Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
What is the primary function of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
The composition of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) includes a high protein content.
The composition of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) includes a high protein content.
False
Name the four ventricles in the ventricular system.
Name the four ventricles in the ventricular system.
Lateral ventricles, Third ventricle, Fourth ventricle
The main part of the blood-brain barrier is formed by __________ cells with tight junctions.
The main part of the blood-brain barrier is formed by __________ cells with tight junctions.
Signup and view all the answers
Match each meningeal layer with its description:
Match each meningeal layer with its description:
Signup and view all the answers
Which structure actively secretes cerebrospinal fluid?
Which structure actively secretes cerebrospinal fluid?
Signup and view all the answers
The spinal meninges contain an epidural space filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
The spinal meninges contain an epidural space filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary role of the blood-brain barrier?
What is the primary role of the blood-brain barrier?
Signup and view all the answers
The flow of cerebrospinal fluid starts from the __________ ventricles.
The flow of cerebrospinal fluid starts from the __________ ventricles.
Signup and view all the answers
Which arteries supply blood to the brain?
Which arteries supply blood to the brain?
Signup and view all the answers
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for decision making and personality?
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for decision making and personality?
Signup and view all the answers
The cerebellum is responsible for processing visual stimuli.
The cerebellum is responsible for processing visual stimuli.
Signup and view all the answers
What role does the thalamus play in the brain?
What role does the thalamus play in the brain?
Signup and view all the answers
The _____ is a clear liquid that circulates in the brain and spinal cord, providing cushioning.
The _____ is a clear liquid that circulates in the brain and spinal cord, providing cushioning.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the part of the brain with its primary function:
Match the part of the brain with its primary function:
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following bones is NOT part of the skull that protects the brain?
Which of the following bones is NOT part of the skull that protects the brain?
Signup and view all the answers
The brain has the ability to store energy for extended periods.
The brain has the ability to store energy for extended periods.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the function of the blood-brain barrier?
What is the function of the blood-brain barrier?
Signup and view all the answers
The middle layer of the cranial meninges is called the _____ mater.
The middle layer of the cranial meninges is called the _____ mater.
Signup and view all the answers
Which section of the cerebellum is primarily involved in balance and eye movement control?
Which section of the cerebellum is primarily involved in balance and eye movement control?
Signup and view all the answers
Which lobe of the brain is primarily associated with receiving sensory information?
Which lobe of the brain is primarily associated with receiving sensory information?
Signup and view all the answers
The cerebellum is located directly beneath the frontal lobe.
The cerebellum is located directly beneath the frontal lobe.
Signup and view all the answers
What structure regulates homeostasis and emotional responses in the brain?
What structure regulates homeostasis and emotional responses in the brain?
Signup and view all the answers
The _____ mater is the innermost layer of the cranial meninges.
The _____ mater is the innermost layer of the cranial meninges.
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following bones is part of the protection structures for the brain?
Which of the following bones is part of the protection structures for the brain?
Signup and view all the answers
The cerebrospinal fluid helps in maintaining homeostasis in the brain.
The cerebrospinal fluid helps in maintaining homeostasis in the brain.
Signup and view all the answers
Name one function of the blood-brain barrier.
Name one function of the blood-brain barrier.
Signup and view all the answers
The _____ connects the pituitary gland to the hypothalamus.
The _____ connects the pituitary gland to the hypothalamus.
Signup and view all the answers
What serves as a relay station for signals and regulates autonomic functions?
What serves as a relay station for signals and regulates autonomic functions?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is a function of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
Which of the following is a function of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)?
Signup and view all the answers
The cranial meninges consist of a single-layered structure.
The cranial meninges consist of a single-layered structure.
Signup and view all the answers
What structure supports the tight junctions of endothelial cells in the blood-brain barrier?
What structure supports the tight junctions of endothelial cells in the blood-brain barrier?
Signup and view all the answers
The cerebrospinal fluid is produced mainly in the __________ of the brain.
