Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which germ layer is responsible for the development of the central and peripheral nervous system?
Which germ layer is responsible for the development of the central and peripheral nervous system?
- Neural crest
- Ectoderm (correct)
- Mesoderm
- Endoderm
What structure induces the ectoderm to form the neural plate during embryonic development?
What structure induces the ectoderm to form the neural plate during embryonic development?
- Neural tube
- Notochord (correct)
- Ectoderm
- Mesoderm
What is the primary role of the notochord in vertebrate embryos?
What is the primary role of the notochord in vertebrate embryos?
- Forms the brain
- Produces neural crest cells
- Promotes the formation of limbs
- Guides development of the nervous system and vertebrae (correct)
During neurulation, what happens to the cranial and caudal ends of the neural tube?
During neurulation, what happens to the cranial and caudal ends of the neural tube?
What condition is characterized by a small brain and cranium, often due to neural tube defects?
What condition is characterized by a small brain and cranium, often due to neural tube defects?
Which structure forms as the edges of the neural plate rise during the process of neurulation?
Which structure forms as the edges of the neural plate rise during the process of neurulation?
What does the neural canal eventually become in the developed nervous system?
What does the neural canal eventually become in the developed nervous system?
Which of the following best describes exencephaly?
Which of the following best describes exencephaly?
What happens to neural crest cells during the formation of the neural tube?
What happens to neural crest cells during the formation of the neural tube?
Which structure differentiates into the brain and spinal cord after neural tube formation?
Which structure differentiates into the brain and spinal cord after neural tube formation?
What structures do the derivatives of the neuroectoderm give rise to?
What structures do the derivatives of the neuroectoderm give rise to?
What is the proximal part of the optic vesicle that becomes the optic nerve called?
What is the proximal part of the optic vesicle that becomes the optic nerve called?
What does the mantle zone eventually form during the development of the spinal cord?
What does the mantle zone eventually form during the development of the spinal cord?
Which cell type rapidly divides into neuroepithelial layers during the neural groove stage?
Which cell type rapidly divides into neuroepithelial layers during the neural groove stage?
The marginal layer of the spinal cord contains what type of fibers?
The marginal layer of the spinal cord contains what type of fibers?
What do the derivatives of the surface ectoderm NOT give rise to?
What do the derivatives of the surface ectoderm NOT give rise to?
How many pairs of cranial nerves arise from the brainstem in humans?
How many pairs of cranial nerves arise from the brainstem in humans?
Which structure of the optic vesicle transforms into the retina?
Which structure of the optic vesicle transforms into the retina?
The development of which system begins with the closure of the neural tube?
The development of which system begins with the closure of the neural tube?
What type of cells produce the myelin sheath in the peripheral nervous system?
What type of cells produce the myelin sheath in the peripheral nervous system?
What is the role of the basal plates in the spinal cord?
What is the role of the basal plates in the spinal cord?
What is the sulcus limitans?
What is the sulcus limitans?
Which of the following cells is primarily responsible for forming the myelin sheath?
Which of the following cells is primarily responsible for forming the myelin sheath?
At which levels of the spinal cord is the intermediate horn found?
At which levels of the spinal cord is the intermediate horn found?
What type of cells appear during the second half of CNS development and function as phagocytic cells?
What type of cells appear during the second half of CNS development and function as phagocytic cells?
What do axons of neurons in the alar plate primarily form?
What do axons of neurons in the alar plate primarily form?
What happens to glial blasts after the production of neuroblasts ceases?
What happens to glial blasts after the production of neuroblasts ceases?
The marginal layer in the spinal cord is primarily associated with which cell type?
The marginal layer in the spinal cord is primarily associated with which cell type?
What is primarily formed by the neuroblasts in the basal plate?
What is primarily formed by the neuroblasts in the basal plate?
Which structure serves as the boundary between the motor and sensory areas of the spinal cord?
Which structure serves as the boundary between the motor and sensory areas of the spinal cord?
What is the result of the fusion of the neural folds during neurulation?
What is the result of the fusion of the neural folds during neurulation?
At which point during development does neurulation begin?
At which point during development does neurulation begin?
What condition results from incomplete closing of the vertebrae?
What condition results from incomplete closing of the vertebrae?
How do the anterior and posterior neuropores differ in their closure timing?
How do the anterior and posterior neuropores differ in their closure timing?
Which part of the neural tube develops into the brain?
