Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following best describes the process of attention?
Which of the following best describes the process of attention?
- The collection of past experiences and knowledge
- A series of cognitive steps in decision making
- The act of filtering and selecting important information (correct)
- A method for storing and retrieving information
How is cognition defined in cognitive psychology?
How is cognition defined in cognitive psychology?
- The set of mental abilities and processes related to knowledge (correct)
- The study of behavioral responses to stimuli
- The hardware aspects related to human thought
- An analysis of brain functions in patients
What defines the mind in the context of cognitive psychology?
What defines the mind in the context of cognitive psychology?
- An organ that processes sensory information
- The biological elements of the nervous system
- The software that enables awareness and thought (correct)
- A physical structure within the skull
What distinguishes cognitive psychology from other approaches in psychology?
What distinguishes cognitive psychology from other approaches in psychology?
Which branch specifically studies the impact of brain damage on cognition?
Which branch specifically studies the impact of brain damage on cognition?
What does rationalism emphasize in the acquisition of knowledge?
What does rationalism emphasize in the acquisition of knowledge?
Which psychological approach aims to analyze the structure of the mind?
Which psychological approach aims to analyze the structure of the mind?
Who is considered the founder of Structuralism in psychology?
Who is considered the founder of Structuralism in psychology?
What was one of the primary criticisms leveled against Structuralism?
What was one of the primary criticisms leveled against Structuralism?
What key concept did William James propose in Functionalism?
What key concept did William James propose in Functionalism?
What method did both Structuralism and Functionalism share in their approaches?
What method did both Structuralism and Functionalism share in their approaches?
Which of the following best describes the aim of Functionalism?
Which of the following best describes the aim of Functionalism?
What was notable about Wilhelm Wundt's contribution to psychology?
What was notable about Wilhelm Wundt's contribution to psychology?
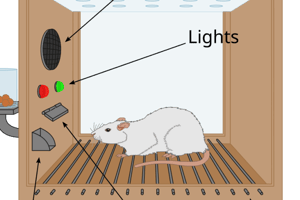
What significant concept did Tolman discover through observing rats in mazes?
What significant concept did Tolman discover through observing rats in mazes?
Which event is recognized as a pivotal moment in the emergence of cognitive psychology?
Which event is recognized as a pivotal moment in the emergence of cognitive psychology?
What is a primary advantage of conducting controlled laboratory experiments in cognitive psychology?
What is a primary advantage of conducting controlled laboratory experiments in cognitive psychology?
What is a characteristic of ecological validity in research?
What is a characteristic of ecological validity in research?
Which hypothesis did cognitive psychology primarily emphasize in its assumptions?
Which hypothesis did cognitive psychology primarily emphasize in its assumptions?
What is a primary characteristic of naturalistic observation?
What is a primary characteristic of naturalistic observation?
What is a significant advantage of computer simulations and artificial intelligence in research?
What is a significant advantage of computer simulations and artificial intelligence in research?
Which of the following is a disadvantage of naturalistic observation?
Which of the following is a disadvantage of naturalistic observation?
In cognitive neuroscience, what is the role of effectors?
In cognitive neuroscience, what is the role of effectors?
Which part of the nervous system is known as the body's master control unit?
Which part of the nervous system is known as the body's master control unit?
What does the parasympathetic nervous system primarily do?
What does the parasympathetic nervous system primarily do?
Which component of cognitive neuroscience serves as a link to the outside world?
Which component of cognitive neuroscience serves as a link to the outside world?
Which of the following treatment conditions is NOT used in the example of teacher's emotional display?
Which of the following treatment conditions is NOT used in the example of teacher's emotional display?
What happens during a Transient Ischemic Stroke?
What happens during a Transient Ischemic Stroke?
Which type of stroke is associated with a blocked artery?
Which type of stroke is associated with a blocked artery?
What is a primary brain tumor?
What is a primary brain tumor?
What is one advantage of Computed Tomography (CT)?
What is one advantage of Computed Tomography (CT)?
Which factor primarily influences spatial resolution in brain imaging techniques?
Which factor primarily influences spatial resolution in brain imaging techniques?
