Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the first step in the process of urine formation in the kidneys?
What is the first step in the process of urine formation in the kidneys?
- Tubular reabsorption
- Ureteral transport
- Glomerular filtration (correct)
- Tubular secretion
Which of the following substances can be excreted during tubular secretion in the kidneys?
Which of the following substances can be excreted during tubular secretion in the kidneys?
- Glucose
- Hydrogen ions (correct)
- Oxygen
- Carbon dioxide
What is the main function of ureters in the urinary system?
What is the main function of ureters in the urinary system?
- Producing urine
- Reabsorbing electrolytes
- Filtering blood
- Transporting urine to the bladder (correct)
Where does urine formation primarily take place in the kidney?
Where does urine formation primarily take place in the kidney?
What is the functional unit of the kidney responsible for urine formation?
What is the functional unit of the kidney responsible for urine formation?
Which step in urine formation involves reabsorbing some water and electrolytes based on the body's needs?
Which step in urine formation involves reabsorbing some water and electrolytes based on the body's needs?
What is the role of the kidneys in the regulation of blood pH?
What is the role of the kidneys in the regulation of blood pH?
Which hormone helps regulate the amount of water and electrolytes in the body?
Which hormone helps regulate the amount of water and electrolytes in the body?
How is renal blood flow important for kidney function?
How is renal blood flow important for kidney function?
Which factor can regulate renal blood flow by increasing it?
Which factor can regulate renal blood flow by increasing it?
What does renal physiology involve?
What does renal physiology involve?
Which process is crucial for the maintenance of fluid and electrolyte balance within living organisms?
Which process is crucial for the maintenance of fluid and electrolyte balance within living organisms?
What percentage of the human body typically consists of intracellular fluid?
What percentage of the human body typically consists of intracellular fluid?
What is the primary component of extracellular fluid?
What is the primary component of extracellular fluid?
In osmosis, the movement of solvent molecules occurs from the region of __________ solute concentration to the region of __________ solute concentration.
In osmosis, the movement of solvent molecules occurs from the region of __________ solute concentration to the region of __________ solute concentration.
Which system plays a vital role in the reabsorption and excretion of fluids to maintain fluid homeostasis in the body's compartments?
Which system plays a vital role in the reabsorption and excretion of fluids to maintain fluid homeostasis in the body's compartments?
What is the term for the process by which two solutions with different solute concentrations are separated by a selectively permeable membrane?
What is the term for the process by which two solutions with different solute concentrations are separated by a selectively permeable membrane?
What is the term used to describe the net flow of solvent through a semipermeable membrane due to a solute concentration difference?
What is the term used to describe the net flow of solvent through a semipermeable membrane due to a solute concentration difference?
How is osmotic pressure defined in relation to solvent movement across a semipermeable membrane?
How is osmotic pressure defined in relation to solvent movement across a semipermeable membrane?
What unit is used to express osmotic pressure, representing the number of particles in a solution?
What unit is used to express osmotic pressure, representing the number of particles in a solution?
In the context of fluid movement under pressure during exercise, what effect does vasodilation have on blood flow to skeletal muscles?
In the context of fluid movement under pressure during exercise, what effect does vasodilation have on blood flow to skeletal muscles?
Which type of fluids are generally preferred over hypertonic fluids in certain scenarios for critically ill patients?
Which type of fluids are generally preferred over hypertonic fluids in certain scenarios for critically ill patients?
How do loop diuretics function in the treatment of edema?
How do loop diuretics function in the treatment of edema?
What is the primary driving force behind the movement of water in osmosis?
What is the primary driving force behind the movement of water in osmosis?
Which electrolyte is mainly responsible for maintaining the extracellular fluid volume and regulating cell membrane potential?
Which electrolyte is mainly responsible for maintaining the extracellular fluid volume and regulating cell membrane potential?
What is the consequence of hypernatremia in the body?
What is the consequence of hypernatremia in the body?
In which condition are serum potassium levels greater than the normal range?
In which condition are serum potassium levels greater than the normal range?
What is the role of passive transport in moving fluids or solutes across a semipermeable membrane?
What is the role of passive transport in moving fluids or solutes across a semipermeable membrane?
What are some common symptoms associated with hyponatremia?
What are some common symptoms associated with hyponatremia?
Under what circumstances does hydrostatic pressure push fluids and solutes through a permeable membrane?
Under what circumstances does hydrostatic pressure push fluids and solutes through a permeable membrane?
In the context of the human body, where does hydrostatic pressure play a significant role in moving fluids?
In the context of the human body, where does hydrostatic pressure play a significant role in moving fluids?
What is the primary mechanism responsible for the movement of fluids and solutes out of capillaries into the interstitial compartment?
What is the primary mechanism responsible for the movement of fluids and solutes out of capillaries into the interstitial compartment?
What happens to hydrostatic pressure at the venous end of capillaries in the context of fluid movement?
What happens to hydrostatic pressure at the venous end of capillaries in the context of fluid movement?
Which factor opposes hydrostatic pressure at the arterial end of capillaries in the movement of fluids and solutes?
Which factor opposes hydrostatic pressure at the arterial end of capillaries in the movement of fluids and solutes?
In the context of fluid and electrolyte movement, what is the role of hydrostatic pressure in the kidneys?
