Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is a hallmark sign of osteoporosis?
Which of the following is a hallmark sign of osteoporosis?
- Joint swelling and tenderness
- Heberden's and Bouchard's nodes
- Loss of height and kyphosis (correct)
- Morning stiffness lasting more than an hour
What is the primary pathophysiological process in osteoporosis?
What is the primary pathophysiological process in osteoporosis?
- Deposition of calcium crystals in joints
- Increased osteoblastic activity
- Imbalance where bone resorption exceeds bone formation (correct)
- Overgrowth of bone and cartilage
Which diagnostic test is considered the gold standard for osteoporosis?
Which diagnostic test is considered the gold standard for osteoporosis?
- DEXA scan (correct)
- Bone biopsy
- X-ray
- MRI
Which medication is commonly prescribed for osteoporosis to inhibit bone resorption?
Which medication is commonly prescribed for osteoporosis to inhibit bone resorption?
Which of the following is a key risk factor for osteoarthritis?
Which of the following is a key risk factor for osteoarthritis?
What is the primary pathological change in osteoarthritis?
What is the primary pathological change in osteoarthritis?
Which of the following surgical interventions is used for severe osteoarthritis?
Which of the following surgical interventions is used for severe osteoarthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis primarily affects which type of joint?
Rheumatoid arthritis primarily affects which type of joint?
Which of the following medications is a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) used in RA?
Which of the following medications is a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) used in RA?
A patient with a femur fracture suddenly develops dyspnea, petechiae, and confusion. What complication should the nurse suspect?
A patient with a femur fracture suddenly develops dyspnea, petechiae, and confusion. What complication should the nurse suspect?
What is a priority nursing intervention for a patient with a newly applied cast?
What is a priority nursing intervention for a patient with a newly applied cast?
Which of the following is a post-operative priority after a laminectomy?
Which of the following is a post-operative priority after a laminectomy?
What is the most common cause of lower limb amputations?
What is the most common cause of lower limb amputations?
Which is an appropriate intervention for preventing phantom limb pain?
Which is an appropriate intervention for preventing phantom limb pain?
Which of the following lab findings is expected in a patient with gout?
Which of the following lab findings is expected in a patient with gout?
What is the first-line pharmacologic treatment for an acute gout attack?
What is the first-line pharmacologic treatment for an acute gout attack?
Which of the following is a sign of compartment syndrome in a patient with a cast?
Which of the following is a sign of compartment syndrome in a patient with a cast?
A patient with an external fixation device should be taught to:
A patient with an external fixation device should be taught to:
The priority action when assessing a patient with a suspected hip fracture is:
The priority action when assessing a patient with a suspected hip fracture is:
The nurse should suspect a fat embolism in a patient with a long bone fracture who develops:
The nurse should suspect a fat embolism in a patient with a long bone fracture who develops:
The most important post-operative intervention after a lumbar laminectomy is:
The most important post-operative intervention after a lumbar laminectomy is:
A patient recovering from a laminectomy should be advised to:
A patient recovering from a laminectomy should be advised to:
To prevent contractures after a below-knee amputation, the nurse should instruct the patient to:
To prevent contractures after a below-knee amputation, the nurse should instruct the patient to:
A patient with an above-knee amputation reports phantom limb pain. Which intervention is most appropriate?
A patient with an above-knee amputation reports phantom limb pain. Which intervention is most appropriate?
A nurse is teaching a patient with gout about dietary changes. Which food should the patient avoid?
A nurse is teaching a patient with gout about dietary changes. Which food should the patient avoid?
The nurse understands that a patient with chronic gout is most likely to be prescribed:
The nurse understands that a patient with chronic gout is most likely to be prescribed:
What is a common symptom of acute gout?
What is a common symptom of acute gout?
