Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) in urine production?
What is the primary function of the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) in urine production?
- To filter blood components
- To rid the blood of additional wastes (correct)
- To conserve water and electrolytes
- To reabsorb large proteins
Which component is NOT part of the filtration membrane in the kidneys?
Which component is NOT part of the filtration membrane in the kidneys?
- Proximal convoluted tubule (correct)
- Visceral layer of the Bowman capsule
- Basement membrane
- Fenestrated glomerular capillaries
What drives the process of filtration in the kidneys?
What drives the process of filtration in the kidneys?
- Osmotic pressure
- Active transport mechanisms
- Renal plasma flow rate
- Blood pressure (correct)
Which of the following best describes tubular reabsorption?
Which of the following best describes tubular reabsorption?
How is the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) calculated?
How is the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) calculated?
What impact does kidney function have on blood pressure regulation?
What impact does kidney function have on blood pressure regulation?
Which component of the nephron is responsible for filtering blood?
Which component of the nephron is responsible for filtering blood?
How do kidneys contribute to the regulation of blood solute concentrations?
How do kidneys contribute to the regulation of blood solute concentrations?
What is the function of erythropoietin (EPO) secreted by the kidneys?
What is the function of erythropoietin (EPO) secreted by the kidneys?
What role do the kidneys play in regulating vitamin D synthesis?
What role do the kidneys play in regulating vitamin D synthesis?
What is one of the primary functions of the urinary system related to body fluids?
What is one of the primary functions of the urinary system related to body fluids?
Which part of the urinary system is responsible for transporting urine from the kidneys to the bladder?
Which part of the urinary system is responsible for transporting urine from the kidneys to the bladder?
How does the urinary system contribute to blood pressure regulation?
How does the urinary system contribute to blood pressure regulation?
In what way does the urinary system affect red blood cell synthesis?
In what way does the urinary system affect red blood cell synthesis?
What is the primary waste product formed from blood filtration in the kidneys?
What is the primary waste product formed from blood filtration in the kidneys?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the urinary system?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the urinary system?
What anatomical structures are primarily involved in urine storage before elimination?
What anatomical structures are primarily involved in urine storage before elimination?
What role does the urinary system play in maintaining acid-base balance in the body?
What role does the urinary system play in maintaining acid-base balance in the body?
What triggers the activation of the micturition reflex?
What triggers the activation of the micturition reflex?
Which of the following factors contributes to the urinary bladder's capacity to distend?
Which of the following factors contributes to the urinary bladder's capacity to distend?
During micturition, what happens to the external urethral sphincter?
During micturition, what happens to the external urethral sphincter?
What type of epithelium is present in the urinary bladder?
What type of epithelium is present in the urinary bladder?
What is the maximum volume the urinary bladder can hold before discomfort begins?
What is the maximum volume the urinary bladder can hold before discomfort begins?
What size and molecular mass of molecules are prevented from passing through the components of the Bowman capsule?
What size and molecular mass of molecules are prevented from passing through the components of the Bowman capsule?
What is the primary site of reabsorption for most solutes in the nephron?
What is the primary site of reabsorption for most solutes in the nephron?
What effect does Anti-Diuretic Hormone (ADH) have on the reabsorption process in the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct?
What effect does Anti-Diuretic Hormone (ADH) have on the reabsorption process in the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct?
Which segment of the Loop of Henle is primarily permeable to water?
Which segment of the Loop of Henle is primarily permeable to water?
What is the main function of tubular secretion in the nephron?
What is the main function of tubular secretion in the nephron?
Which statement about osmosis is accurate in the context of tubular reabsorption?
Which statement about osmosis is accurate in the context of tubular reabsorption?
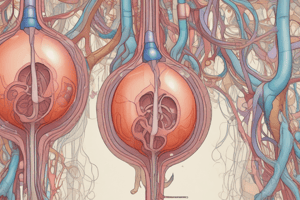
What role do podocytes play in the filtration process of the Bowman capsule?
What role do podocytes play in the filtration process of the Bowman capsule?
In which part of the nephron are K+ and H+ ions primarily reabsorbed under hormonal control?
