Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the role of saliva in the digestive process?
What is the role of saliva in the digestive process?
- Contracting rhythmically to push food towards the stomach
- Moistening the food and containing enzymes for carbohydrate digestion (correct)
- Transporting food from mouth to stomach
- Mechanically breaking down large chunks of food
Where does the initiation of the breakdown process of food begin?
Where does the initiation of the breakdown process of food begin?
- Esophagus
- Stomach
- Small intestine
- Mouth (correct)
What is the function of taste buds on the tongue?
What is the function of taste buds on the tongue?
- Contract rhythmically to push food towards the stomach
- Identify foods' nature and allow you to taste different flavors (correct)
- Help with carbohydrate digestion
- Initiate the chemical process of digestion
Which organ acts as a conduit between the mouth and stomach?
Which organ acts as a conduit between the mouth and stomach?
What is the main function of the upper alimentary canal in digestion?
What is the main function of the upper alimentary canal in digestion?
What is the primary function of the stomach in the digestive system?
What is the primary function of the stomach in the digestive system?
Which digestive organ contains muscles that contract rhythmically to push food towards the stomach?
Which digestive organ contains muscles that contract rhythmically to push food towards the stomach?
Which organ is responsible for producing bile, which aids in fat digestion?
Which organ is responsible for producing bile, which aids in fat digestion?
What is the primary function of the gallbladder in the digestive system?
What is the primary function of the gallbladder in the digestive system?
Which organ releases pancreatic juice containing enzymes that further break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats?
Which organ releases pancreatic juice containing enzymes that further break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats?
What is the primary role of the small intestine in the digestive system?
What is the primary role of the small intestine in the digestive system?
Which organ is primarily responsible for regulating blood sugar levels through the production of insulin?
Which organ is primarily responsible for regulating blood sugar levels through the production of insulin?
Study Notes
Human Digestive System Overview
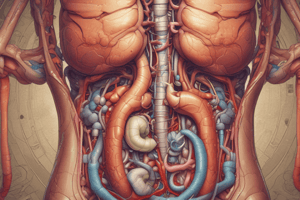
The human digestive system is essentially a series of organs that work together to transform food into nutrients your body can absorb and utilize. These organs form two major divisions: an upper alimentary canal that transports food from mouth to stomach, and a lower gastrointestinal tract where most of the actual processing occurs.
Upper Alimentary Canal
The first part of this process begins with the teeth, which mechanically break down large chunks of food. This initiation of the breakdown process enables easier access for enzymes to attack food molecules, starting the chemical process of digestion. Saliva also plays an essential role by moistening the food and containing enzymes that initiate the chemical process of carbohydrate digestion.
Mouth
Inside the mouth, there are small pits located on the tongue called papillae, filled with taste buds that help identify foods' nature. The back section of the tongue has microscopic hair-like structures called taste buds, each with specialized cells named receptor cells. They send information to the brain via the cranial nerve, allowing you to enjoy different flavors like sweet, salty, sour, bitter, and umami.
Esophagus
After chewing, the partially digested food is swallowed and passes through the esophagus. Located behind the windpipe, it acts as a conduit between your mouth and stomach. It contains muscles that contract rhythmically to push the food towards the stomach.
Stomach
The stomach serves as the mixing chamber of the digestive system. It secretes gastric juices containing hydrochloric acid, mucus, and the enzyme pepsin, breaking down proteins, killing bacteria, and dissolving the food particles. In addition to the stomach's inner lining, the esophagus possesses a sphincter, a circular muscle that contracts to prevent the contents from moving back into the esophagus.
Lower Gastrointestinal Tract
This part of the digestive system is made up of small intestine, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.
Small Intestine
The role of the small intestine is to break down food particles into smaller ones. It is lined with glands that release digestive enzymes into the intestinal lumen, breaking down proteins, carbohydrates, and fats into their respective monomers. The small intestine is also responsible for the absorption of these nutrients into the circulatory system, which is then transported to the liver for processing.
Liver
The liver is an integral organ in the human body. It plays a vital role in the digestive system, particularly in the small intestine. It produces bile, which is stored in the gallbladder. The bile emulsifies fats, breaking them into small droplets, making them more accessible to lipase enzymes present in the intestine. This emulsification allows for proper absorption of fats into the bloodstream.
Gallbladder
The gallbladder stores bile produced by the liver until it is needed to aid in fat digestion. When food enters the small intestine, the gallbladder contracts, releasing bile into the duodenum, the initial segment of the small intestine.
Pancreas
The pancreas produces both pancreatic juice and insulin hormone. It releases the pancreatic juice into the small intestine, containing enzymes like amylases, proteases, and lipases, responsible for further breaking down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats respectively. Additionally, amylase continues its action within the small intestine, converting complex sugars into simple ones to facilitate their transportation across cell membranes.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Test your knowledge of the human digestive system with this quiz covering the upper alimentary canal and the lower gastrointestinal tract. Explore topics like the functions of the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.