Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of a body cavity?
Which of the following organs is NOT found in the ventral cavity?
What distinguishes the dorsal cavity from the ventral cavity?
What is one feature common to both the ventral and dorsal cavities?
Signup and view all the answers
What allows the lungs to expand within the ventral cavity?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary characteristic of body cavities?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following organs is housed in the dorsal cavity?
Signup and view all the answers
Which statement about the ventral cavity is correct?
Signup and view all the answers
What separates the various body cavities?
Signup and view all the answers
What defines the location of the ventral cavity in the human body?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following body cavities is located within the dorsal cavity?
Signup and view all the answers
What cavities are included in the dorsal cavity?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following statements about body cavities is true?
Signup and view all the answers
Which cavity is specifically responsible for housing the brain and spinal cord?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following is NOT found within the dorsal cavity?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the visceral membrane?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following correctly describes the parietal pleura?
Signup and view all the answers
Which cavity is described as the space between the parietal and visceral membranes in the abdomen?
Signup and view all the answers
What characteristic distinguishes visceral membranes from parietal membranes?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the role of the parietal layer of the pericardium?
Signup and view all the answers
Which layer of the peritoneum covers the internal organs?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name of the membrane that lines the cavity wall in the abdomen and pelvis?
Signup and view all the answers
Which statement correctly differentiates between the visceral and parietal membranes?
Signup and view all the answers
Which of the following best describes the function of the peritoneum?
Signup and view all the answers
Where is the parietal layer of the peritoneum specifically located?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
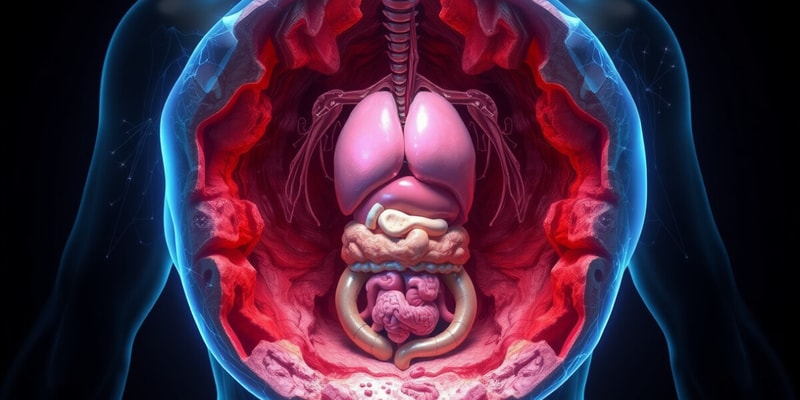
Body Cavities Overview
- Body cavities are fluid-filled spaces that protect and contain internal organs.
- Various membranes and structures separate these cavities within the human body.
Ventral Cavity
- Located at the anterior (front) section of the trunk.
- Contains essential organs including:
- Lungs
- Heart
- Stomach
- Intestines
- Internal reproductive organs
- Allows expansion and movement within the body, facilitating functions like lung inflation and fetal development.
Dorsal Cavity
- Encompasses the head and posterior (back) portion of the trunk.
- Houses critical structures such as:
- Brain
- Spinal cord
Subdivisions of Body Cavities
- Both the ventral and dorsal cavities are further divided into smaller cavities, enhancing organization and function.
Body Cavities Overview
- Body cavities are fluid-filled spaces that protect and contain internal organs.
- Various membranes and structures separate these cavities within the human body.
Ventral Cavity
- Located at the anterior (front) section of the trunk.
- Contains essential organs including:
- Lungs
- Heart
- Stomach
- Intestines
- Internal reproductive organs
- Allows expansion and movement within the body, facilitating functions like lung inflation and fetal development.
Dorsal Cavity
- Encompasses the head and posterior (back) portion of the trunk.
- Houses critical structures such as:
- Brain
- Spinal cord
Subdivisions of Body Cavities
- Both the ventral and dorsal cavities are further divided into smaller cavities, enhancing organization and function.
Body Cavities Overview
- Body cavities: fluid-filled spaces providing protection and support for internal organs.
- Human body cavities are separated by membranes and other structures.
Major Body Cavities
-
Ventral Cavity
- Located at the anterior (front) of the trunk.
- Houses critical organs: lungs, heart, stomach, intestines, and internal reproductive organs.
- Allows for expansion, as seen in lung inflation and fetal development.
-
Dorsal Cavity
- Comprises the head and posterior (back) portion of the trunk.
- Encloses vital structures including the brain and spinal cord.
Subdivisions of Body Cavities
- Ventral and dorsal cavities can be further divided into smaller cavities:
- Cranial Cavity: Holds the brain.
- Spinal Cavity: Contains the spinal cord.
- Pelvic Cavity: Part of the dorsal cavity related to lower body organs.
Parietal and Visceral Membranes
- Serous membranes are categorized into parietal and visceral layers based on their location relative to body cavities.
- Parietal Membrane: The outer layer that adheres to the wall of the body cavity.
- Visceral Membrane: The inner layer that envelops the organs within the cavity.
Examples of Membranes
-
Pleura:
- A serous membrane forming a double-layered sac around the lungs.
- Parietal pleura connects to the chest wall.
- Visceral pleura covers the lungs along with associated blood vessels, nerves, and bronchi.
-
Peritoneum:
- Lines the abdominal and pelvic cavities.
- Comprises a parietal layer attached to the abdominal and pelvic walls.
- Visceral layer covers internal organs, with the space between layers known as the peritoneal cavity.
-
Pericardium:
- Encloses the heart with both parietal and visceral layers.
- Parietal layer is the outer component attached to the fibrous pericardium.
- Visceral layer is the innermost layer that directly covers the heart and the roots of major blood vessels.
Serous Membrane
- Visceral membrane covers internal organs, providing a protective layer.
- Parietal membrane covers the cavity wall, creating a barrier between organs and the cavity.
Peritoneum
- Serves as a lining for the inside of the abdomen and pelvis (parietal layer).
- Covers various internal organs within the abdominal cavity (visceral layer).
- Plays a crucial role in supporting organs and facilitating movement within the abdominal cavity.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
This quiz explores the various body cavities in the human body. It covers the definition, structure, and the two largest cavities, including their significance and the organs they contain. Test your knowledge on how these cavities protect and organize internal organs.