The cerebrospinal fluid is produced mainly in the __________ of the brain.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the meningeal layers with their descriptions:
Match the meningeal layers with their descriptions:
Signup and view all the answers
Both cranial and spinal meninges contain an epidural space.
Both cranial and spinal meninges contain an epidural space.
Signup and view all the answers
How much cerebrospinal fluid is produced daily?
How much cerebrospinal fluid is produced daily?
Signup and view all the answers
Cerebrospinal fluid flows from the lateral ventricles to the __________ foramen.
Cerebrospinal fluid flows from the lateral ventricles to the __________ foramen.
Signup and view all the answers
Which artery is NOT involved in supplying blood to the brain?
Which artery is NOT involved in supplying blood to the brain?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the cerebellum's lateral hemispheres?
What is the primary function of the cerebellum's lateral hemispheres?
Signup and view all the answers
Which structure acts as a relay station for signals and is involved in crucial autonomic functions?
Which structure acts as a relay station for signals and is involved in crucial autonomic functions?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary role of the arachnoid mater?
What is the primary role of the arachnoid mater?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following statements about the blood-brain barrier is false?
Which of the following statements about the blood-brain barrier is false?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the significance of the dural venous sinuses?
What is the significance of the dural venous sinuses?
Signup and view all the answers
Which structure is primarily responsible for integrating sensory information and projecting it to the cerebral cortex?
Which structure is primarily responsible for integrating sensory information and projecting it to the cerebral cortex?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of cerebrospinal fluid?
What is the primary function of cerebrospinal fluid?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is NOT a component of the cranial meninges?
Which of the following is NOT a component of the cranial meninges?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary component that helps cerebrospinal fluid maintain buoyancy for the brain?
What is the primary component that helps cerebrospinal fluid maintain buoyancy for the brain?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is true about the composition of cerebrospinal fluid?
Which of the following is true about the composition of cerebrospinal fluid?
Signup and view all the answers
In which part of the central nervous system does the production of cerebrospinal fluid primarily occur?
In which part of the central nervous system does the production of cerebrospinal fluid primarily occur?
Signup and view all the answers
Which structure primarily prevents the entry of toxins into the brain from the circulatory system?
Which structure primarily prevents the entry of toxins into the brain from the circulatory system?
Signup and view all the answers
Which characteristic distinguishes the cranial meninges from the spinal meninges?
Which characteristic distinguishes the cranial meninges from the spinal meninges?
Signup and view all the answers
Which sequence correctly represents the flow of cerebrospinal fluid through the ventricular system?
Which sequence correctly represents the flow of cerebrospinal fluid through the ventricular system?
Signup and view all the answers
What role do astrocytes play in the function of the blood-brain barrier?
What role do astrocytes play in the function of the blood-brain barrier?
Signup and view all the answers
What feature is unique to the spinal meninges compared to cranial meninges?
What feature is unique to the spinal meninges compared to cranial meninges?
Signup and view all the answers
Which pathway represents the arterial supply to the brain?
Which pathway represents the arterial supply to the brain?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
Learning Outcomes - Brain & Meninges
- Recognize the functions of cerebrum, primary motor/sensory cortex, cerebellum, thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, brain stem, pons & medulla.
- List structures that support, nourish, and protect the brain and describe how each performs these functions.
- Describe the functions of the cranial meninges and compare/contrast them with spinal meninges (layer differences).
- Recognize the arterial supply to the brain.
- Describe the function, production, and flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the ventricular system.
- Identify the components and functions of the Blood Brain Barrier (BBB).
Cerebrum
- Largest part of the brain, divided into right and left hemispheres, with four lobes.
- Frontal Lobe: Voluntary motor control, decision-making, planning, concentration, and personality.
- Parietal Lobe: Receives sensory information.
- Temporal Lobe: Hearing and smell.
- Occipital Lobe: Vision.
Thalamus
- Largest part of the diencephalon receiving sensory information (auditory and visual), projecting to the cerebral cortex.
- Plays roles in motor function regulation, emotional responses, and mood development.
