Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is one of the primary functions of the lymphatic system?
What is one of the primary functions of the lymphatic system?
- Regulation of heart rate
- Production of red blood cells
- Transport of oxygen
- Maintenance of fluid balance (correct)
Which of the following is NOT considered a component of lymphatic tissue?
Which of the following is NOT considered a component of lymphatic tissue?
- Bone marrow (correct)
- Peyer's patches
- Appendix
- Tonsils
What is lymph primarily composed of?
What is lymph primarily composed of?
- Cellular debris
- Blood plasma
- High protein content
- Clear fluid with low protein content (correct)
Which of the following organs is part of the lymphatic system?
Which of the following organs is part of the lymphatic system?
Which of the following statements about the carotid artery is correct?
Which of the following statements about the carotid artery is correct?
What is the primary location where gas exchange occurs in the lungs?
What is the primary location where gas exchange occurs in the lungs?
Which statement accurately describes the right lung?
Which statement accurately describes the right lung?
Which sign of inflammation involves the leakage of fluid from capillaries?
Which sign of inflammation involves the leakage of fluid from capillaries?
What defines bradypnea?
What defines bradypnea?
Which respiratory condition is characterized by a deep gasping pattern associated with diabetic ketoacidosis?
Which respiratory condition is characterized by a deep gasping pattern associated with diabetic ketoacidosis?
What occurs during hyperventilation?
What occurs during hyperventilation?
Which lung characteristic is unique to the left lung?
Which lung characteristic is unique to the left lung?
What is a common site for aspirated foreign substances?
What is a common site for aspirated foreign substances?
What is the primary filtration unit of the kidneys?
What is the primary filtration unit of the kidneys?
What does glomerular filtration rate (GFR) measure?
What does glomerular filtration rate (GFR) measure?
Which substance is converted into angiotensin I by renin?
Which substance is converted into angiotensin I by renin?
What role does aldosterone play in the body?
What role does aldosterone play in the body?
Which condition refers to the presence of excessive protein in urine?
Which condition refers to the presence of excessive protein in urine?
What is the primary role of the SA Node in the cardiac conduction system?
What is the primary role of the SA Node in the cardiac conduction system?
Which of the following symptoms is NOT typically associated with left ventricular failure?
Which of the following symptoms is NOT typically associated with left ventricular failure?
What is the primary function of veins in the vascular system?
What is the primary function of veins in the vascular system?
Which component of the cardiac conduction system follows the AV Node?
Which component of the cardiac conduction system follows the AV Node?
What is a common consequence of left-sided heart failure?
What is a common consequence of left-sided heart failure?
What is the largest tarsal bone that also bears much of the body's weight?
What is the largest tarsal bone that also bears much of the body's weight?
Which type of joint is classified as synarthroses due to its structure?
Which type of joint is classified as synarthroses due to its structure?
Which of the following joints is classified as a diarthrosis?
Which of the following joints is classified as a diarthrosis?
What type of movement is associated with a hinge joint?
What type of movement is associated with a hinge joint?
Which statement about the shoulder joint is true?
Which statement about the shoulder joint is true?
What makes the knee more susceptible to injuries compared to the hip?
What makes the knee more susceptible to injuries compared to the hip?
Which condition is characterized by the body's antibodies attacking the synovial membrane?
Which condition is characterized by the body's antibodies attacking the synovial membrane?
What is a common reason for the slow healing of cartilage injuries?
What is a common reason for the slow healing of cartilage injuries?
What role does calcitonin play in blood calcium regulation?
What role does calcitonin play in blood calcium regulation?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for increasing blood calcium levels during deficiency?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for increasing blood calcium levels during deficiency?
Which of the following is a symptom of hypercalcemia?
Which of the following is a symptom of hypercalcemia?
What is the primary action of parathyroid hormone when blood calcium levels are low?
What is the primary action of parathyroid hormone when blood calcium levels are low?
Which process occurs when blood calcium levels are excessively high?
Which process occurs when blood calcium levels are excessively high?
What hormone is primarily responsible for stimulating the thyroid gland to secrete thyroid hormones?
