Podcast Beta
Questions and Answers
Which pairing of nitrogenous bases is considered complementary in DNA?
What type of bond holds the two strands of a DNA molecule together?
What is the role of the sugar-phosphate backbone in nucleic acids?
Which of the following correctly describes a characteristic of RNA?
Signup and view all the answers
Which nucleotide sequence correctly identifies a purine and a pyrimidine?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following best describes the role of buffer systems in the body?
Signup and view all the answers
What elements are commonly found in organic compounds?
Signup and view all the answers
Which organic compound class contributes significantly to total body weight?
Signup and view all the answers
Functional groups in organic molecules are primarily responsible for which aspect?
Signup and view all the answers
What characteristic of organic compounds allows them to dissolve in water?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the pH range considered normal for blood and tissues?
Signup and view all the answers
What occurs when pH levels drop below 7.35?
Signup and view all the answers
What effect can high acidity levels in body fluids have on proteins?
Signup and view all the answers
What is indicated by a pH level above 7.45?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following statements about the pH scale is true?
Signup and view all the answers
What happens to cells when pH levels deviate significantly from the normal range?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following describes a condition with a pH below 7?
Signup and view all the answers
Understanding pH is essential because it impacts which aspect of cellular structures?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of monosaccharides in the body?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following statements is true regarding disaccharides?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary purpose of glycogen in the body?
Signup and view all the answers
How do isomers differ from one another?
Signup and view all the answers
Which lipids are primarily responsible for energy storage?
Signup and view all the answers
What is true about the absorption of fatty acids?
Signup and view all the answers
What distinguishes eicosanoids from other lipid types?
Signup and view all the answers
In what form do polysaccharides primarily exist in plants?
Signup and view all the answers
What must occur for disaccharides to provide energy?
Signup and view all the answers
Which lipid type is characterized by a hydrophobic nature?
Signup and view all the answers
What role do hydration spheres play in aqueous solutions?
Signup and view all the answers
Which statement about electron conduction in the body is true?
Signup and view all the answers
How is ion concentration in body fluids primarily regulated?
Signup and view all the answers
What property do hydrophobic molecules exhibit?
Signup and view all the answers
What happens to water during dissociation?
Signup and view all the answers
Which characteristic is true of nonpolar molecules?
Signup and view all the answers
What effect can an imbalance in body fluid pH have?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of soluble, polar molecules?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
Nitrogenous Bases
- Adenine and Guanine are purines
- Cytosine and Thymine are pyrimidines
- Thymine is found only in DNA
- Uracil is found only in RNA
Nucleic Acid Structure
- Phosphate and sugar molecules join via dehydration synthesis
- This forms the sugar-phosphate backbone with nitrogenous bases for genetic information
- The sequence of nitrogenous bases carries information for protein synthesis
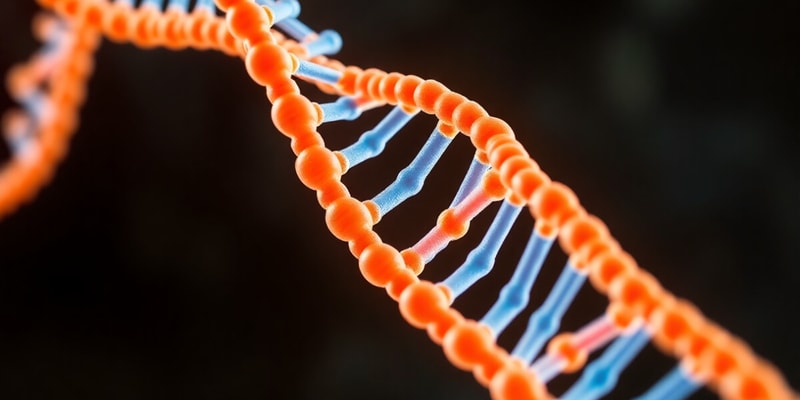
DNA Molecule
- Consists of nucleotide chains
- Has complementary strands
- Strands twist around each other to form a double helix (spiral staircase)
- Hydrogen bonds and nitrogenous bases hold the two strands together