Which part of the neural tube develops into the brain?
Where are neural crest cells located after detachment during neural tube formation?
Where are neural crest cells located after detachment during neural tube formation?
What role does the notochord play in embryonic development?
What role does the notochord play in embryonic development?
What is a potential consequence of exencephaly?
What is a potential consequence of exencephaly?
What happens during the neurulation process regarding the neural plate?
What happens during the neurulation process regarding the neural plate?
What structures are derived from the neural crest?
What structures are derived from the neural crest?
Which part of the optic vesicle becomes the retina?
Which part of the optic vesicle becomes the retina?
What do neuroblasts primarily form during development?
What do neuroblasts primarily form during development?
Which cell type produces the myelin sheath in the peripheral nervous system?
Which cell type produces the myelin sheath in the peripheral nervous system?
What is the primary feature of the marginal layer in the spinal cord?
What is the primary feature of the marginal layer in the spinal cord?
During what stage of development do neuroepithelial cells begin to give rise to neuroblasts?
During what stage of development do neuroepithelial cells begin to give rise to neuroblasts?
What does the mantle zone later develop into?
What does the mantle zone later develop into?
What is the role of the retina in the eye?
What is the role of the retina in the eye?
What does the optic stalk develop into?
What does the optic stalk develop into?
What is NOT a derivative of surface ectoderm?
What is NOT a derivative of surface ectoderm?
What do the ventral thickening and dorsal thickening of the neural tube develop into?
What do the ventral thickening and dorsal thickening of the neural tube develop into?
What is the primary function of floor plates and roof plates in the neural tube?
What is the primary function of floor plates and roof plates in the neural tube?
At which levels of the spinal cord is the intermediate horn present?
At which levels of the spinal cord is the intermediate horn present?
What type of cells differentiate from glial blasts primarily found in the mantle layer?
What type of cells differentiate from glial blasts primarily found in the mantle layer?
What is the primary role of oligodendroglia cells in the nervous system?
What is the primary role of oligodendroglia cells in the nervous system?
Which of the following describes the function of axons from neurons in the basal plate?
Which of the following describes the function of axons from neurons in the basal plate?
What cells develop primarily after neuroblasts stop proliferating?
What cells develop primarily after neuroblasts stop proliferating?
Which structure marks the boundary between the basal and alar plates?
Which structure marks the boundary between the basal and alar plates?
What is primarily formed in the alar plate?
What is primarily formed in the alar plate?
What do microglial cells primarily do in the central nervous system?
What do microglial cells primarily do in the central nervous system?
Flashcards
Basal Plate
Basal Plate
The ventral thickening of the mantle layer, containing ventral motor horn cells that form the motor areas of the spinal cord.
Alar Plate
Alar Plate
The dorsal thickening of the mantle layer, forming the sensory areas of the spinal cord.
Sulcus Limitans
Sulcus Limitans
A longitudinal groove marking the boundary between the basal and alar plates.
Floor Plate
Floor Plate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Roof Plate
Roof Plate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intermediate Horn (Lateral Horn)
Intermediate Horn (Lateral Horn)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adult Nerve Cells (Neurons)
Adult Nerve Cells (Neurons)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oligodendroglia Cells
Oligodendroglia Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glial Blasts
Glial Blasts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Microglial Cells
Microglial Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell Differentiation and Migration
Cell Differentiation and Migration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ectoderm
Ectoderm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neuroectoderm
Neuroectoderm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neural Tube
Neural Tube
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neural Crest
Neural Crest
Signup and view all the flashcards
Surface Ectoderm
Surface Ectoderm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Optic Cup
Optic Cup
Signup and view all the flashcards
Optic Stalk
Optic Stalk
Signup and view all the flashcards
Marginal Layer
Marginal Layer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trilaminar Embryonic Disc
Trilaminar Embryonic Disc
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mantle Layer
Mantle Layer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Notochord
Notochord
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neurulation
Neurulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neuropores
Neuropores
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exencephaly
Exencephaly
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spinal Bifida
Spinal Bifida
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neural Crest Cells
Neural Crest Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neural Canal
Neural Canal
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the trilaminar embryonic disc?
What is the trilaminar embryonic disc?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the ectoderm?
What is the ectoderm?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the notochord?
What is the notochord?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is neurulation?
What is neurulation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are neuropores?
What are neuropores?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is exencephaly?
What is exencephaly?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is spinal bifida?
