Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the function of simple squamous?
What is the function of simple squamous?
Diffusion & filtration. Also secrete lubricating substances in serosae.
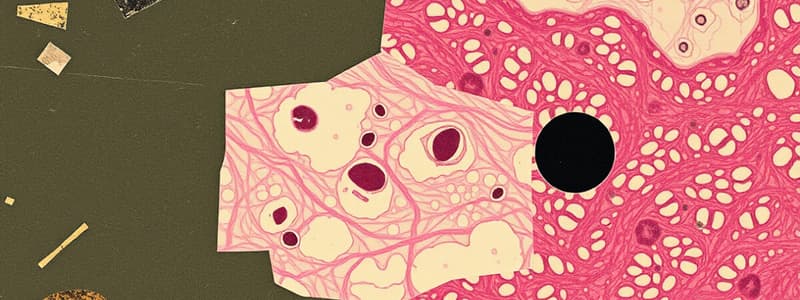
Describe simple squamous.
Describe simple squamous.
Single layer of flattened cells with central nuclei. Simplest epithelia.
Where is simple squamous located?
Where is simple squamous located?
- Kidney glomeruli 2. Alveoli of lungs 3. Lining of heart/blood vessels/lymph vessels 4. Lining of serosae
What does simple cuboidal look like?
What does simple cuboidal look like?
What is the function of simple cuboidal?
What is the function of simple cuboidal?
Where can you find simple cuboidal?
Where can you find simple cuboidal?
What does simple columnar look like?
What does simple columnar look like?
What is the function of simple columnar?
What is the function of simple columnar?
Where can you find non-ciliated simple columnar?
Where can you find non-ciliated simple columnar?
Where can you find ciliated simple columnar?
Where can you find ciliated simple columnar?
Describe pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
Describe pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
What is the function of pseudostratified columnar?
What is the function of pseudostratified columnar?
Where can you find pseudostratified columnar?
Where can you find pseudostratified columnar?
What is the function of stratified squamous?
What is the function of stratified squamous?
What is the location of non-keratinized squamous epithelium?
What is the location of non-keratinized squamous epithelium?
What is the location of keratinized squamous epithelium?
What is the location of keratinized squamous epithelium?
What are two rare types of epithelium?
What are two rare types of epithelium?
Where is stratified cuboidal located?
Where is stratified cuboidal located?
What is the function of stratified cuboidal?
What is the function of stratified cuboidal?
Where is stratified columnar located?
Where is stratified columnar located?
What is the function of stratified columnar?
What is the function of stratified columnar?
What is the description of transitional epithelium?
What is the description of transitional epithelium?
What is the function of transitional epithelium?
What is the function of transitional epithelium?
Where can you find transitional epithelium?
Where can you find transitional epithelium?
What is metaplasia?
What is metaplasia?
In Barrett's esophagus, what happens to the stratified squamous?
In Barrett's esophagus, what happens to the stratified squamous?
What is dysplasia?
What is dysplasia?
What are the two frequent sites of dysplasia?
What are the two frequent sites of dysplasia?
Is dysplasia reversible?
Is dysplasia reversible?
Is dysplasia a precursor to cancer?
Is dysplasia a precursor to cancer?
Flashcards
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Simple Squamous Epithelium
A single layer of flattened cells enabling diffusion, filtration, and secretion.
Functions of Simple Squamous Epithelium
Functions of Simple Squamous Epithelium
Involved in diffusion, filtration, and secretion of lubricating substances.
Locations of Simple Squamous Epithelium
Locations of Simple Squamous Epithelium
Found in kidney glomeruli, alveoli of lungs, and lining of heart and blood vessels.
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functions of Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Functions of Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Locations of Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Locations of Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functions of Simple Columnar Epithelium
Functions of Simple Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Locations of Simple Columnar Epithelium
Locations of Simple Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functions of Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Functions of Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Locations of Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Locations of Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Non-keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Non-keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transitional Epithelium
Transitional Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functions of Transitional Epithelium
Functions of Transitional Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Metaplasia
Metaplasia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dysplasia
Dysplasia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reversibility of Dysplasia
Reversibility of Dysplasia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Precancerous Nature of Dysplasia
Precancerous Nature of Dysplasia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Common Locations of Dysplasia
Common Locations of Dysplasia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Goblet Cells
Goblet Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ciliated Epithelium
Ciliated Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Role of Serosae
Role of Serosae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Single Layer Epithelia
Single Layer Epithelia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Simple Squamous Epithelium
- Functions in diffusion, filtration, and secretion of lubricating substances in serosae.
- Comprises a single layer of flattened cells with central nuclei; simplest form of epithelial tissue.
- Found in kidney glomeruli, alveoli of lungs, lining of heart, blood vessels, lymph vessels, and serosae.
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
- Features a single layer of cube-shaped cells with large spherical nuclei in the center.
- Functions primarily in secretion and absorption.
- Located in kidney tubules, ducts and secretory portions of small glands, and the surface of ovaries.
Simple Columnar Epithelium
- Characterized by a single layer of tall cells with round or oval nuclei; may contain cilia or goblet cells.
- Functions in absorption and secretion of mucus and enzymes; ciliated types help in propelling mucus or reproductive cells.
- Non-ciliated found in the lining of the digestive tract (stomach to anal canal), gallbladder, and some glands' excretory ducts; ciliated types are found in small bronchi, uterine tubes, and parts of the uterus.
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
- Composed of a single layer of cells of varying heights; some cells do not reach the surface and may contain goblet cells and cilia.
- Functions in the secretion of mucus and propulsion of mucus via ciliary action.
- Non-ciliated version found in males' sperm carrying ducts and large gland ducts; ciliated lines the trachea and upper respiratory tract.
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
- Serves to protect underlying tissues from abrasion.
- Non-keratinized type found in moist linings of the esophagus, mouth, tongue, and vagina; keratinized version forms the epidermis of skin.
Rare Types of Epithelial Tissue
- Stratified cuboidal and stratified columnar epithelia are categorized as rare.
- Stratified cuboidal located in ducts of adult sweat glands, esophageal glands, and parts of the male urethra; functions mainly in protection and limited secretion/absorption.
- Stratified columnar found in the urethra, large ducts of some glands, small regions of the anus, and parts of the conjunctiva in the eye; functions in protection and secretion.
Transitional Epithelium
- Characterized by dome-shaped surface cells.
- Functions to stretch readily and permit distention.
- Lines the ureters, bladder, and part of the urethra.
Metaplasia
- Refers to the reversible replacement of one mature cell type by another, sometimes less differentiated type.
- In Barrett's esophagus, stratified squamous epithelium transforms to stratified columnar due to chronic gastric acid irritation.
Dysplasia
- Represents deranged cell growth resulting in variations in size, shape, appearance, and organization of cells.
- Commonly seen in the female cervix and respiratory tract.
- Dysplasia may be reversible if the inciting stimulus is removed and is considered a precursor to cancer.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.