What hormone is primarily responsible for stimulating the thyroid gland to secrete thyroid hormones?
Which hormone is produced by the thyroid gland that helps to lower blood calcium levels?
Which hormone is produced by the thyroid gland that helps to lower blood calcium levels?
What condition results from an overactive thyroid gland?
What condition results from an overactive thyroid gland?
Which hormone is not directly produced by the thyroid gland?
Which hormone is not directly produced by the thyroid gland?
What is the main function of parathyroid hormone (PTH)?
What is the main function of parathyroid hormone (PTH)?
Which gland produces hormones that control milk production and uterine contractions?
Which gland produces hormones that control milk production and uterine contractions?
What is the role of calcitonin within the endocrine system?
What is the role of calcitonin within the endocrine system?
Which hormone is primarily involved in kidney function and managing hydration?
Which hormone is primarily involved in kidney function and managing hydration?
Which chamber of the heart receives deoxygenated blood from the body?
Which chamber of the heart receives deoxygenated blood from the body?
What is the primary function of the right ventricle?
What is the primary function of the right ventricle?
Which valve prevents backflow from the left ventricle to the left atrium?
Which valve prevents backflow from the left ventricle to the left atrium?
Which structure carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart?
Which structure carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart?
What is the role of the semilunar valves?
What is the role of the semilunar valves?
Which blood vessel carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs?
Which blood vessel carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs?
Which of the following structures is considered an atrioventricular valve?
Which of the following structures is considered an atrioventricular valve?
What distinguishes the atria from the ventricles in the heart's structure?
What distinguishes the atria from the ventricles in the heart's structure?
What is the primary function of the quadriceps femoris muscle?
What is the primary function of the quadriceps femoris muscle?
Which condition is characterized by the body producing antibodies against acetylcholine receptors?
Which condition is characterized by the body producing antibodies against acetylcholine receptors?
Which muscle is considered the bulkiest in the human body?
Which muscle is considered the bulkiest in the human body?
What effect does the bacterium Clostridium tetani have on the muscles?
What effect does the bacterium Clostridium tetani have on the muscles?
Which of the following muscles aids in hip and knee flexion as well as thigh abduction?
Which of the following muscles aids in hip and knee flexion as well as thigh abduction?
Which endocrine gland is located near the kidneys?
Which endocrine gland is located near the kidneys?
What is the strongest tendon in the body?
What is the strongest tendon in the body?
Which hormone is produced by the anterior pituitary gland?
Which hormone is produced by the anterior pituitary gland?
Flashcards
What is lymph?
What is lymph?
A clear, colorless fluid similar to plasma but with a lower protein content. It contains lipids and is part of the lymphatic system.
Signs of Inflammation
Signs of Inflammation
Swelling, redness, heat, and pain. It's the body's response to injury or infection.
Where does gas exchange occur?
Where does gas exchange occur?
The process of gas exchange in the lungs happens here. Oxygen enters the blood and carbon dioxide leaves.
What is the lymphatic system?
What is the lymphatic system?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is lymphatic tissue?
What is lymphatic tissue?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Differences between the left and right lung
Differences between the left and right lung
Signup and view all the flashcards
Apnea
Apnea
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the carotid artery?
What is the carotid artery?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bradypnea
Bradypnea
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are tonsils?
What are tonsils?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cheyne-Stokes respirations
Cheyne-Stokes respirations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dyspnea
Dyspnea
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hyperventilation
Hyperventilation
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the right atrium receive?
What does the right atrium receive?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the tricuspid valve do?
What does the tricuspid valve do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the right ventricle pump?
What does the right ventricle pump?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the pulmonary valve prevent?
What does the pulmonary valve prevent?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What do the pulmonary veins carry?
What do the pulmonary veins carry?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the left atrium receive?
What does the left atrium receive?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the mitral valve prevent?
What does the mitral valve prevent?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What pumps oxygenated blood to the body?
What pumps oxygenated blood to the body?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the thyroid gland?
What is the thyroid gland?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are thyroid follicles?
