Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is NOT a function of epithelial tissue?
Which of the following is NOT a function of epithelial tissue?
- Storage of nutrients (correct)
- Protection
- Secretion
- Absorption
What is a common characteristic shared by all types of connective tissue?
What is a common characteristic shared by all types of connective tissue?
- They all have a high degree of vascularity.
- They all originate from mesenchyme. (correct)
- They all arise from neural tissue.
- They are all avascular.
Which type of gland releases hormones directly into the bloodstream?
Which type of gland releases hormones directly into the bloodstream?
- Salivary gland
- Endocrine gland (correct)
- Exocrine gland
- Sebaceous gland
Which type of connective tissue is characterized by a solid matrix and the presence of collagen fibers?
Which type of connective tissue is characterized by a solid matrix and the presence of collagen fibers?
What term describes the unstructured gel-like material found in connective tissue's extracellular matrix?
What term describes the unstructured gel-like material found in connective tissue's extracellular matrix?
What type of cells are responsible for maintaining the extracellular matrix in connective tissues?
What type of cells are responsible for maintaining the extracellular matrix in connective tissues?
Which is an example of an exocrine gland?
Which is an example of an exocrine gland?
Which type of connective tissue is responsible for storing energy?
Which type of connective tissue is responsible for storing energy?
What is the primary function of areolar connective tissue?
What is the primary function of areolar connective tissue?
Where is adipose tissue primarily located in the body?
Where is adipose tissue primarily located in the body?
Which connective tissue is specifically designed to support free blood cells?
Which connective tissue is specifically designed to support free blood cells?
What is the primary function of dense regular connective tissue?
What is the primary function of dense regular connective tissue?
What characteristic distinguishes brown adipose tissue from white adipose tissue?
What characteristic distinguishes brown adipose tissue from white adipose tissue?
What role does the ground substance play in areolar connective tissue?
What role does the ground substance play in areolar connective tissue?
Which function does reticular connective tissue NOT perform?
Which function does reticular connective tissue NOT perform?
Which of the following statements about dense connective tissue is true?
Which of the following statements about dense connective tissue is true?
Study Notes
Four Basic Tissue Types
- Nervous tissue: Transmits signals throughout the body.
- Connective tissue: Supports, protects, and binds other tissues.
- Epithelial tissue: Covers surfaces and lines cavities.
- Muscle tissue: Enables movement.
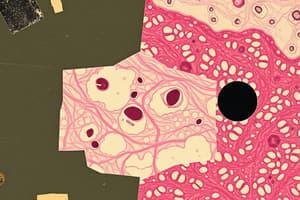
Epithelial Tissue
- Functions: Protection, absorption, filtration, excretion, secretion, sensory reception.
- Characteristics:
- Polarity: Apical (free) surface exposed to the environment, basal surface attached to underlying connective tissue.
- Specialized contacts: Tight junctions and desmosomes for cell-to-cell adhesion.
- Supported by connective tissue: Attached to a basement membrane for structure and support.
- Avascular but innervated: No blood vessels, but supplied with nerves.
- Regeneration: Can repair themselves quickly.
Glands
- Endocrine glands: Secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. Example: Pancreas releasing insulin.
- Exocrine glands: Secrete products through ducts onto body surfaces or cavities. Example: Sweat glands.
Connective Tissue
-
Characteristics:
- Common embryonic origin: All connective tissues develop from mesenchyme.
- Varying degrees of vascularity: Some, like cartilage, are avascular, while others, like bone, are highly vascularized.
- Cells suspended in extracellular matrix (ECM): Provides structure and support.
-
Structural elements:
- Ground substance: Unstructured gel-like material containing interstitial fluid, cell adhesion proteins, proteoglycans, and water.
- Fibers: Provide support.
- Collagen: Strongest, providing tensile strength.
- Elastic: Allows stretching and recoiling.
- Reticular: Fine, branched fibers forming networks for support within organs.
- Cells: Responsible for production of fibers and ground substance.
- Blast cells (immature): Actively secrete ECM components.
- Fibroblasts (connective tissue proper)
- Chondroblasts (cartilage)
- Osteoblasts (bone)
- Hematopoietic stem cells (bone marrow)
- Cyte cells (mature): Help maintain the ECM.
- Fat cells: Store nutrients.
- White blood cells: Immune response (neutrophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes)
- Mast cells: Initiate inflammatory response.
- Macrophages: Phagocytic cells that engulf debris and microorganisms.
- Blast cells (immature): Actively secrete ECM components.
Connective Tissue Types
- Connective tissue proper:
- Loose connective tissue:
- Areolar: Supports and binds other tissues, holds fluids, defends against infection, stores fat. Found beneath epithelial tissue, digestive and respiratory systems.
- Adipose: Stores nutrients (white fat), supports local nutrient needs, generates heat (brown fat). Found under skin, around organs, between muscles.
- Reticular: Supports blood cells, forms stroma of organs. Found in lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow.
- Dense connective tissue:
- Dense regular: Provides tensile strength in one direction, forms tendons, ligaments, aponeuroses.
- Dense irregular: Provides tensile strength in multiple directions, found in dermis, fibrous capsules of organs.
- Loose connective tissue:
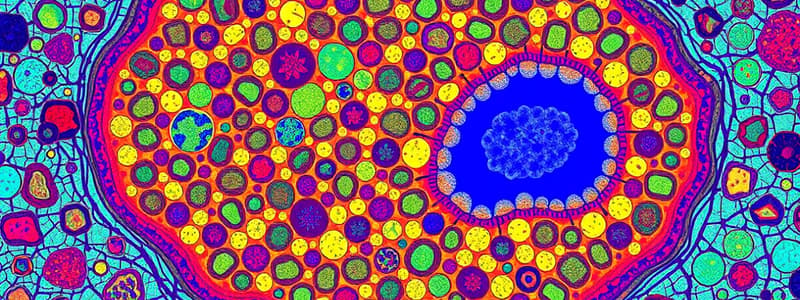
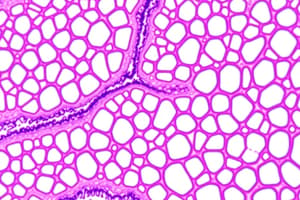
- Cartilage:
- Hyaline: Strong, flexible, found in joints, nose, trachea.
- Elastic: More flexible, found in ears, epiglottis.
- Fibrocartilage: Very strong, found in intervertebral discs, menisci of knee.
- Blood: Fluid connective tissue, transports oxygen, nutrients, waste products.
- Bone: Hard, rigid connective tissue, provides support, protection, mineral storage.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Explore the four basic types of tissues in the human body, with a focus on epithelial tissue. This quiz covers functions, characteristics, and various types of glands related to epithelial tissue, enhancing your understanding of histology.