Podcast
Questions and Answers
What type of epithelial tissue is found in the proximal convoluted tubule?
What type of epithelial tissue is found in the proximal convoluted tubule?
Cortical nephrons have longer nephron loops compared to juxtamedullary nephrons.
Cortical nephrons have longer nephron loops compared to juxtamedullary nephrons.
False
What structure collects filtrate in the nephron?
What structure collects filtrate in the nephron?
Glomerular capsule (Bowman's capsule)
The __________ in the renal tubule monitor and respond to ion concentrations in the filtrate.
The __________ in the renal tubule monitor and respond to ion concentrations in the filtrate.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following components of the nephron with their functions:
Match the following components of the nephron with their functions:
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of cells in the uterine tubes secrete mucus to nourish the oocyte?
Which type of cells in the uterine tubes secrete mucus to nourish the oocyte?
Signup and view all the answers
The endometrium is the outermost layer of the uterus.
The endometrium is the outermost layer of the uterus.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the main role of the myometrium in the uterus?
What is the main role of the myometrium in the uterus?
Signup and view all the answers
The ___________ is the muscular layer of the uterus that contracts during labor.
The ___________ is the muscular layer of the uterus that contracts during labor.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following layers of the uterine wall with their functions:
Match the following layers of the uterine wall with their functions:
Signup and view all the answers
What is the function of ciliated cells in the uterine tubes?
What is the function of ciliated cells in the uterine tubes?
Signup and view all the answers
The broad ligament supports the ovaries and uterine tubes.
The broad ligament supports the ovaries and uterine tubes.
Signup and view all the answers
Identify the structure that connects the ovary to the pelvic wall.
Identify the structure that connects the ovary to the pelvic wall.
Signup and view all the answers
Which layer of the endometrium changes in thickness during the uterine cycle?
Which layer of the endometrium changes in thickness during the uterine cycle?
Signup and view all the answers
The basal layer of the endometrium is lost during menstruation.
The basal layer of the endometrium is lost during menstruation.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the function of the Leydig cells?
What is the function of the Leydig cells?
Signup and view all the answers
Sperm matures and is stored in the __________.
Sperm matures and is stored in the __________.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following male reproductive structures with their functions:
Match the following male reproductive structures with their functions:
Signup and view all the answers
During which phase does the functional layer of the endometrium thicken in preparation for pregnancy?
During which phase does the functional layer of the endometrium thicken in preparation for pregnancy?
Signup and view all the answers
The ejaculatory ducts are formed from the union of the vas deferens and the seminal vesicle ducts.
The ejaculatory ducts are formed from the union of the vas deferens and the seminal vesicle ducts.
Signup and view all the answers
Where are sperm produced in the male reproductive system?
Where are sperm produced in the male reproductive system?
Signup and view all the answers
The thickening of the functional layer is primarily influenced by _______ and _______.
The thickening of the functional layer is primarily influenced by _______ and _______.
Signup and view all the answers
Which gland adds fluid to the semen and nourishes sperm?
Which gland adds fluid to the semen and nourishes sperm?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of epithelium lines the renal pelvis?
Which type of epithelium lines the renal pelvis?
Signup and view all the answers
The proximal convoluted tubule is mainly involved in the secretion of waste products.
The proximal convoluted tubule is mainly involved in the secretion of waste products.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the glomerulus in the renal corpuscle?
What is the primary function of the glomerulus in the renal corpuscle?
Signup and view all the answers
The ___ collects urine from the major calyces and funnels it into the ureter.
The ___ collects urine from the major calyces and funnels it into the ureter.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following anatomical structures with their primary epithelium type:
Match the following anatomical structures with their primary epithelium type:
Signup and view all the answers
The major calyces are formed by the merging of which structures?
The major calyces are formed by the merging of which structures?
Signup and view all the answers
Simple cuboidal epithelium is found in the distal convoluted tubule.
Simple cuboidal epithelium is found in the distal convoluted tubule.
Signup and view all the answers
What type of epithelium characterizes the minor calyces?
What type of epithelium characterizes the minor calyces?
Signup and view all the answers
The main function of the distal convoluted tubule is the regulation of ___ and pH.
The main function of the distal convoluted tubule is the regulation of ___ and pH.
Signup and view all the answers
Hormones are primarily produced by which type of cells?
