue assessment.
Management Approaches
- Surgery should be performed as soon as feasible for torn ligaments, often involving exploration and repair, with augmentation if needed.
- Associated injuries should ideally be addressed during the same surgical procedure to prevent complications from added loading.
Ligament Healing Tendencies
- Posterolateral complex has limited healing potential; surgical intervention is necessary.
- Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) and Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) require surgical treatment.
- Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) injuries can often be managed conservatively.
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL)
- PCL is the thickest knee ligament, with a primary stabilizing role.
- It originates from the medial femoral condyle and extends to the tibia, 1-2 cm below the joint line.
- Compared to the ACL, the PCL has a better potential for healing, hence conservative treatment may be effective.
Biomechanics of PCL
- PCL controls posterior tibial displacement and varus/valgus stress.
- Tension increases with knee flexion; evaluations through radiology are indicated when there are doubts regarding bone injuries.
Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Anatomy
- MCL is a broad ligament on the medial side, composed of superficial and deep layers.
- The superficial layer is between 10-12cm long, attaching near the medial epicondyle of the femur.
- The deep layer connects to the medial femoral condyle and stabilizes the joint through dynamic responses.
MCL Biomechanics and Injury Classification
- MCL primarily restrains valgus stress between 5-25 degrees of knee flexion.
- Injuries classified as:
- Grade I: Minor sprain with tenderness and minimal joint opening.
- Grade II: Moderate sprain with discernible joint opening and an endpoint.
- Grade III: Complete tear with continuous joint opening.
Non-operative Management of MCL Injuries
- Grade I and II injuries are treated conservatively with rehabilitation.
- Hinged knee braces support movement while protecting against excessive stress.
- Surgical intervention is reserved for Grade III injuries with significant instability or bone avulsion.
Posterolateral Corner Structures
- The posterolateral corner consists of static (LCL, posterolateral capsule) and dynamic structures (iliotibial band, popliteus tendon complex).
- LCL extends from the lateral epicondyle to the head of the fibula, critical for knee stability.
- Injury often results from trauma while playing contact sports or from non-contact hyperextension.
Rehabilitation Protocols
- Rehabilitation should start immediately post-surgery, emphasizing muscle activation and maintaining full knee extension.
- A gradual increase in range of motion and strength is essential, with a focus on preventing long-term complications such as stiffness.
- Duration typically spans 6 months, requiring close monitoring to avoid complications associated with knee surgeries.
Summary of Treatment Strategies
- PCL injuries may allow conservative measures, particularly if minimal tears are identified.
- Combined ligament injuries often necessitate simultaneous surgical reconstruction to prevent overstretching other ligaments' repairs during rehabilitation. ### X-rays and Management of Bony Injury
- X-rays are essential when there is suspicion of bony injury, such as an avulsion fracture or cases of joint instability.
- Medial ligament injuries have a high potential for healing; conservative management is preferred.
- Hinged knee braces are effective for Grade I and II injuries, allowing normal motion while protecting the knee from varus and valgus stress.
- Healing time for medial ligament injuries is typically between 6 to 8 weeks.
Treatment for Medial Ligament Injuries
- Local measures and physical therapy should commence early, considering side-to-side limitations.
- Operative management is indicated for Grade III tears or if there is an avulsed bone fragment.
- For Grade III tears, open repair using sutures or fixation of the avulsed fragment is recommended.
- Postoperative rehabilitation can be lengthy, with attention to preventing stiffness post-surgery.
Posterolateral Corner Anatomy
- The posterolateral corner is complex and includes static structures like the lateral collateral ligament (LCL) and the posterolateral capsule.
- Dynamic structures include the iliotibial band, biceps tendon, popliteus tendon complex, popliteofibular ligament, and arcuate ligament.
- The head of the fibula is connected to the LCL, biceps tendon, and popliteofibular ligament. A fracture here greatly affects posterolateral corner stability.
Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL) Anatomy
- The MCL consists of two principal parts: the superficial and deep ligaments.
- The superficial ligament is broad (10-12 cm long, 1.5 cm wide) and connects from the medial epicondyle of the femur to the medial proximal tibia.
- The deep ligament is stronger and is a thickened section of the knee capsule, extending distally from the femoral condyle.
Biomechanics of the MCL
- The MCL primarily restrains valgus stress when the knee is flexed between 5 to 25 degrees.
- The anterior fibers of the MCL can function independently from the posterior fibers based on knee flexion angles.
- Valgus stress with full extension predominantly affects the MCL, while increased flexion heightens the risk of ACL injury.
Classification of MCL Injuries
- Injuries are classified into three grades:
- Grade I: Pain and tenderness with minimal joint line opening on valgus stress test.
