29 Questions
What is the periodontium composed of?
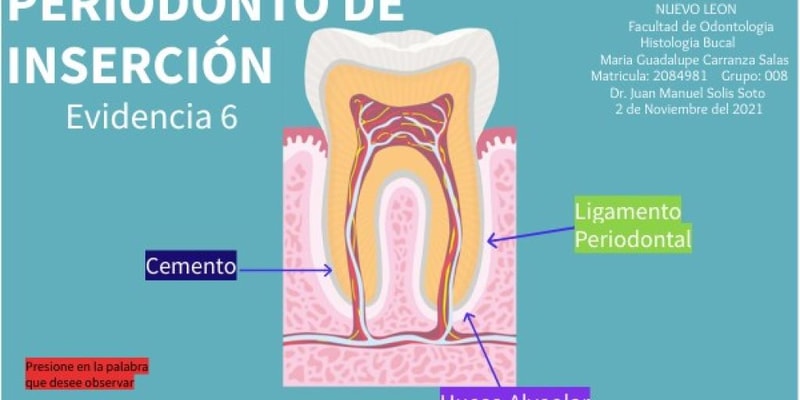
Gingiva, periodontal ligament, cementum, and alveolar bone
Which of the following is a part of the peri-implant structure?
Fixture and abutment
What is the primary objective of this content as stated in the learning objectives?
To describe relevant physiology and its application to patient management
What is the term for the process of bone formation around a titanium implant?
Osseointegration
Which General Dental Council outcomes is this content mapped to?
1.1.7, 1.2, 1.4, 1.5, 1.7
What is the function of the gingiva?
Protection
Which of the following is NOT a part of the gingiva?
Periodontal ligament
What is the thickness of the gingival epithelium?
0.2 to 0.3mm
What is the shape of the interdental gingival tissue (papilla) where teeth are relatively narrow?
Pyramidal
What is the term for the area where the gingiva meets the tooth?
Mucogingival junction
What is the type of keratinisation in the gingival epithelium?
All of the above
What percentage of collagen is found in the inner zone of the peri-implant tissue?
87%
What happens when toxins and bacterial products enter the connective tissue?
The junctional epithelium becomes inflamed
What is the purpose of hemidesmosomes?
To attach the junctional epithelium to the titanium surface
Where does the blood supply of peri-implant tissues come from?
Supra-alveolar connective tissue
What is required for a stable biological seal?
3mm supracrestal soft tissue attachment, 1mm CT, and 2mm JE
What type of fibres are present in the peri-implant tissue, which are not present in the gingiva?
Multidirectional fibres
What happens when the probe enters the junctional epithelium in unhealthy conditions?
The probe hurts and the site bleeds
What is the characteristic of the outer zone of the peri-implant tissue?
Less collagen and more cells and vessels
What is the term for the bone that makes up the alveolar ridge?
Alveolar bone
What is the implication of a weaker junctional epithelium attachment?
A weaker implant attachment is formed
What is the difference in probing depth between healthy and diseased sites?
The probe stops 0.7 mm deeper in diseased sites
What is the thickness of the inner zone of the peri-implant tissue?
50-100um
What is the primary function of Merkel cells in the stratum basale?
To act as sensory touch receptors
What is the characteristic of the crevicular epithelium?
It is non-keratinised and has a rapid turnover
How often is the junctional epithelium completely replaced?
Every 4 to 6 days
What type of cells are found in the junctional epithelium?
All cells look like basal cells
What is the function of hemidesmosomes in the junctional epithelium?
To anchor the epithelium to the enamel
What is the purpose of the free gingival groove?
To regulate the movement of cells and fluids
Learn about the anatomy and function of gingiva and peri-implant tissues in health. This quiz covers relationships between periodontal diseases and systemic health, and is mapped to General Dental Council Outcomes. Assess your knowledge of patient assessment and management.
Make Your Own Quizzes and Flashcards
Convert your notes into interactive study material.