Hormones are primarily produced by which type of cells?
Signup and view all the answers
Cortical nephrons have nephron loops that extend deep into the medulla.
Cortical nephrons have nephron loops that extend deep into the medulla.
Signup and view all the answers
What type of epithelium is found in the distal convoluted tubule?
What type of epithelium is found in the distal convoluted tubule?
Signup and view all the answers
The renal tubule collects filtrate from the renal corpuscle and is comprised of the proximal convoluted tubule, descending tubule, nephron loop, ascending tubule, and the __________.
The renal tubule collects filtrate from the renal corpuscle and is comprised of the proximal convoluted tubule, descending tubule, nephron loop, ascending tubule, and the __________.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following structures with their corresponding features:
Match the following structures with their corresponding features:
Signup and view all the answers
Which layer of the uterine wall is responsible for uterine contractions during labor?
Which layer of the uterine wall is responsible for uterine contractions during labor?
Signup and view all the answers
The endometrium is the innermost layer of the uterus where implantation occurs.
The endometrium is the innermost layer of the uterus where implantation occurs.
Signup and view all the answers
What type of cells in the uterine tubes help in the transport of the oocyte?
What type of cells in the uterine tubes help in the transport of the oocyte?
Signup and view all the answers
The __________ layer of the uterus provides outer protection and support.
The __________ layer of the uterus provides outer protection and support.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of non-ciliated cells in the uterine tubes?
What is the primary function of non-ciliated cells in the uterine tubes?
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following histological features with their functions:
Match the following histological features with their functions:
Signup and view all the answers
The ovarian ligament supports the ovary in connection to the pelvic wall.
The ovarian ligament supports the ovary in connection to the pelvic wall.
Signup and view all the answers
The __________ is a fold of the broad ligament that supports the ovary.
The __________ is a fold of the broad ligament that supports the ovary.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the functional layer of the endometrium?
What is the primary function of the functional layer of the endometrium?
Signup and view all the answers
The basal layer of the endometrium changes in thickness during the uterine cycle.
The basal layer of the endometrium changes in thickness during the uterine cycle.
Signup and view all the answers
Where does sperm maturation occur?
Where does sperm maturation occur?
Signup and view all the answers
Leydig cells are primarily responsible for the production of __________.
Leydig cells are primarily responsible for the production of __________.
Signup and view all the answers
What happens to the functional layer if implantation does not occur?
What happens to the functional layer if implantation does not occur?
Signup and view all the answers
Sperm passes through the ovaries before entering the urethra.
Sperm passes through the ovaries before entering the urethra.
Signup and view all the answers
What fluid does the prostate gland add to semen?
What fluid does the prostate gland add to semen?
Signup and view all the answers
The __________ transports sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts.
The __________ transports sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts.
Signup and view all the answers
Which hormone primarily influences the thickening of the functional layer of the endometrium?
Which hormone primarily influences the thickening of the functional layer of the endometrium?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of epithelium is found in the glomerulus?
What type of epithelium is found in the glomerulus?
Signup and view all the answers
The collecting ducts are lined with simple columnar epithelium.
The collecting ducts are lined with simple columnar epithelium.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the proximal convoluted tubule?
What is the primary function of the proximal convoluted tubule?
Signup and view all the answers
The major calyces are formed by the merging of __________.
The major calyces are formed by the merging of __________.
Signup and view all the answers
Match the following structures with their primary epithelium type:
Match the following structures with their primary epithelium type:
Signup and view all the answers
Which structure directs urine into the ureter?
Which structure directs urine into the ureter?
Signup and view all the answers
Transitional epithelium is found in the proximal convoluted tubule.
Transitional epithelium is found in the proximal convoluted tubule.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the role of hormones in the body?
What is the role of hormones in the body?
Signup and view all the answers
The _______________ is the structure that collects urine from the major calyces.
The _______________ is the structure that collects urine from the major calyces.
Signup and view all the answers
Which segment of the nephron has a dense microvilli lining?
Which segment of the nephron has a dense microvilli lining?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the glomerular capsule within the nephron?
What is the primary function of the glomerular capsule within the nephron?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of nephron is primarily responsible for the concentration of urine?
Which type of nephron is primarily responsible for the concentration of urine?