- Grade II: Similar to Grade I with joint line opening but an endpoint present.
- Grade III: Non-stop opening on valgus stress, often referred to as "open book."
Diagnosis and Clinical Presentation
- The MCL is the most commonly injured knee ligament, often due to valgus stress injury.
- Pain is localized on the medial side of the knee, particularly at the medial epicondyle or medial proximal tibia.
- Valgus stress tests should be performed at full extension and during 30 degrees of flexion.
- Minimal swelling and instability symptoms are observed in Grades I and II injuries.
Radiological Assessment
- MRI is the best diagnostic tool to assess the MCL, showing irregularities and edema.
- X-rays are used to assess potential avulsion fractures and should be performed alongside MRI for complete assessment.
- Careful assessment through varus stress testing, dial test, and other examinations is critical for accurate diagnosis.
Non-operative Management
- Conservative treatment is recommended for older recreational athletes, which may include lifestyle modification and specific sport adaptations.
- Management goals focus on regaining knee stability and proprioception.
Postoperative Rehabilitation
- Rehabilitation should begin immediately post-surgery to maintain muscle awareness and prevent complications.
- Early goals include achieving full extension to avoid complications such as flexion deformity.
- Successful rehabilitation mandates strict adherence to instructions over approximately six months.
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL) Anatomy and Function
- The PCL is the thickest ligament in the knee and stabilizes against posterior displacement.
- It originates from the medial condyle of the femur and attaches to the posterior area of the tibia below the meniscus.
- Compared to the ACL, the PCL has a better healing capacity, allowing for conservative treatment options.
Overall Management of Ligament Injuries
- Surgical intervention is preferred for the PCL, while MCL injuries often undergo conservative treatment.
- The posterolateral corner injuries require surgical intervention due to minimal healing potential. All associated injuries should ideally be addressed during the same surgical procedure.### Hip Dislocation
- Types of hip dislocation include posterior, anterior, and central.
- Posterior dislocation typically caused by RTA, knee strike, or falls; femoral head displaced superiorly.
- Anterior dislocation occurs less frequently, often due to a posterior force on the femur in abduction and external rotation.
- Central dislocation leads to the femoral head being pushed inward through the acetabulum.
Posterior Dislocation of the Hip
- Key X-ray findings: femoral head out of the acetabulum, lesser trochanter not visible due to rotation, possible acetabulum fracture.
- Treatment goals: rapid reduction under general anesthesia, closed manipulation, and traction for 3 weeks after reduction.
- Complications can include sciatic and vascular injuries, associated fractures, avascular necrosis, myositis ossificans, and osteoarthritis.
Anterior Dislocation of the Hip
- Clinical features: leg in external rotation and abduction, with palpation of the femoral head in the groin.
- Treatment involves gentle traction and internal rotation, followed by 3 weeks of traction.
- Complications include avascular necrosis and traumatic ossification.
Intertrochanteric Fracture
- Common in elderly, particularly women; associated risk factors include osteoporosis and resultant good healing without avascular necrosis.
- Mechanisms: twisting injuries or direct falls; often presents with external rotation, shortening, and severe pain.
- X-rays used for both identification and assessment of stability; treatment includes conservative skeletal traction or surgical intervention (ORIF using dynamic hip screws or nails).
- Complications from conservative treatment may involve varus deformity and prolonged bed recumbency symptoms.
Subtrochanteric Fracture
- Can occur at any age; slow healing is common, with presentations including severe pain, deformity, and inability to walk.
- Non-operative treatment may include traction; surgical treatment focuses on reduction and internal fixation.
Knee Ligament Injuries
- Medial collateral ligament (MCL) injuries involve two parts: the superficial (broad and healing capable) and deep ligaments (thicker and stronger).
- MCL treatment primarily conservative, using hinged knee braces for grades I and II; surgical intervention needed for grade III tears.
- Posterolateral corner injuries demand surgical exploration and repair due to low healing potential.
Rehabilitation and Surgical Considerations
- Focuses on stability and proprioception, with rehabilitation starting immediately post-surgery.
- Following ACL surgery, rehabilitation is crucial to rebuilding strength and range of motion over approximately 6 months.
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL)
- The thickest ligament of the knee, important for stabilizing against posterior displacement.
- Rehabilitation often conservative with effective healing potential; assessed through the posterior drawer test.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
This quiz assesses your knowledge of the gentle varus stress test, dial test, and other critical assessments for knee evaluation. It emphasizes the importance of comparing findings with the normal side and reviewing associated imaging techniques like X-rays and MRI for diagnosis. Test your understanding of knee examinations and management techniques.