Podcast
Questions and Answers
What do the adrenal glands refer to?
What do the adrenal glands refer to?
- adren/o (correct)
- acr/o
- gonad/o
- -dipsia
What does the suffix '-ism' indicate?
What does the suffix '-ism' indicate?
- to secrete
- thirst
- extremities
- condition (correct)
The hormone _____ stimulates ovulation in the female.
The hormone _____ stimulates ovulation in the female.
luteinizing
The _____ gland secretes hormones that control the activity of the other endocrine glands.
The _____ gland secretes hormones that control the activity of the other endocrine glands.
The _____ hormone stimulates the growth and secretions of the adrenal cortex.
The _____ hormone stimulates the growth and secretions of the adrenal cortex.
The _____ gland functions as part of the endocrine system by secreting a hormone that functions as part of the immune system.
The _____ gland functions as part of the endocrine system by secreting a hormone that functions as part of the immune system.
The hormone _____ works with the parathyroid hormone to decrease calcium levels in the blood and tissues.
The hormone _____ works with the parathyroid hormone to decrease calcium levels in the blood and tissues.
Cortisol is secreted by the _____.
Cortisol is secreted by the _____.
The amount of glucose in the bloodstream is increased by the hormone ____.
The amount of glucose in the bloodstream is increased by the hormone ____.
Norepinephrine is secreted by the _____.
Norepinephrine is secreted by the _____.
The hormone _____ stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth.
The hormone _____ stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth.
The development of the male secondary sex characteristics is stimulated by the hormone _____.
The development of the male secondary sex characteristics is stimulated by the hormone _____.
A pheochromocytoma is a rare, benign tumor of the adrenal gland that causes too much release of epinephrine and norepinephrine.
A pheochromocytoma is a rare, benign tumor of the adrenal gland that causes too much release of epinephrine and norepinephrine.
The beta cells of the pancreatic islets secrete glucagon in response to low blood glucose levels.
The beta cells of the pancreatic islets secrete glucagon in response to low blood glucose levels.
What condition is characterized by excessive thirst?
What condition is characterized by excessive thirst?
Mrs. Wei's condition is known as _____.
Mrs. Wei's condition is known as _____.
The condition known as _____ is characterized by abnormally high concentrations of calcium circulating in the blood instead of being stored in the bones.
The condition known as _____ is characterized by abnormally high concentrations of calcium circulating in the blood instead of being stored in the bones.
A condition of excessive secretion of insulin in the bloodstream is known as _____.
A condition of excessive secretion of insulin in the bloodstream is known as _____.
Damage to the retina of the eye caused by diabetes mellitus is known as diabetic ____.
Damage to the retina of the eye caused by diabetes mellitus is known as diabetic ____.
Hyperpituitarism is the excess secretion of growth hormone by the pituitary gland, causing ____.
Hyperpituitarism is the excess secretion of growth hormone by the pituitary gland, causing ____.
What is the term for inflammation of the thyroid gland?
What is the term for inflammation of the thyroid gland?
What term is used for the surgical removal of the pancreas?
What term is used for the surgical removal of the pancreas?
What does insulinoma refer to?
What does insulinoma refer to?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
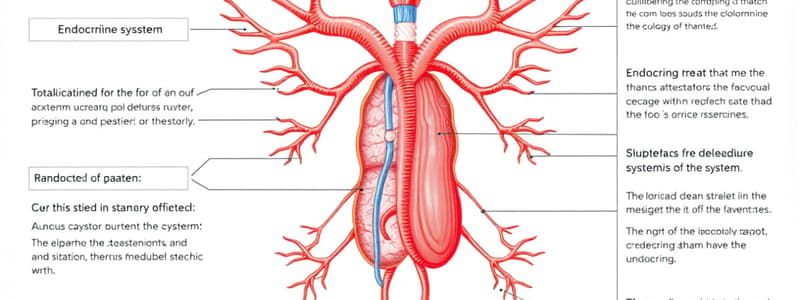
Endocrine System Terminology
- Adren/o: Refers to the adrenal glands which produce hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline.
- Acr/o: Relates to extremities, including hands and feet.
- Gonad/o: Pertains to reproductive organs, including ovaries in females and testicles in males.
- -dipsia: A suffix meaning thirst.
- Crin/o: Indicates the act of secretion, as in hormones.
- -ism: A suffix denoting a condition or state.
- Pancreat/o: Relates to the pancreas, an organ involved in insulin and glucagon production.
- Parathyroid/o: Refers to the parathyroid glands that regulate calcium levels in the blood.
- Pineal/o: Pertains to the pineal gland, which secretes melatonin.
- Pituitar/o: Relates to the pituitary gland, known as the "master gland."
- Somat/o: Refers to the body.
- Poly-: A prefix meaning many or excessive.
- Glyc/o: Indicates sugar or glucose.
- Thyroid/o: Pertains to the thyroid gland, which regulates metabolism.
- Thym/o: Relates to the thymus, important for immune function.
Hormones and Their Functions
- Luteinizing Hormone: Stimulates ovulation in females.
- Pituitary Gland: Secretes hormones that control other endocrine glands.
- Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH): Stimulates growth and secretions of the adrenal cortex.
- Calcitonin: Works with parathyroid hormone to lower blood calcium levels.
- Cortisol: Secreted by the adrenal cortex, it helps manage stress and metabolism.
- Glucagon: Increases blood glucose levels, opposite effect of insulin.
- Norepinephrine: Released by the adrenal medulla, it affects fight or flight response.
- Oxytocin: Stimulates uterine contractions during childbirth.
- Testosterone: Influences the development of male secondary sex characteristics.
Conditions and Disorders
- Acromegaly: Caused by excess growth hormone in adults, leading to enlarged features.
- Cushing's Syndrome: Result of prolonged exposure to high cortisol levels.
- Diabetes Insipidus: Caused by insufficient ADH production, leading to excessive urination.
- Diabetes Mellitus: A group of diseases characterized by high blood glucose due to insulin issues.
- Hashimoto's Disease: An autoimmune disorder destroying thyroid cells, leading to hypothyroidism.
- Gigantism: Excessive growth due to growth hormone overproduction before puberty.
Diagnostic Terms and Tests
- Fasting Blood Sugar (FBS): Measures baseline glucose levels after fasting.
- Fructosamine Test: Assesses average blood glucose levels over the past 3 weeks.
- Insulinemia: High levels of insulin in the blood.
- Thyroid Storm: Life-threatening condition due to extreme hyperthyroidism.
Anatomic Terminology
- Pancreatic Islets: Cluster of cells in the pancreas that regulate blood glucose.
- Pineal Gland: Influences circadian rhythms through melatonin onset.
- Adrenal glands: Regulate electrolyte levels and homeostasis.
- Thyroid Gland: Stimulates metabolism, affecting overall energy levels.
Surgeries and Procedures
- Pancreatectomy: Surgical removal of the pancreas.
- Thyroidectomy: Surgical procedure to remove the thyroid gland.
- Thymectomy: Removal of the thymus gland.
- Electrolytes: Essential minerals like sodium and potassium that regulate cellular functions.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.