A patient who had a total hip replacement should avoid:
A patient who had a total hip replacement should avoid:
The nurse knows that the first sign of osteoarthritis is typically morning stiffness lasting more than 1 hour
The nurse knows that the first sign of osteoarthritis is typically morning stiffness lasting more than 1 hour
The nurse knows that the first sign of osteoarthritis is typically symmetric joint inflammation?
The nurse knows that the first sign of osteoarthritis is typically symmetric joint inflammation?
The nurse knows that the first sign of osteoarthritis is typically:
The nurse knows that the first sign of osteoarthritis is typically:
Which intervention is most effective in reducing fall risk for an elderly patient with osteoporosis?
Which intervention is most effective in reducing fall risk for an elderly patient with osteoporosis?
What should the nurse teach a patient taking alendronate for osteoporosis?
What should the nurse teach a patient taking alendronate for osteoporosis?
Which statement by a patient with a cast indicates a need for further teaching?
Which statement by a patient with a cast indicates a need for further teaching?
A patient in skeletal traction complains of severe pain unrelieved by medication. The patient is becoming tolerant to pain medications?
A patient in skeletal traction complains of severe pain unrelieved by medication. The patient is becoming tolerant to pain medications?
A patient in skeletal traction complains of severe pain unrelieved by medication. The weights need to be increased?
A patient in skeletal traction complains of severe pain unrelieved by medication. The weights need to be increased?
A patient in skeletal traction complains of severe pain unrelieved by medication. The weights are incorrectly applied?
A patient in skeletal traction complains of severe pain unrelieved by medication. The weights are incorrectly applied?
A patient in skeletal traction complains of severe pain unrelieved by medication. What should the nurse suspect?
A patient in skeletal traction complains of severe pain unrelieved by medication. What should the nurse suspect?
A patient with an open fracture is at risk for which complication?
A patient with an open fracture is at risk for which complication?
After a spinal surgery, which assessment finding should be reported immediately?
After a spinal surgery, which assessment finding should be reported immediately?
What is the best sleeping position for a patient after lumbar laminectomy?
What is the best sleeping position for a patient after lumbar laminectomy?
What is a priority intervention in the immediate post-op period for an above-knee amputation?
What is a priority intervention in the immediate post-op period for an above-knee amputation?
Which exercise should be encouraged for a patient with a below-knee amputation?
Which exercise should be encouraged for a patient with a below-knee amputation?
What is a major lifestyle modification to prevent recurrent gout attacks?
What is a major lifestyle modification to prevent recurrent gout attacks?
Which medication is used for long-term management of gout?
Which medication is used for long-term management of gout?
What is the best non-pharmacologic intervention for an acute gout attack?
What is the best non-pharmacologic intervention for an acute gout attack?
The nurse is preparing a teaching plan for a patient with osteoarthritis. Which statement should be included?
The nurse is preparing a teaching plan for a patient with osteoarthritis. Which statement should be included?
Which vitamin is essential for calcium absorption in osteoporosis prevention?
Which vitamin is essential for calcium absorption in osteoporosis prevention?
A patient taking long-term corticosteroids is at risk for which condition?
A patient taking long-term corticosteroids is at risk for which condition?
Which of the following is a symptom of hip dislocation after total hip replacement?
Which of the following is a symptom of hip dislocation after total hip replacement?
Which activity should be avoided after a total knee replacement (TKR)?
Which activity should be avoided after a total knee replacement (TKR)?
A patient with osteoporosis asks how to prevent fractures. The nurse should recommend:
A patient with osteoporosis asks how to prevent fractures. The nurse should recommend:
What is the best way to evaluate effective pain management in a patient with osteoarthritis?
What is the best way to evaluate effective pain management in a patient with osteoarthritis?
What is the primary goal of treatment for rheumatoid arthritis?
What is the primary goal of treatment for rheumatoid arthritis?
Which intervention is best for managing stiffness in rheumatoid arthritis?
Which intervention is best for managing stiffness in rheumatoid arthritis?