What is spinal bifida?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are neural crest cells?
What are neural crest cells?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the neural canal?
What is the neural canal?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the surface ectoderm?
What is the surface ectoderm?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell Differentiation & Migration in Neural Development
Cell Differentiation & Migration in Neural Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Development of the Nervous System
- During week 3 of embryonic development, the trilaminar embryonic disc consists of three germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
- The ectoderm develops the central and peripheral nervous systems, as well as parts of the visual system and the epidermis.
- The notochord, a rod-like structure, provides structural support, defines the body axis, and guides the development of the nervous system and vertebrae in embryos of chordates.
- Notochord eventually is replaced by the spine in most vertebrates.
- The notochord stimulates the conversion of overlying surfaces.
Neurulation
- Neurulation is a process that occurs bidirectionally, starting around day 17 and completing by the end of week 4.
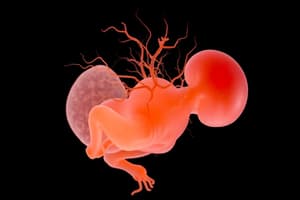
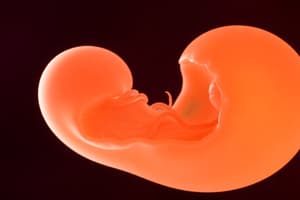
- Neural tube formation involves the notochord inducing the ectoderm to form the neural plate.
- The edges of the neural plate fold into neural folds, creating a neural groove.
- The neural folds fuse, forming the neural tube with a neural canal inside.
- The neural tube separates from the surface ectoderm eventually producing the brain and spinal cord.
- Fusion of the neural tube proceeds bidirectionally, with the cranial and caudal ends initially remaining open as neuropores.
- The posterior neuropore closes two days after the anterior neuropore.
- The cephalic part of the neural tube forms the brain, and the caudal part forms the spinal cord.
- Neuropores are the openings of the neural tube.
Neural Tube Defects
- Exencephaly: A failure of closure of the anterior neuropore, leading to the brain developing outside the skull. This is a precursor to anencephaly.
- Anencephaly: A condition in which the brain is absent or poorly formed, lacking significant parts or structure.
- Microcephaly: A condition characterized by a small brain in a small cranium.
- Spina bifida: Occurs when the neural tube fails to close completely. Incomplete closure can lead to spinal cord and meninges protruding outside the vertebral canal.
Derivatives of the Ectoderm
- Neuroectoderm: Gives rise to the neural tube (central nervous system - brain and spinal cord), and the neural crest (bones of the face and skull, autonomic ganglia, cranial nerves, and parts of the peripheral nervous system, meninges, and Schwann cells).
- Surface ectoderm: Develops into the epidermis, hair, nails, enamel of teeth and the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland.
Optic Nerve Development
- The optic vesicle, an extension of the forebrain, develops into the optic cup (retina) and the optic stalk.
- The optic stalk becomes the optic nerve.
Development of the Spinal Cord
- The spinal cord develops during the neural groove stage and immediately after closure of the neural tube.
- The alar plate gives rise to sensory structures, whereas the basal plate forms motor neuron structures.
- The sulcus limitans is a groove that marks the boundary between the alar and basal plates.
- Floor and roof plates are regions of the neural tube that do not contain neuroblasts.
Histological Differentiation: Nerve Cells
- Multipolar neuroblasts form adult nerve cells (neurons).
- Axons from cells in the basal plate form ventral roots, responsible for carrying impulses from the spinal cord to muscles.
- Axons originating in the alar plate penetrate the marginal layer and form association neurons that travel to higher or lower levels.
Histological Differentiation: Glial Cells
- Glial blasts are produced by neuroepithelial cells after neuroblast production ceases.
- They differentiate into astrocytes (protoplasmic and fibrillar) for support and blood vessel regulation to neurons.
- Microglial cells are phagocytic cells in the CNS and appear later in development.
- Ependymal cells form the lining of the central canal of the spinal cord.
Brainstem
- The brainstem acts as a direct continuation from the spinal cord and displays similar organisational patterns despite the subtle accentuation of the alar plate and regression of the basal plate.
- It differs from the spinal cord as the lateral walls are everted, and the alar and basal plate separation is noted.
- The medulla differs from the spinal cord by having everted lateral walls separated by the sulcus limitans. Basal plates contain motor nuclei, and alar plates contain sensory nuclei.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.