What distinguishes a malignant brain tumor from a benign one?
What distinguishes a malignant brain tumor from a benign one?
Which stroke is characterized by blood leaking into the brain?
Which stroke is characterized by blood leaking into the brain?
What is the major consequence of a stroke?
What is the major consequence of a stroke?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Brain vs. Mind
- The brain is the hardware, a physical organ made of nervous tissue responsible for coordinating sensation, intellect, and nervous activity.
- The mind is the software, the non-physical aspect responsible for awareness, thinking, and feeling. It uses the brain's resources to gather, store, and manage information.
Cognitive Psychology
- Studies how people perceive, learn, remember, and think about information.
- Aims to understand human cognition by using behavioral evidence.
- Cognitive psychologists explore various mental processes, such as attention, memory, problem-solving, decision-making, language acquisition, and forgetting.
- Cognition is the scientific synonym for thinking, derived from the Latin word "Cogito" meaning "to know."
Approaches to Human Cognition
- Cognitive Neuropsychology: Studies brain-damaged patients to gain insights into normal human cognition.
- Cognitive Neuroscience: Combines behavioral and neural evidence to comprehend human cognition.
Rationalism vs. Empiricism
- Rationalism: Knowledge is gained through logic and deduction, independent of sensory experiences.
- Empiricism: Knowledge is acquired through experiences and observations.
Physiological Roots of Cognitive Psychology
- Structuralism: Focuses on the structure of the mind by analyzing perceptions into their components (affection, attention, memory, sensation).
- Wilhelm Wundt: Established the first psychological laboratory in Leipzig, Germany, and used introspection to study the contents of consciousness.
- Edward Titchener: Wundt's student, considered the first full-fledged structuralist, focused on sensations, images, and feelings.
- Functionalism: Emphasizes the purpose and function of mental processes rather than their content.
- William James: Stressed the adaptive functions of the mind and proposed a multicomponent memory system.
Research Methods in Cognitive Psychology
- Assumptions:
- Mental processes exist.
- People actively process information.
- Mental processes and structures can be revealed by time and accuracy measurements.
- Research Methods:
- Controlled Laboratory Experiments: Highly controlled environments for isolating causal factors, but may lack ecological validity.
- Naturalistic Observation: Observing real-life situations for high ecological validity but lacking experimental control.
- Computer Simulations and Artificial Intelligence: Use computers to simulate human cognitive performance, offering clear testing of theoretical models.
Cognitive Neuroscience
- Focuses on the relationship between brain structure and function, and cognitive processes.
- Techniques:
- Spatial Resolution: The precision with which a technique can pinpoint the location of brain activity.
- Temporal Resolution: The precision with which a technique can determine the timing of brain activity.
- Brain Imaging Techniques:
- Computed Tomography (CT or CAT): Uses X-rays to reveal structural features of the brain, showing bone and hard tissue more clearly than soft tissue.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Generates detailed images of brain structures using magnetic fields.
- Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI): Measures blood flow in the brain to reveal areas of activity.
- Electroencephalography (EEG): Records electrical activity in the brain through electrodes placed on the scalp.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET): Measures brain activity by tracking the flow of a radioactive tracer.
Brain Structures
- Receptors (Eyes): Sense organs that perceive information from the environment.
- Effectors (Skin): Muscles and glands that produce responses.
- Connectors (Nervous System): Integrates the functions of receptors and effectors.
Nervous System
- Central Nervous System (CNS): The body's master control unit, including the brain and spinal cord.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Connects the CNS to the outside world.
CNS Structures
- Spinal Cord: Connects the brain to the PNS.
- Brain Stem: Regulates basic life functions, connects brain to spinal chord.
- Brain: Divided into three major parts: hindbrain, midbrain, and forebrain.
PNS Structures
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): Regulates involuntary bodily functions.
- Sympathetic Nervous System: Prepares the body for action and stress.
- Parasympathetic Nervous System: Calms the body and conserves energy.
Disorders of the Brain
- Stroke: An interruption of blood supply to the brain, caused by a blocked or ruptured blood vessel.
- Brain Tumor: A mass of abnormal cells in the brain, either cancerous or non-cancerous.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.