Flashcards
Osteoporosis Sign
Osteoporosis Sign
Loss of height and exaggerated curvature of the thoracic spine due to vertebral fractures.
Osteoporosis Pathophysiology
Osteoporosis Pathophysiology
Bone resorption (breakdown) exceeds bone formation, decreasing bone density.
Gold Standard Osteoporosis Test
Gold Standard Osteoporosis Test
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry scan.
Alendronate
Alendronate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteoarthritis Risk Factors
Osteoarthritis Risk Factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteoarthritis Change
Osteoarthritis Change
Signup and view all the flashcards
Total Knee Replacement (TKR)
Total Knee Replacement (TKR)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Joint Affected
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Joint Affected
Signup and view all the flashcards
Methotrexate
Methotrexate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fat Embolism Syndrome
Fat Embolism Syndrome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Priority for New Cast
Priority for New Cast
Signup and view all the flashcards
Post-Laminectomy Priority
Post-Laminectomy Priority
Signup and view all the flashcards
Common Cause of Amputation
Common Cause of Amputation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mirror Therapy
Mirror Therapy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lab Finding for Gout
Lab Finding for Gout
Signup and view all the flashcards
Colchicine
Colchicine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sign of Compartment Syndrome
Sign of Compartment Syndrome
Signup and view all the flashcards
External Fixation Teaching
External Fixation Teaching
Signup and view all the flashcards
Priority Action: Hip Fracture
Priority Action: Hip Fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Suspect Fat Embolism
Suspect Fat Embolism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Post-Lumbar Laminectomy Action
Post-Lumbar Laminectomy Action
Signup and view all the flashcards
Laminectomy Advice
Laminectomy Advice
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prone After Amputation
Prone After Amputation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gabapentin
Gabapentin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gout and Foods
Gout and Foods
Signup and view all the flashcards
Allopurinol Use
Allopurinol Use
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acute Gout Symptoms
Acute Gout Symptoms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Avoid This Post THR
Avoid This Post THR
Signup and view all the flashcards
First sign of Osteoarthritis
First sign of Osteoarthritis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Exercise for Elderly
Exercise for Elderly
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Osteoporosis
- A hallmark sign is loss of height and kyphosis, resulting from vertebral compression fractures.
- The primary pathophysiological process involves an imbalance where bone resorption exceeds bone formation.
- The gold standard diagnostic test is a DEXA scan (Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry).
- Alendronate is commonly prescribed to inhibit bone resorption by slowing osteoclast activity and is a bisphosphonate.
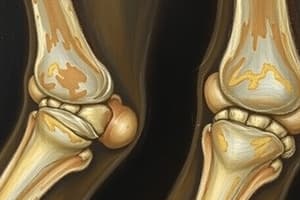
Osteoarthritis
- Key risk factors include obesity and aging.
- The primary pathological change is erosion of articular cartilage.
- Total knee replacement (TKR) and total hip replacement (THR) are common surgical treatments for severe cases.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
- Primarily affects diarthrodial (synovial) joints, leading to inflammation and deformities.
- Methotrexate is a first-line DMARD (disease-modifying antirheumatic drug) that slows RA progression by suppressing immune function.
Fractures
- Fat embolism syndrome should be suspected in a patient with a femur fracture who develops dyspnea, petechiae, and confusion, due to fat globules entering circulation and causing respiratory and neurologic symptoms.
- Elevating the extremity and assessing neurovascular status is the priority nursing intervention for a patient with a newly applied cast to reduce swelling and prevent complications like compartment syndrome.
- Use sterile technique for pin care and monitor for signs of infection, sterile cleaning with prescribed solutions should be done regularly, for patients with an external fixation device.
Hip Fracture
- Checking neurovascular status is the priority action when assessing a patient with a suspected hip fracture to prevent complications of neurovascular compromise.
Fat Embolism
- Dyspnea, petechiae, and confusion are symptoms that may indicate a fat embolism in a patient with a long bone fracture.
