Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the teeth?
What is the primary function of the teeth?
What is the term for the fibrous joint that connects a tooth to its alveolus?
What is the term for the fibrous joint that connects a tooth to its alveolus?
Where are the alveolar processes located?
Where are the alveolar processes located?
Which part of the tooth is visible above the gum line?
Which part of the tooth is visible above the gum line?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name of the tissue that attaches the tooth to the alveolar bone?
What is the name of the tissue that attaches the tooth to the alveolar bone?
Signup and view all the answers
How many permanent teeth do adults typically have?
How many permanent teeth do adults typically have?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name of the soft tissue that covers the alveolar processes?
What is the name of the soft tissue that covers the alveolar processes?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is NOT a function of the oral cavity?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the oral cavity?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the gastric juice produced by the stomach's glandular cells?
What is the primary function of the gastric juice produced by the stomach's glandular cells?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following arteries supplies blood to the stomach?
Which of the following arteries supplies blood to the stomach?
Signup and view all the answers
Where does the venous drainage from the stomach flow into?
Where does the venous drainage from the stomach flow into?
Signup and view all the answers
Which portion of the small intestine is located in the epigastrium and umbilical region?
Which portion of the small intestine is located in the epigastrium and umbilical region?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the approximate length of the duodenum?
What is the approximate length of the duodenum?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the relationship between the duodenum and the pancreas?
What is the relationship between the duodenum and the pancreas?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following structures does the duodenum receive?
Which of the following structures does the duodenum receive?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name of the structure that marks the transition between the duodenum and the jejunum?
What is the name of the structure that marks the transition between the duodenum and the jejunum?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the approximate weight of the liver?
What is the approximate weight of the liver?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is NOT a function of the liver?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the liver?
Signup and view all the answers
Which anatomical division of the liver is located in the epigastric region?
Which anatomical division of the liver is located in the epigastric region?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name of the structure that connects the liver to the stomach and duodenum?
What is the name of the structure that connects the liver to the stomach and duodenum?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following structures forms the portal triad?
Which of the following structures forms the portal triad?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the function of bile in the digestive process?
What is the function of bile in the digestive process?
Signup and view all the answers
The liver is responsible for the metabolism and elimination of which of the following?
The liver is responsible for the metabolism and elimination of which of the following?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name of the structure that separates the right and left lobes of the liver?
What is the name of the structure that separates the right and left lobes of the liver?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the soft palate during swallowing?
What is the primary function of the soft palate during swallowing?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following describes the structure of the tongue?
Which of the following describes the structure of the tongue?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of muscles are intrinsic muscles of the tongue responsible for?
What type of muscles are intrinsic muscles of the tongue responsible for?
Signup and view all the answers
Which receptors are found on the papillae of the tongue?
Which receptors are found on the papillae of the tongue?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the role of the lingual frenulum?
What is the role of the lingual frenulum?
Signup and view all the answers
What condition can arise from a shorter or more rigid lingual frenulum?
What condition can arise from a shorter or more rigid lingual frenulum?
Signup and view all the answers
Which flavor is NOT one of the five recognized flavors that the tongue can detect?
Which flavor is NOT one of the five recognized flavors that the tongue can detect?
Signup and view all the answers
Which muscles are categorized as extrinsic muscles of the tongue?
Which muscles are categorized as extrinsic muscles of the tongue?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of dentin in a tooth?
What is the primary function of dentin in a tooth?
Signup and view all the answers
Which substance covers the dentin of the tooth root?
Which substance covers the dentin of the tooth root?
Signup and view all the answers
What primarily composes the pulp within the pulp cavity?
What primarily composes the pulp within the pulp cavity?
Signup and view all the answers
Which nerve is responsible for sensation in the upper jaw and teeth?
Which nerve is responsible for sensation in the upper jaw and teeth?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the role of the cementum in relation to the tooth?
What is the role of the cementum in relation to the tooth?
Signup and view all the answers
What separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity?
What separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity?
Signup and view all the answers
Which part of the oral region is involved in separating the oral cavity from the nasopharynx?
Which part of the oral region is involved in separating the oral cavity from the nasopharynx?
Signup and view all the answers
Which nerve provides sensitivity to the lower lip and chin?
Which nerve provides sensitivity to the lower lip and chin?
Signup and view all the answers
Which vein is directly associated with the superior rectal vein in the portal system?
Which vein is directly associated with the superior rectal vein in the portal system?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the abdominopelvic splanchnic nerves?
What is the primary function of the abdominopelvic splanchnic nerves?
Signup and view all the answers
Which artery is NOT part of the irrigation of the abdominal viscera?
Which artery is NOT part of the irrigation of the abdominal viscera?
Signup and view all the answers
The inferior vena cava is associated with which of the following veins in the abdominal region?
The inferior vena cava is associated with which of the following veins in the abdominal region?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following arteries contributes to the blood supply of the colon?
Which of the following arteries contributes to the blood supply of the colon?
Signup and view all the answers
The prevertebral sympathetic ganglia are primarily associated with which aspect of abdominal function?
The prevertebral sympathetic ganglia are primarily associated with which aspect of abdominal function?
Signup and view all the answers
Which structure is part of the abdominal aortic plexus?
Which structure is part of the abdominal aortic plexus?