- Complementary base pairs form from the shapes of the bases: adenine-thymine and cytosine-guanine
RNA Molecule
- A single chain of nucleotides
- Shape and function depend on the nucleotides and interactions between them
- Three types: mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
Aqueous Solutions
- Anions and cations form hydration spheres, attracting water molecules
- Hydrophilic molecules, like glucose, dissolve strongly in water
- Electrons conduct electrical currents in the body, affecting all cells
- Ion concentration in body fluids is regulated by kidneys, digestive tract, and skeletal system
Organic Molecules
- Lack covalent bonds
- Polar molecules are hydrophilic
- Nonpolar molecules are hydrophobic, lacking a hydration sphere and not dissolving in water
- Hydrophobic molecules exhibit a fear of water, like fats and oils
Regulation of Body Fluid pH
- Water dissociates into hydrogen and hydroxide ions
- Ions can disrupt cell and tissue function, break chemical bonds, and regulate body concentration
- pH is a measure of hydrogen ion concentration in body fluids (negative logarithm, ranging from 0-14)
- Acidic: below 7 (contains more hydrogen ions)
- Neutral: equal to 7 (equal numbers of hydrogen and hydroxide ions)
- Alkaline (basic): above 7 (more hydroxide ions)
- Normal pH of blood and tissues is 7.35-7.45
- Damaging cells, changing shapes of proteins, and altering cellular functions are consequences of changes in pH
- Acidosis: below 7.35 pH, causing coma
- Alkalosis: above 7.45 pH, causing skeletal muscle contractions
Buffers
- Stabilize pH by removing or replacing hydrogen ions
- Maintain normal pH of body fluids
- Common buffer systems include the carbonic acid-bicarbonate system and salt-related systems
Organic Compounds
- Contain C, H, and O
- Long chains of C linked with covalent bonds
- Soluble in water
- Functional groups influence the properties of the molecule
Carbohydrates
- Contain C, H, and O
- Examples include sugars and starches
- Make up 1-5% of total body weight
- Serve as energy resources
- Contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
Carbohydrate Structural Classes and Examples
- Monosaccharides (simple sugars): glucose, fructose, serve as energy sources, manufactured in the body and obtained from food, distributed in body fluids
- Disaccharides: sucrose, lactose, maltose, serve as energy sources, sucrose is table sugar, lactose is in milk, maltose is malt sugar, all must be broken down to monosaccharides before absorption
- Polysaccharides: glycogen, glucose storage, glycogen is in animal cells, other starches and cellulose are within or around plant cells
Hydrolysis
- Hydrolysis breaks disaccharides into monosaccharides
Isomers
- Molecules with the same molecular formula but different structures
- Important in molecular function
- Example: Glucose and Fructose
Lipids (Fats)
- Contain C, H, and O, with a higher C-H ratio and less O compared to carbohydrates with similar numbers of carbon atoms
- May contain phosphorus, nitrogen, and sulfur
- Examples: fats, oils, waxes
- Insoluble in water
- Require special transport mechanisms in the blood
Lipid Types and Examples
- Fatty acids: Lauric acid, serve as energy sources, absorbed from food, or synthesized in cells, transported in the blood
- Glycerides: monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, serve as energy sources, energy storage, insulation, and physical protection, stored in fat deposits, must be broken down to fatty acids and glycerol before use as an energy source
- Eicosanoids: prostaglandins, leukotrienes, chemical messengers coordinating local cellular functions, produced in most body tissues
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Test your knowledge on the structures of DNA and RNA, including the roles of nitrogenous bases and the formation of nucleotide chains. This quiz covers essential concepts like complementary base pairing and the differences between DNA and RNA. Challenge yourself to understand the molecular foundations of genetics!