What are thyroid follicles?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Name the two main thyroid hormones.
Name the two main thyroid hormones.
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Grave's disease?
What is Grave's disease?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the parathyroid glands?
What are the parathyroid glands?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is parathyroid hormone (PTH)?
What is parathyroid hormone (PTH)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is hypothyroidism?
What is hypothyroidism?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is calcitonin?
What is calcitonin?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Calcitonin
Calcitonin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hypocalcemia
Hypocalcemia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tetany
Tetany
Signup and view all the flashcards
Calcaneus
Calcaneus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibrous Joints (Synarthroses)
Fibrous Joints (Synarthroses)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cartilaginous Joints (Amphiarthroses)
Cartilaginous Joints (Amphiarthroses)
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a nephron?
What is a nephron?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Synovial Joints (Diarthroses)
Synovial Joints (Diarthroses)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ball and Socket Joint
Ball and Socket Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
What is glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)?
What is the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hinge Joint
Hinge Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
What triggers RAAS activation?
What triggers RAAS activation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Condyloid Joint
Condyloid Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is aldosterone's role in the RAAS?
What is aldosterone's role in the RAAS?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pivot Joint
Pivot Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are automaticity cells?
What are automaticity cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the SA Node?
What is the SA Node?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Describe the cardiac conduction system.
Describe the cardiac conduction system.
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens in left ventricular failure?
What happens in left ventricular failure?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens in right ventricular failure?
What happens in right ventricular failure?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Botulism?
What is Botulism?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Myasthenia Gravis?
What is Myasthenia Gravis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Tetanus?
What is Tetanus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Quadriceps femoris?
What is the Quadriceps femoris?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Achilles Tendon?
What is the Achilles Tendon?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Sartorius muscle?
What is the Sartorius muscle?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Gluteus Maximus?
What is the Gluteus Maximus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Hypothalamus?
What is the Hypothalamus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Immune System Study Notes
- Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell
- Bacteria, viruses, and cellular debris are also part of the immune system
- Signs and symptoms of inflammation include swelling, redness, heat, and pain
- Inflammatory fluid leaking out the capillaries causes these symptoms.
- Injuries from pressure or bacterial toxins can also cause inflammation.
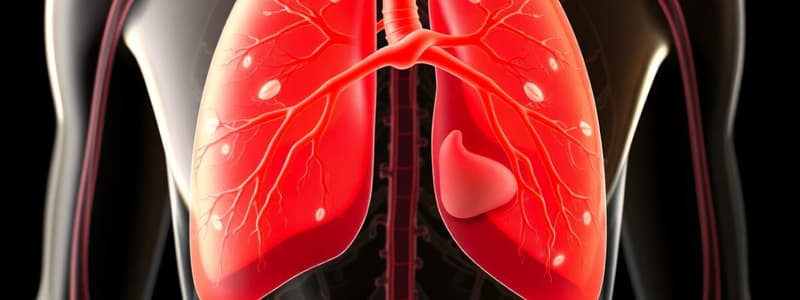
- The right lung is shorter, broader, and larger than the left lung. The right lung has 3 lobes—superior, middle, and inferior. The left lung has 2 lobes—superior and inferior. The left lung has a cardiac notch that accommodates the heart. The left lung handles 45% of gas exchange, and the right lung handles 55%.
- Common respiratory terms include apnea (temporary cessation of breathing), bradypnea (abnormally slow breathing), Cheyne-Stokes respirations (an abnormal breathing pattern), dyspnea (labored or difficult breathing), hyperventilation (increased rate and depth of respirations resulting in lowered blood levels of carbon dioxide), hypoventilation (reduced rate and depth of respirations resulting in increased blood levels of carbon dioxide ), Kussmaul respirations (deep gasping respirations associated with diabetic ketoacidosis), orthopnea (labored breathing that occurs when a person is lying flat but improves when standing or sitting up), and tachypnea (rapid breathing)
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Test your knowledge on the lymphatic and respiratory systems with this comprehensive quiz. Explore key functions, components, and processes related to these essential biological systems. Perfect for students studying human biology or healthcare.