Back Problems and Laminectomy
- Post-operative priorities after a laminectomy include monitoring for urinary retention and CSF leakage (clear fluid at the incision site) as these require immediate intervention.
- CSF leakage and neurological deficits require immediate intervention after lumbar laminectomy.
- Post-laminectomy patients are advised to avoid bending, twisting, or heavy lifting, as these movements increase pressure on the spine and inhibit healing.
- Side-lying with a pillow between the knees is the best sleeping position after a lumbar laminectomy as it maintains spinal alignment and reduces strain.
- Inability to move toes after spinal surgery should be reported immediately, as it may indicate spinal cord compression or nerve damage.
Amputations
- Peripheral vascular disease (PVD), often caused by diabetes, is the most common cause of non-traumatic lower limb amputations.
- Mirror therapy helps reduce phantom limb pain by providing visual feedback.
- Patients should lie prone several times a day to prevent hip flexor contractures after a below-knee amputation.
- Gabapentin is commonly used for neuropathic pain, including phantom limb pain in patients with above-knee amputation.
- Monitor for excessive bleeding, the most immediate risk after amputation for a above-knee amputation.
- Strengthening the upper body helps with mobility and the use of assertive devices after a below-knee amputation.
Gout
- Elevated uric acid levels are expected in a patient with gout due to hyperuricemia, leading to crystal deposits in joints.
- Colchicine reduces inflammation in acute gout attacks, while allopurinol is used for prevention.
- Organ meats, high in purines, should be avoided in the diet, as they elevate uric acid levels and worsen gout.
- Allopurinol reduces uric acid production and is likely to be prescribed to patients with chronic gout.
- A common symptom of acute gout is severe joint pain in the big toe.
- Reduce alcohol consumption as a major lifestyle modification to prevent recurrent gout attacks, because alcohol increases uric acid levels.
- Allopurinol prevents uric acid buildup and is used for chronic gout management.
- Immobilizing and elevating the joint is the best non-pharmacologic intervention for a acute gout attack.
General Mobility-Related Questions
- Crossing legs increases the risk of hip dislocation post-THR (total hip replacement) and should be avoided.
- Sudden pain and shortening of the affected leg is a symptom of hip dislocation after total hip replacement.
- Osteoarthritis pain increases with joint use and improves with rest.
- Weight-bearing exercise helps maintain bone density and reduces fall risk for elderly patients with osteoporosis.
- A patient taking alendronate for osteoporosis should remain upright for 30 minutes after taking it to prevent esophageal irritation.
- Compartment syndrome should be suspected in a patient in skeletal traction complaining of severe pain unrelieved by medication.
- Osteomyelitis is a risk for patients with open fractures due to exposure to bacteria.
- "I can insert a small object to scratch inside the cast if it itches" indicates a need for further teaching the patient.
- The first sign of osteoarthritis is typically pain that worsens with activity.
- Regular weight-bearing exercise can help maintain joint function in patients with osteoarthritis.
- Assessing pain levels before and after intervention is the best way to evaluate effective pain management in a patient with osteoarthritis.
- Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium and is essential for bone health.
- Patients taking long-term corticosteroids are at risk for osteoporosis.
- Crossing legs should be avoided after a total knee replacement (TKR), as it can cause knee dislocation.
- Daily weight-bearing exercise stimulates bone formation, and reduces fracture risk.
- The primary goal of treatment for rheumatoid arthritis is to prevent joint destruction and maintain function.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic condition with no cure, so treatment focuses on slowing progression and preserving function.
- Applying warm compresses and gentle exercises is best for managing stiffness in rheumatoid arthritis, movement and heat therapy improve circulation and reduce stiffness.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Explore osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and fractures. Osteoporosis involves bone resorption, diagnosed by DEXA scans, and treated with medications like alendronate. Osteoarthritis relates to cartilage erosion, while rheumatoid arthritis affects synovial joints and is treated with methotrexate.