Hypothalamus
- Located at the bottom of the diencephalon.
- Regulates homeostasis, emotional responses to odors connected to the pituitary gland via the infundibulum.
- Crucial for autonomic functions and maintaining physiological processes.
Brainstem
- Consists of the medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain.
- Medulla Oblongata: Relay station for signals, autonomic functions (respiration, heart rate, blood pressure), coordination of reflexes, and contains cranial nerve nuclei (trigeminal, facial, vestibulocochlear, glossopharyngeal, vagus, and hypoglossal). Contains ascending and descending tracts.
- Pons: Connects different brain regions, relays cerebellum information, and contains nuclei for cranial nerves (trigeminal, abducens, facial, vestibulocochlear, glossopharyngeal, vagus, and hypoglossal.)
- Midbrain: Serves as a pathway for nerve connections between the cerebral hemispheres and contains auditory and visual centers (inferior and superior colliculi). Contains ascending and descending tracts.
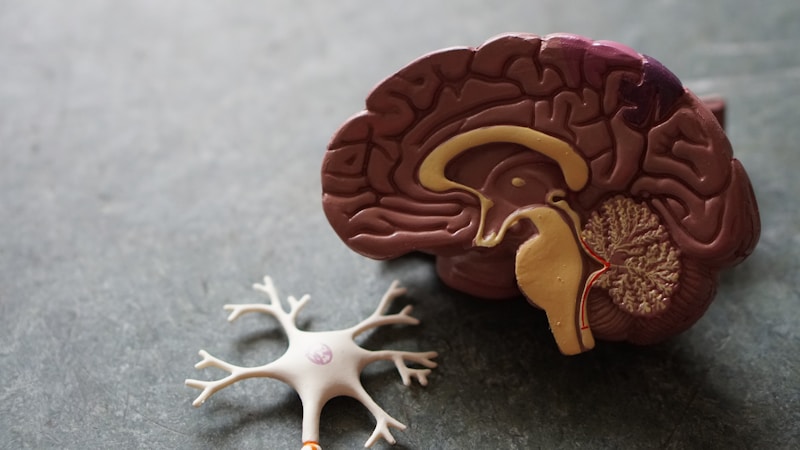
Cerebellum
- Located beneath the occipital lobe, connected to the brainstem via the pons.
- Cortex made of gray matter with deep cerebellar nuclei (arbor vitae).
- Sections include flocculonodular lobe, vermis, and medial/lateral hemispheres.
- Involved in balance, posture, locomotion, fine motor coordination, and learning complex movements.
Structures Protecting the Brain
- Bones of the skull: Frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, sphenoid, and ethmoid bones.
- Cranial meninges:
- Dura mater (superficial layer with two layers – meningeal and periosteal, with dural sinuses between, forming venous sinuses).
- Arachnoid mater (mid-layer, with web-like threads).
- Pia mater (innermost layer, very vascular).
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): Provides protection, buoyancy, homeostasis, and circulation of nutrients and waste.
Blood-Brain Barrier
- Protects the brain by filtering out harmful substances (toxins, viruses), allowing essential nutrients to pass through.
- Structure includes tight junctions, astrocyte feet, and pericytes.
Blood Supply To Brain
- Blood reaches the brain via the common carotid arteries (internal carotid and vertebral arteries) connecting at the circle of Willis.
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- Fluid that circulates in the ventricular system (composed of 4 ventricles).
- Produced by choroid plexus within the ventricles (lateral, third & fourth).
- Has a clear, colorless composition with water, glucose, ions (Na+, K+, Cl-), and proteins, playing a protective role, maintaining brain buoyancy and homeostasis.
- Fluid flows from the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle, then the cerebral aqueduct, fourth ventricle, subarachnoid space, and into the bloodstream through arachnoid granulations.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Test your understanding of the brain structures, their functions, and the protective mechanisms surrounding the brain. This quiz covers the cerebrum, cranial meninges, cerebrospinal fluid dynamics, and the blood-brain barrier. Engage with the critical components that support brain health and functionality.