In which part of the nephron are K+ and H+ ions primarily reabsorbed under hormonal control?
Flashcards
Kidney function: Blood filtering
Kidney function: Blood filtering
Kidneys filter waste products from blood, separating large molecules, leaving smaller molecules and ions in the filtered fluid.
Kidney function: Blood volume regulation
Kidney function: Blood volume regulation
Kidney production of urine regulates blood volume and blood pressure. High volume = dilute urine. Low volume = concentrated urine.
Kidney role in vitamin D
Kidney role in vitamin D
Kidneys are crucial for regulating vitamin D and calcium levels in the blood.
Nephron: Functional unit
Nephron: Functional unit
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal corpuscle
Renal corpuscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urinary System Function
Urinary System Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Function
Kidney Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urinary System Components
Urinary System Components
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urine Formation
Urine Formation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urinary System Regulation
Urinary System Regulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urinary Diagnostics
Urinary Diagnostics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urinary System Diseases
Urinary System Diseases
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urinary System Physiology
Urinary System Physiology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glomerular Filtration
Glomerular Filtration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Filtration Membrane
Filtration Membrane
Signup and view all the flashcards
GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate)
GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tubular Reabsorption
Tubular Reabsorption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Micturition Reflex
Micturition Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urinary Bladder Capacity
Urinary Bladder Capacity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Transitional Epithelium
Transitional Epithelium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Detrusor Muscle
Detrusor Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
External Urethral Sphincter
External Urethral Sphincter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Podocytes
Podocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Filtration
Filtration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osmosis
Osmosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Loop of Henle
Loop of Henle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tubular Secretion
Tubular Secretion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Prayer Before Class
- The prayer is directed to the Holy Spirit, the source of light and wisdom.
- It asks for the dissipation of darkness (sin and ignorance).
- It requests a penetrating mind, retentive memory, method, and ease of learning.
- Guidance is sought for work progress, and completion.
- The prayer concludes with a request through Jesus Christ, a plea for divine help, and a concluding phrase.
Anatomy and Physiology with Pathophysiology: Unit 13 - The Urinary System
- The module is part of a course in Anatomy and Physiology with Pathophysiology at UST General Santos.
- It covers Unit 13: The Urinary System.
Course Content
- Urinary System Physiology
- Urine formation and characteristics
- Diseases relevant to the Philippines
- Urinary disorders relevant to medical technologists
- Diagnostic tests relevant to medical technologists
Unit Intended Learning Outcomes
- Explain the urinary system in its normal state and pathophysiologic state.
- Discuss the physiological tests and procedures.
- Apply knowledge to actual health situations.
Formative Assessment: Guess the word (Multiple assessments)
- Somioso
- Rutbalu
- Barptoeinor
- Yiksden
- Umrlugolse
Overview of the Urinary System
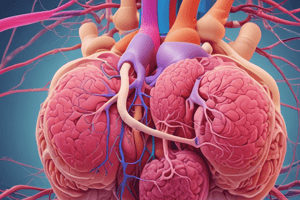
- The urinary system involves two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra.
- The diagram provides a visual representation of these organs.
Each kidney filters a large volume of blood
- Kidneys filter a large volume of blood.
- Wastes are collected and form urine.
- An anatomical illustration of the kidney is presented.
Urine Characteristics
- Urine typically consists of approximately 95% water.
- Key components such as urea, chloride, sodium, and potassium are also present in urine, along with peptides, proteins, and other inorganic substances.
Functions of the Urinary System
- Excretion: removes waste products from the blood.
- Regulates blood volume and pressure.
- Regulates blood solute concentrations.
- Regulates extracellular fluid pH.
- Regulates red blood cell synthesis (EPO).
- Regulates vitamin D synthesis.
Urinary System Function: Excretion
- Kidneys filter waste products from the blood.
- Fluid and waste are captured and transported through tubes throughout the kidney.
- Large molecules remain in the blood, while smaller molecules and ions are filtered.
- Blood is transformed into urine.
Urinary System Function: Regulation of Blood Volume and Pressure
- Hydration status determines urine production.
- Large volume → dilute urine.
