Podcast Beta
Questions and Answers
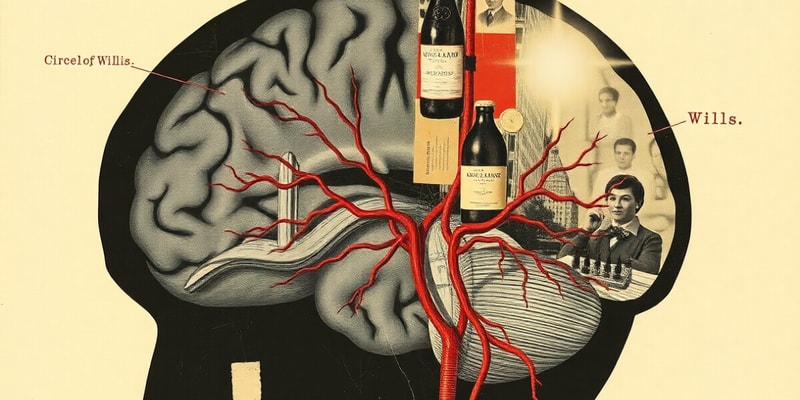
Which arteries contribute to the anterior circulation of the Circle of Willis?
What is the role of the bilateral posterior communicating arteries in the Circle of Willis?
Where does the internal carotid artery originate?
What happens if one part of the Circle of Willis is compromised?
Signup and view all the answers
Which artery is most commonly absent from the Circle of Willis?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the significance of the internal carotid artery passing through the cavernous sinus?
Signup and view all the answers
Which artery originates from the internal carotid artery and is primarily responsible for supplying the orbital structures?
Signup and view all the answers
Which artery serves as the termination point for the internal carotid artery?
Signup and view all the answers
What key structural transition occurs as the internal carotid artery enters the cranium?
Signup and view all the answers
Which arterial connection is most commonly absent in the Circle of Willis?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
Circle of Willis
- Brain receives blood from internal carotid arteries and vertebral arteries
- Arteries join at the inferior aspect of the brain
- Form the Circle of Willis
- Circulation categorized into anterior and posterior circulation
- Both circulations are paired (two of each)
- Anterior circulation arises from internal carotid arteries
- Posterior circulation arises from vertebral arteries
- Circulations are interconnected by bilateral posterior communicating arteries
- Alternate circulation can be provided if one part of the circulation is compromised
- Prevents brain ischemia
- Allows for compensation
Internal Carotid Artery
- Originates at the bifurcation of the common carotid artery at the level of C4
- Travels superiorly within the carotid sheath
- Enters the cranium through the carotid canal (opening in temporal bone)
- Passes anteriorly through the cavernous sinus
- Branches of the Internal Carotid Artery (ICA):
- Ophthalmic artery: supplies orbital structures
- Posterior communicating artery: anastomoses with posterior cerebral arteries (PCA)
- Anterior choroidal artery
- Anterior cerebral artery (ACA):
- Connected by a single anterior communicating artery
- Most common artery absent from Circle of Willis
- Terminates as the middle cerebral artery (MCA): supplies lateral cerebrum
Internal Carotid Artery Course
- Originates from the bifurcation of the common carotid artery at the level of the fourth cervical vertebra (C4)
- Ascends within the carotid sheath
- Enters the skull through the carotid canal, an opening in the temporal bone
- Travels anteriorly through the cavernous sinus, a large venous sinus located within the sphenoid bone, which surrounds the pituitary gland and optic chiasm
- Branches of the internal carotid artery (ICA):
- Ophthalmic artery: supplies blood to the structures within the orbit, including the eye and surrounding tissues
- Posterior communicating artery (PCA): connects to the posterior cerebral artery, completing part of the Circle of Willis. This vessel allows for collateral blood flow to the brain, ensuring a constant supply of blood even in case of a blockage in another vessel.
- Anterior choroidal artery: supplies the choroid plexus, a network of blood vessels located within the brain ventricles, along with structures like the thalamus and internal capsule
-
Anterior cerebral artery (ACA): supplies the medial and superior aspects of the frontal and parietal lobes.
- Connected by a single anterior communicating artery, which is the most common artery to be absent from the Circle of Willis
- Middle cerebral artery (MCA): the largest branch of the ICA, supplying the lateral aspect of the cerebrum, including the temporal lobe and most of the parietal lobe.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
This quiz covers the anatomy and physiology of the Circle of Willis and the Internal Carotid Artery. Learn how these structures contribute to brain circulation and their significance in preventing ischemia. Understand the connections and origins of these vital arteries.