Signup and view all the answers
What is one of the primary functions of autonomic nerves in relation to arteries?
What is one of the primary functions of autonomic nerves in relation to arteries?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
Digestive System
- The digestive system is a complex process involving several organs and regions.
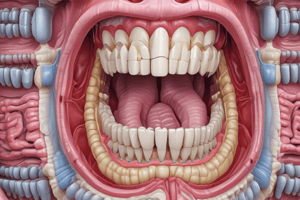
- The oral region, including the oral cavity, teeth, gums, tongue, hard and soft palate, and palatine tonsils, prepares food for digestion.
- The oral cavity consists of the buccal vestibule, the oral cavity itself, and the cheeks.
- Teeth are responsible for mastication (chewing) and word articulation. Adults have 32 permanent teeth, while children have 20.
- The mouth's function includes chewing, swallowing, digestion, nutrient absorption, and fecal formation.
- Teeth are located in the alveolar processes of the mandible and maxilla, with each tooth having a crown, root, and neck. Enamel covers the crown, while dentin makes up the majority of the tooth.
- The oral region is innervated by branches of the maxillary nerve.
- The tongue is a muscular organ crucial for chewing, swallowing, and speech. It has intrinsic and extrinsic muscles. Tastes sensations are felt inside the tongue.
- The tongue also aids in moving food in the mouth before it's swallowed.
- Salivary glands (parotid, submandibular, and sublingual) produce saliva essential for digestion, lubrication, and bacterial control, crucial for chewing and initiating starch digestion.
- The pharynx acts as a passageway for food and air during swallowing.
- The oropharynx is involved in swallowing, while the nasopharynx is part of the respiratory system.
- The esophagus is a muscular tube transporting food from the pharynx to the stomach, having three constrictions (narrowings) with a mix of involuntary and voluntary muscle.
- The abdominal region houses the majority of the digestive organs, including the stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and spleen.
- The peritoneum is a transparent membrane lining the abdominal cavity and surrounding most of the organs, consisting of two layers: parietal and visceral. Retroperitoneal organs lie outside the peritoneum.
- The stomach is an organ responsible for mixing and enzymatically digesting food, with a muscular lining, producing gastric juice including enzymes, acid, and mucus.
- The small intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum) processes and absorbs nutrients, has several parts and three narrowings. The duodenum receives secretions from the pancreas and liver and is retroperitoneal, except for the ampulla.
- The large intestine (cecum, appendix, colon, rectum, and anus) absorbs water and electrolytes, and forms and expels solid waste. The cecum, appendix, descending and sigmoid regions are intraperitoneal.
Stomach
- The stomach is located in the epigastric, umbilical, hypochondrium, and left flank regions of the abdomen.
- The stomach's main function is mixing, digesting, and storing food, via churning and enzymatic digestion. The mixture, chyme, is then pushed into the small intestine.
- The stomach lining has glands that produce gastric juice.
- The gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid (HCI), pepsinogen, and mucus.
- The stomach has three layers of muscle (longitudinal, circular, and oblique).
- The stomach has an intraperitoneal location.
- There is an arterial and venous supply to the stomach.
Small Intestine
- The small intestine comprises the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
- It's primarily responsible for nutrient absorption.
- It is located in the epigastric and umbilical regions.
- The duodenum, as the first part of the small intestine, is roughly C-shaped surrounding the head of the pancreas.
- It receives digestive enzymes from the pancreas and bile from the liver, essential for digestion.
- The small intestine's inner lining increases the surface area for absorption.
- The jejunum and ileum are intraperitoneal.
Large Intestine
- The large intestine consists of the cecum, appendix, colon (ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid), rectum, and anal canal.
- Its function is absorption of water and electrolytes, and the formation and expulsion of feces.
- The large intestine is partly intraperitoneal and partly retroperitoneal.
Liver
- The liver is a vital organ located in the right hypochondrium and part of the epigastric region, and has a convex diaphragmatic and visceral face.
- The liver's functions include producing bile for fat digestion, bile synthesis and storage, filtering blood, and metabolizing nutrients.
- The liver stores glycogen for energy and helps eliminate toxins.
- The liver is supplied blood from the hepatic artery and portal vein.
Pancreas
- The pancreas, located in the epigastric region, is an accessory digestive gland.
- It has both exocrine (pancreatic juice) and endocrine (insulin, glucagon) functions.
- Pancreatic juice helps digestion, and insulin and glucagon regulate blood sugar.
- The pancreas is retroperitoneal.
Spleen
- The spleen is an intraperitoneal lymphatic organ located in the left hypochondrium region.
- It filters the blood, removing old red blood cells and broken platelets. It also produces lymphocytes.
- The spleen helps with the immune response.
Irrigation
- The abdominal viscera is irrigated by various arteries arising from the celiac trunk, superior and inferior mesenteric arteries .
- The venous drainage primarily flows into the hepatic portal vein.
- The sympathetic and parasympathetic autonomic nervous systems innervate the abdominal viscera impacting motility and secretion functions of the various organs within the digestive system.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
This quiz covers essential concepts related to human teeth and the digestive system. You'll explore the functions of teeth, their connections to the jaw, and the roles of various digestive organs. Test your knowledge on the anatomy and functions involved in oral and gastric processes.