- Small volume → concentrated urine.
- Urine is a mechanism to regulate blood pressure.
Urinary System Function: Regulation of Blood Solute Concentrations
- Kidneys regulate major ions in the blood's concentration.
- A diagram illustrating solute concentration regulation within the kidney is presented.
Urinary System Function: Regulation of Extracellular Fluid pH
- Kidneys secrete variable amounts of H+ to regulate extracellular fluid pH.
- This process helps maintain a balanced pH level.
Urinary System Function: Regulation of Red Blood Cell Synthesis
- EPO (erythropoietin) promotes RBC synthesis in the red bone marrow.
- This process addresses anemia conditions.
Urinary System Function: Regulation of Vitamin D Synthesis
- Kidneys control calcium levels indirectly by regulating vitamin D synthesis.
- UV radiation on the skin facilitates vitamin D production.
Renal Cortex
- The outer region of the kidney.
- Location of blood filtration structures.
Renal Medulla
- The inner region of the kidney
- Cone-shaped pyramids, tubes, and ducts are part of the medulla, functioning in fluid transport.
- Urine modification takes place here.
Nephron
- Functional unit of the kidney.
- 1.3 Million nephrons.
- Distributed throughout the cortex and medulla.
Nephron Structures
- Renal corpuscle (glomerulus & Bowman's capsule)
- Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
- Loop of Henle
- Distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
Renal Corpuscle
- Filters blood.
- Returns filtered substances to the blood.
- Helps conserve water and solutes.
- Rid the blood of wastes.
Urine Production
- Glomerular filtration.
- Tubular reabsorption.
- Tubular secretion.
- Kidney sorts substances from the blood for either removal in the urine or return to the blood.
Filtration
- Blood pressure forces fluid and small molecules out of the blood.
- Filtered fluid is known as filtrate.
- First step in urine production, where most substances except blood cells and proteins are filtered.
- Filtration is indicated by the percentage of blood sent across the kidneys.
Filtration Membrane
- Fenestrated glomerular capillaries
- Basement membrane (visceral and parietal layers of Bowman's capsule)
- Podocytes of the visceral layer of Bowman's capsule
- Prevents larger molecules from passing through.
Filtration Diagram and Pressures
- Diagrammatic representation of glomerular capillary and capsular hydrostatic pressures and blood colloid osmotic pressure.
- Filtration pressure is calculated as the difference between capillary and osmotic pressures.
Tubular Reabsorption
- Movement of water and solutes from filtrate to blood.
- Osmosis is essential in movement towards solutions with higher solute concentration.
- Critical for preventing dehydration.
Tubular Reabsorption: PCT
- Majority of reabsorption occurs in the PCT
- Solutes and water are actively transported into the interstitial fluid and then into peritubular capillaries.
Tubular Reabsorption: Loop of Henle
- Descending limb: permeable to water.
- Ascending limb: impermeable to water and solutes.
Tubular Reabsorption: DCT & Collecting Duct
- K+ and H+ reabsorbed.
- Reabsorption is hormonally controlled (ADH).
- ADH increases water reabsorption; without ADH, water is not reabsorbed.
Tubular Secretion
- Reabsorption in reverse.
- Movement of non-filtered substances from the blood.
Tubular Secretion: Hydrogen Ions
- Hydrogen ions are secreted to maintain blood pH.
Checkpoint
- Organs of the urinary system.
- Functions of the urinary system.
- Steps in urine formation.
Urine Movement
- Urine flow pathway.
- Micturition reflex mechanism.
Micturition Reflex
- Bladder stretches when filled triggering reflex.
- Walls of the bladder contain folds for expansion.
- Transitional epithelium accommodates large volumes.
- Smooth muscle contraction leads to urination.
References
- VanPutte and Seeley (2020). Seeley's Anatomy & Physiology (12th ed.). McGraw-Hill
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
This quiz tests your knowledge on Unit 13 of the Anatomy and Physiology course focused on the Urinary System. You will explore urinary system physiology, urine formation, and pathophysiological conditions as they relate to medical technologists, with a special emphasis on diseases in the Philippines.