Signup and view all the answers
What histological feature is characteristic of the proximal convoluted tubule?
What histological feature is characteristic of the proximal convoluted tubule?
Signup and view all the answers
Which component of the nephron is directly connected to the collecting ducts?
Which component of the nephron is directly connected to the collecting ducts?
Signup and view all the answers
In what part of the nephron is the macula densa located?
In what part of the nephron is the macula densa located?
Signup and view all the answers
Which structure in the ovary contains oocytes at various stages of maturation?
Which structure in the ovary contains oocytes at various stages of maturation?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the main function of the ciliated cells in the uterine tubes?
What is the main function of the ciliated cells in the uterine tubes?
Signup and view all the answers
Which layer of the uterine wall is continuous with the serosa of the uterine tubes?
Which layer of the uterine wall is continuous with the serosa of the uterine tubes?
Signup and view all the answers
Which component of the uterine tubes is responsible for secreting mucus to nourish the oocyte?
Which component of the uterine tubes is responsible for secreting mucus to nourish the oocyte?
Signup and view all the answers
What feature of the endometrium changes throughout the menstrual cycle?
What feature of the endometrium changes throughout the menstrual cycle?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of cells in the ovaries secrete estrogen and progesterone?
What type of cells in the ovaries secrete estrogen and progesterone?
Signup and view all the answers
Which structure serves as a fold of the broad ligament that supports the ovary?
Which structure serves as a fold of the broad ligament that supports the ovary?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary histological feature of the functional layer of the endometrium?
What is the primary histological feature of the functional layer of the endometrium?
Signup and view all the answers
Which characteristic best describes the cells found in the basal layer of the endometrium?
Which characteristic best describes the cells found in the basal layer of the endometrium?
Signup and view all the answers
Which cell type is responsible for testosterone production within the testes?
Which cell type is responsible for testosterone production within the testes?
Signup and view all the answers
What tissue type primarily composes the seminiferous tubules where sperm is produced?
What tissue type primarily composes the seminiferous tubules where sperm is produced?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the epithelium in the functional layer during the uterine cycle?
What is the primary function of the epithelium in the functional layer during the uterine cycle?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a significant histological characteristic of the prostate gland?
What is a significant histological characteristic of the prostate gland?
Signup and view all the answers
Which structural feature distinguishes Leydig cells from other cell types in the testes?
Which structural feature distinguishes Leydig cells from other cell types in the testes?
Signup and view all the answers
What histological changes occur in the functional layer of the endometrium if implantation does not take place?
What histological changes occur in the functional layer of the endometrium if implantation does not take place?
Signup and view all the answers
Which characteristic best describes the epithelial tissue involved in sperm storage and maturation in the epididymis?
Which characteristic best describes the epithelial tissue involved in sperm storage and maturation in the epididymis?
Signup and view all the answers
Which type of epithelium is found in the renal pelvis?
Which type of epithelium is found in the renal pelvis?
Signup and view all the answers
What is a primary function of the simple cuboidal epithelium in the proximal convoluted tubule?
What is a primary function of the simple cuboidal epithelium in the proximal convoluted tubule?
Signup and view all the answers
Which structure utilizes simple columnar epithelium to facilitate urine drainage into the minor calyces?
Which structure utilizes simple columnar epithelium to facilitate urine drainage into the minor calyces?
Signup and view all the answers
In the context of the nephron, what is the purpose of the transitional epithelium in the minor and major calyces?
In the context of the nephron, what is the purpose of the transitional epithelium in the minor and major calyces?
Signup and view all the answers
What histological feature is characteristic of Bowman's capsule in the renal corpuscle?
What histological feature is characteristic of Bowman's capsule in the renal corpuscle?
Signup and view all the answers
Which epithelial type is primarily involved in the secretion of waste products in the distal convoluted tubule?
Which epithelial type is primarily involved in the secretion of waste products in the distal convoluted tubule?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the main role of the transitional epithelium in the minor calyces?
What is the main role of the transitional epithelium in the minor calyces?
Signup and view all the answers
The glomerulus is characterized by which histological feature for its function?
The glomerulus is characterized by which histological feature for its function?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the significance of microvilli present in the proximal convoluted tubule?
What is the significance of microvilli present in the proximal convoluted tubule?
Signup and view all the answers
What type of epithelium lines the loop of Henle, and what is its functional significance?
