Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the estimated rate at which one person in the United States has a heart attack?
What is the estimated rate at which one person in the United States has a heart attack?
- Every minute
- Every 5 minutes
- Every 20 seconds
- Every 40 seconds (correct)
What is the leading cause of death in Americans since the early 1900s?
What is the leading cause of death in Americans since the early 1900s?
- Stroke
- Diabetes
- Heart disease (correct)
- Cancer
What surrounds the heart muscle?
What surrounds the heart muscle?
- Visceral layer
- Endocardium
- Pericardium (correct)
- Myocardium
What is the smooth inner lining of the chambers of the heart and the surface of the valves?
What is the smooth inner lining of the chambers of the heart and the surface of the valves?
What is the strongest and largest ventricle responsible for pumping blood through vessels throughout the entire body?
What is the strongest and largest ventricle responsible for pumping blood through vessels throughout the entire body?
What is the function of the atrioventricular valves and semilunar valves in the heart?
What is the function of the atrioventricular valves and semilunar valves in the heart?
What is the primary function of the coronary arteries?
What is the primary function of the coronary arteries?
Which part of the cardiac conduction system has an intrinsic rate of 60-100 beats per minute?
Which part of the cardiac conduction system has an intrinsic rate of 60-100 beats per minute?
What is the term for the ability of cells to respond to electrical impulses?
What is the term for the ability of cells to respond to electrical impulses?
What is the percentage of blood pumped from the heart with each contraction?
What is the percentage of blood pumped from the heart with each contraction?
What is the term for the amount of blood returned to the heart to be pumped out?
What is the term for the amount of blood returned to the heart to be pumped out?
What is the system that carries blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs and then back to the left side of the heart?
What is the system that carries blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs and then back to the left side of the heart?
Study Notes
- The American Heart Association (AHA) estimates that one person in the United States has an acute myocardial infarction or heart attack every 40 seconds.
- Heart disease has been the leading cause of death in Americans since the early 1900s.
- Deaths from cardiovascular disease can be reduced with better public awareness, early access to EMS, increased numbers of lay people trained in CPR, increased use of evolving technology in dispatch and cardiac arrest response, public access to defibrillation devices, and transportation to hospitals that can provide coronary catheterization and post-arrest care.
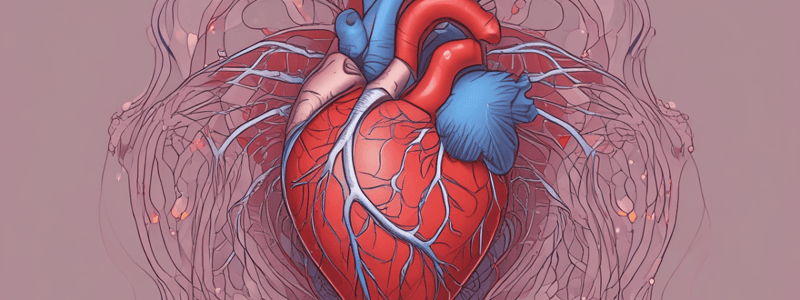
- The cardiovascular system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood.
- The heart is a muscular, cone-shaped organ that pumps blood through the body.
- The heart muscle is referred to as the myocardium, and it is surrounded by a thick, fibrous membrane called the paricardium or pericardial sac.
- The visceral layer of the pericardium lies against the heart, and the endocardium is the smooth inner lining of the chambers of the heart and the surface of the valves.
- Each atrium receives blood returned to the heart from other parts of the body, and each ventricle pumps blood out of the heart.
- The left ventricle is the strongest and largest ventricle, responsible for pumping blood through vessels throughout the entire body.
- The atrioventricular valves and semilunar valves (tricuspid valve, mitral valve, aortic valve, and pulmonic valve) ensure blood flow through the heart.
- The papillary muscles and ventricles contract to tighten the cordae tendineae, which keep the valves opening and closing.
- The coronary arteries supply oxygen and nutrients to the heart muscle, emanating from the left and right coronary arteries.
- The left main coronary artery divides into the left anterior descending (LAD) and circumflex coronary arteries, which supply most of the left ventricle and the intraventricular septum.
- Blood is transported through the body via arteries, which branch into arterioles, then capillaries, and eventually enlarge to form venules.
- The superior vena cava and inferior vena cava return deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium, while blood from the four pulmonary veins enters the left atrium.
- Blood consists of plasma and formed elements (red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets).
- The electrical conduction system initiates the pumping of the heart in response to electrical stimuli, with the sinoatrial (SA) node being the normal site of origin for electrical impulses.
- The SA node has an intrinsic rate of 60-100 beats per minute, while the atrioventricular (AV) node has an intrinsic rate of 40-60 beats per minute.
- The electrical impulse spreads through the conduction system, resulting in ventricular contraction (systole).
- Excitability refers to the ability of cells to respond to electrical impulses, conductivity refers to the ability of cells to conduct electrical impulses, and automaticity refers to the ability to contract without a stimulus from a nerve source.
- The heart's chronotropic, dromotropic, and inotropic states are controlled by the autonomic nervous system, hormones of the endocrine system, and heart tissue.
- The cardiac cycle begins with myocardial contraction and concludes at the beginning of the next contraction.
- The cardiac cycle involves systole (contraction of the ventricles and pumping of blood into the systemic circulation) and diastole (relaxation of the heart).
- Preload refers to the amount of blood returned to the heart to be pumped out, which directly affects afterload (the pressure in the aorta or peripheral vascular resistance).
- Factors that influence heart rate, stroke volume, or both will affect cardiac output and perfusion.
- The Starling law of the heart states that increased venous return to the heart stretches the ventricles, resulting in increased cardiac contractility.
- Ejection fraction is the percentage of blood pumped from the heart with each contraction.
- The pulmonary system carries blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs and then back to the left side of the heart.
- The systemic arterial circulation makes oxygenated blood leave the heart through the aortic valve and pass into the aorta, distributing blood to all parts of the body.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
This quiz covers the structure and function of the heart, including its muscular and membranous components, blood flow, and the cardiac cycle. It also explores the electrical conduction system, cardiac output, and perfusion. Test your knowledge of the cardiovascular system!