Podcast Beta
Questions and Answers
What type of fibers are present in the tunica adventitia of large elastic arteries?
What is the main component of the tunica media in muscular arteries?
What is unique about the subendothelial layer in smaller muscular arteries?
What type of capillaries are characterized by fenestrations in the cytoplasm of endothelial cells?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the function of arterioles?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the characteristic of the tunica adventitia in muscular arteries?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of capillaries have an uninterrupted, solid endothelial lining?
Signup and view all the answers
In which tissues can fenestrated capillaries be found?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the difference between the internal elastic lamina in muscular arteries and arterioles?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the characteristic of the tunica intima in arterioles?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a characteristic of sinusoidal capillaries?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the number of layers of smooth muscle fibers in the walls of arterioles?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of cells are found at intervals along capillaries, enclosed by the basal lamina of the endothelium?
Signup and view all the answers
In which organs are sinusoidal capillaries found?
Signup and view all the answers
What do capillaries connect to?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the purpose of valves in veins?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following veins typically do not have valves?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the thickest layer in the walls of large veins?
Signup and view all the answers
What is characteristic of the muscular layer in vein walls?
Signup and view all the answers
What is present in the connective tissue of the tunica adventitia in large veins?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the characteristic of the tunica intima in medium-sized veins?
Signup and view all the answers
What is characteristic of the tunica media in medium-sized veins compared to arteries?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the heart's function?
Signup and view all the answers
Which chamber of the heart receives blood from the body?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the middle layer of the heart wall?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of cells form the endocardium?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the function of the subendocardial layer?
Signup and view all the answers
What is unique about Purkinje fibers?
Signup and view all the answers
Where are Purkinje fibers located?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the shape of the nuclei of endothelial cells?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of fibers are present in the walls of venules?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the function of vasa vasorum?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the main mechanism of venous blood flow in the head and trunk?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the main function of valves in the large veins of the extremities?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the size of capillaries compared to?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the main reason for the structural variations in capillaries?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the characteristic of the tunica intima in venules?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of muscle cells are present in the walls of venules?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
Cardiovascular System
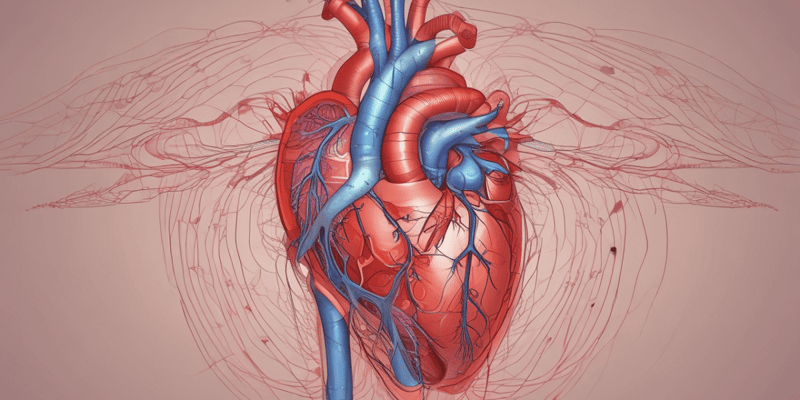
Heart
- The heart is a modified blood vessel that serves as a double pump and consists of four chambers.
- The right side of the heart receives blood from the body and propels it to the lungs, while the left side receives blood from the lungs and distributes it throughout the body.
- The heart wall consists of three layers: endocardium, myocardium, and epicardium.
Endocardium
- The endocardium forms the inner lining of the atria and ventricles and is continuous with the inner lining of blood vessels.
- It consists of a single layer of polygonal squamous (endothelial) cells with oval or rounded nuclei.
- The endothelial cells rest on a continuous layer of fine collagen fibers, separated from it by a basement membrane.
- The fibrous layer is called the subendothelial layer, and deep to it is a thick layer of denser connective tissue that forms the bulk of the endocardium and contains elastic fibers and some smooth muscle cells.
- The subendocardial layer binds the endocardium to the underlying heart muscle and contains collagen fibers, elastic fibers, and blood vessels.
Purkinje Fibers
- Purkinje fibers are thicker and larger than cardiac muscle fibers and contain a greater amount of glycogen.
- They also contain fewer contractile filaments and are located beneath the endocardium on either side of the interventricular septum.
Large Elastic Artery
- The walls of large elastic arteries contain a greater amount of elastic fibers.
- The tunica intima consists of an endothelium, a subendothelial layer, and an internal elastic lamina.
- The tunica media is the thickest coat and consists mainly of elastic fibers.
- The tunica adventitia is relatively thin and contains bundles of collagen fibers (type 1) and a few elastic fibers.
Muscular Arteries
- The walls of muscular arteries contain greater amounts of smooth muscle fibers.
- The tunica intima consists of an endothelium, a subendothelial layer, and an internal elastic lamina.
- The tunica media is the thickest coat and consists mainly of smooth muscle cells arranged in concentric, helical layers.
- The tunica adventitia is prominent in muscular arteries and consists of collagen and elastic fibers that are longitudinal in orientation.
Arterioles
- Arterioles are the smallest branches of the arterial system.
- The walls of arterioles consist of one to five layers of smooth muscle fibers.
- The tunica intima consists only of endothelium and a fenestrated internal elastic lamina.
- The tunica adventitia decreases in thickness, becoming extremely thin in the smallest arterioles.
Veins
- The walls of veins are typically thinner and more numerous than those of arteries.
- The tunica intima in large veins exhibits a prominent endothelium and subendothelial connective tissue.
- The muscular tunica media is thin, and the smooth muscles intermix with connective tissue fibers.
- The tunica adventitia is the thickest and best-developed layer in large veins.
- Vasa vasorum are present in the walls of larger veins and extend into the media.
Venules
- Venules are the smallest blood vessels that unite to form larger blood vessels.
- The tunica intima consists of a thin, continuous endothelium.
- The tunica media is missing in the smallest venules, and the relatively thin adventitia contains a few collagen fibers.
Vasa Vasorum
- The walls of larger arteries and veins are supplied by their own small blood vessels called vasa vasorum.
- The vasa vasorum allows for exchange of nutrients and metabolites with cells in the tunica adventitia and tunica media.
Capillaries
- Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels and have a diameter similar to that of an erythrocyte.
- There are three types of capillaries: continuous, fenestrated, and sinusoidal.
- The basic structure of capillaries is similar and represents an extreme simplification of the vessel wall.
Continuous Capillaries
- Continuous capillaries are the most common and are found in muscle, connective tissue, nervous tissue, skin, respiratory organs, and exocrine glands.
- The endothelial cells are joined and form an uninterrupted, solid endothelial lining.
- Pericytes are irregular, branched, isolated cells that occur at intervals along capillaries, enclosed by the basal lamina of the endothelium.
Fenestrated Capillaries
- Fenestrated capillaries are characterized by fenestrations (pores) in the cytoplasm of endothelial cells.
- They are designed for a rapid exchange of molecules between blood and tissues.
- Fenestrated capillaries are found in endocrine tissues and glands, small intestine, and kidney glomeruli.
Sinusoidal Capillaries
- Sinusoidal capillaries are blood vessels that exhibit irregular, tortuous paths.
- They have a wider diameter than continuous capillaries, which slows down the flow of blood.
- The cells may be separated by gaps, and they rest on a discontinuous basal lamina.
- Direct exchange of molecules occurs between blood contents and cells.
- Sinusoidal capillaries are found in the liver, spleen, and bone marrow.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Learn about the heart's structure and function, including its chambers and blood flow. This quiz is designed for college students in the Department of Clinical Laboratory Science.