What type of epithelium lines the loop of Henle, and what is its functional significance?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
Learning Outcomes Examined in Chapter 26
- State the functions and histological features of ovaries, uterine tubes, and the uterus.
- Differentiate between the layers of the uterine wall and identify which layers change during the uterine cycle.
- Recall the structures sperm travel through from formation to ejaculation.
- Recall the cells/structures that produce testosterone.
Ovaries
- Functions:
- Oocyte production: Produce oocytes (eggs) for fertilization.
- Hormone secretion:
- Estrogen (E): Supports sexual and reproductive development.
- Progesterone (P): Maintains the uterus during pregnancy.
- Histological Features:
- Follicles: Contain oocytes at various stages of maturation.
- Interstitial cells: Secrete hormones (estrogen and progesterone).
- Support Structures:
- Ovarian ligament: Anchors the ovary to the uterus.
- Suspensory ligament: Connects the ovary to the pelvic wall.
- Mesovarium: A fold of the broad ligament supporting the ovary.
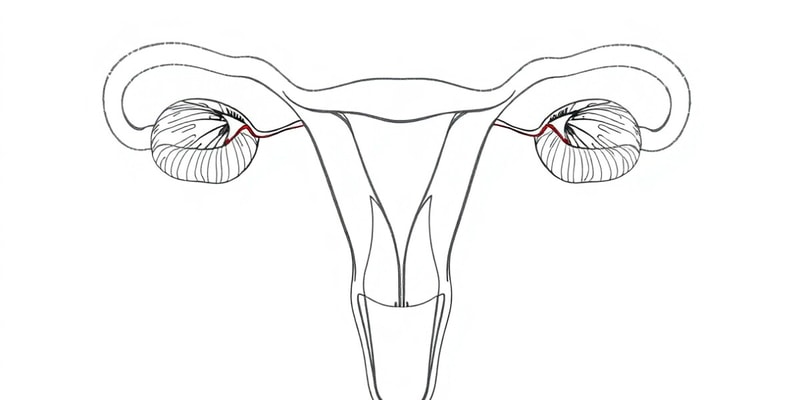
Uterine Tubes (Fallopian Tubes)
- Functions:
- Oocyte transport: Transports the oocyte from the ovary to the uterus.
- Fertilization site: Typically where fertilization occurs after the oocyte is released from the ovary.
- Histological Features:
- Mucosal layer:
- Ciliated cells: Move the oocyte toward the uterus.
- Non-ciliated cells: Secrete mucus to nourish the oocyte.
- Muscularis layer: Two smooth muscle layers facilitating peristalsis to move the oocyte to the uterus.
Uterus
- Functions:
- Protection and nutritional support: Provides a safe environment and nourishment for the developing embryo/fetus.
- Waste Removal: Removes waste produced by the embryo/fetus.
- Histological Features:
- Endometrium: Innermost layer where implantation occurs and changes throughout the menstrual cycle.
- Myometrium: Muscular layer that contracts during labor.
- Perimetrium: Outer serous layer.
- Regions:
- Fundus: The upper portion of the uterus above the fallopian tube openings.
- Body: Main portion of the uterus where the embryo implants
- Isthmus: The narrow portion connecting the body of the uterus to the cervix.
- Cervix: Lower portion of the uterus that connects to the vagina.
Structures Passed by Sperm from Formation to Ejaculation
- Testes: Located in the scrotum; produce sperm in the seminiferous tubules.
- Epididymis: Located on the posterior side of each testicle; sperm mature and are stored here.
- Vas Deferens: Transport sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts.
- Ejaculatory Ducts: Formed by the union of vas deferens and seminal vesicle ducts.
- Prostate Gland: Surrounds the urethra below the bladder; adds prostatic fluid to semen to nourish sperm and protect from acidity.
- Urethra: Carries semen from the ejaculatory ducts to the external opening.
Cells/Structures That Produce Testosterone
- Leydig cells (interstitial cells): Located in the testes, primarily responsible for testosterone production. Respond to luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Test your knowledge on reproductive anatomy and functions in Chapter 26. This quiz covers the histological features of ovaries, uterine tubes, and the uterus, as well as hormone production and the layers of the uterine wall. Challenge yourself to recall important details related to the female reproductive cycle.