In the context of fluid and electrolyte movement, what is the role of hydrostatic pressure in the kidneys?
What is the primary function of hydrostatic pressure in maintaining electrolyte balance within living organisms?
What is the primary function of hydrostatic pressure in maintaining electrolyte balance within living organisms?
What is the primary purpose of a buffer system in chemistry?
What is the primary purpose of a buffer system in chemistry?
In the carbonic acid/bicarbonate buffer system, what role does the bicarbonate ion play?
In the carbonic acid/bicarbonate buffer system, what role does the bicarbonate ion play?
What is the key component of the phosphate buffer system in chemistry?
What is the key component of the phosphate buffer system in chemistry?
How do proteins act as buffer systems in biological systems?
How do proteins act as buffer systems in biological systems?
What happens when an acid is added to a buffer solution?
What happens when an acid is added to a buffer solution?
Which pair forms the conjugate pair in the carbonic acid/bicarbonate buffer system?
Which pair forms the conjugate pair in the carbonic acid/bicarbonate buffer system?
How do buffer systems assist in maintaining a narrow pH range?
How do buffer systems assist in maintaining a narrow pH range?
What is the main function of proteins in the protein buffer system?
What is the main function of proteins in the protein buffer system?
When a base is added to a buffer solution, what is the result?
When a base is added to a buffer solution, what is the result?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Urinary System Physiology
The urinary system is responsible for regulating the balance of fluids and electrolytes in the body through the process of urine formation, kidney function, and urinary system regulation.
Urine Formation
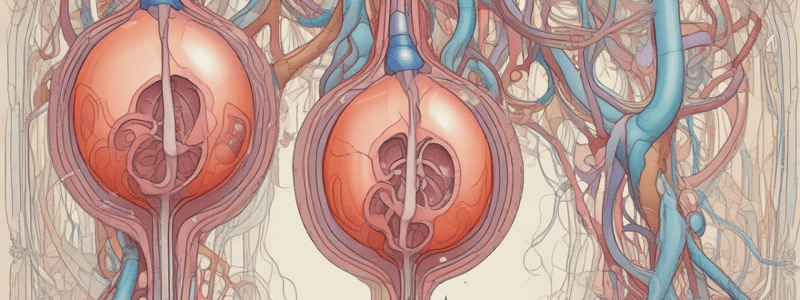
Urine formation occurs when water and waste products are filtered from the blood by the kidneys. The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs located near the lower back. Each kidney is about the size of a fist and weighs about 150 grams. The kidneys are connected to the bladder by two narrow tubes called ureters.
Inside the kidneys, the blood circulates through tiny blood vessels called glomeruli. The glomeruli have tiny pores that allow water, electrolytes, and waste products to pass into the tubules of the nephron, the functional unit of the kidney.
The process of urine formation involves the following steps:
- Glomerular filtration: Blood flows into the kidney where the glomeruli filter water, electrolytes, and waste products from the blood into the tubules of the nephron.
- Tubular reabsorption: The tubules reabsorb some of the water and electrolytes. The amount of water and electrolytes reabsorbed depends on the body's need.
- Tubular secretion: The tubules can also excrete waste products, such as hydrogen ions and certain medications.
- Ureteral transport: Urine forms in the pelvis of the kidney and flows into the ureters, which transport it to the bladder.
Kidney Function
The kidneys perform several essential functions:
- Urine formation: The kidneys filter waste and excess water from the blood, which is then excreted as urine.
- Regulation of blood pH: The kidneys regulate the acid-base balance of the body by excreting acidic or alkaline waste products.
- Regulation of electrolyte balance: The kidneys help maintain the balance of electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and calcium, in the body.
- Regulation of blood pressure: The kidneys produce a hormone called renin, which helps regulate blood pressure.
Urinary System Regulation
The urinary system is regulated by several factors:
- Hormones: Hormones such as antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and aldosterone help regulate the amount of water and electrolytes in the body.
- Renal blood flow: The kidneys receive about 25% of the total blood flow in the body. Renal blood flow is regulated by the sympathetic nervous system and hormones such as ADH and angiotensin II.
- Osmoregulation: The body maintains a balance of water and electrolytes in the body through a process called osmoregulation.
Renal Blood Flow
Renal blood flow is important for kidney function. The blood flow delivers oxygen and nutrients to the kidneys and carries waste products away for excretion. Renal blood flow can be regulated by:
- Sympathetic nervous system: The sympathetic nervous system can increase renal blood flow.
- Renin: Renin is a hormone that can increase renal blood flow.
- Antidiuretic hormone (ADH): ADH can increase renal blood flow.
- Angiotensin II: Angiotensin II can increase renal blood flow.
Renal Physiology
Understanding the physiology of the kidney is crucial for maintaining health. Renal physiology involves the study of the structure and function of the kidney and its role in maintaining the balance of fluids and electrolytes in the body. Renal physiology can help in the diagnosis and treatment of kidney-related conditions.
In summary, the urinary system plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of fluids and electrolytes in the body. Urine formation is a complex process that involves the filtration and reabsorption of water and electrolytes. The kidneys perform essential functions, such as regulating blood pH and electrolyte balance. The urinary system is regulated by various factors, including hormones and renal blood flow. Understanding renal physiology is essential for maintaining kidney health and treating kidney-related conditions.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.