Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which structure is affected in carpal tunnel syndrome?
Which structure is affected in carpal tunnel syndrome?
- Carpal bones (correct)
- Scapula
- Humerus
- Ulna
What bone articulates with the head of the femur, forming the hip joint?
What bone articulates with the head of the femur, forming the hip joint?
- Ilium (correct)
- Ischium
- Ulna
- Pubis
Which structure marks the level of the fourth lumbar vertebral body (L4)?
Which structure marks the level of the fourth lumbar vertebral body (L4)?
- Sacrum
- Acetabulum
- Symphysis pubis
- Ischial spine (correct)
In which part of the pelvic girdle do we find red bone marrow used in bone marrow transplantation?
In which part of the pelvic girdle do we find red bone marrow used in bone marrow transplantation?
The plane of obstetric outlet passes from the lower border of the symphysis pubis anteriorly to which structure posteriorly?
The plane of obstetric outlet passes from the lower border of the symphysis pubis anteriorly to which structure posteriorly?
Which joint is formed by the articulation of the humerus with the ulna and radius?
Which joint is formed by the articulation of the humerus with the ulna and radius?
Where is the triangular articular disc located in relation to the carpal bones?
Where is the triangular articular disc located in relation to the carpal bones?
The hip bone is formed by the fusion of which three bones?
The hip bone is formed by the fusion of which three bones?
Which structure forms a socket for articulation with the head of the femur?
Which structure forms a socket for articulation with the head of the femur?
The iliac crest is used for which medical procedure due to its large amount of red bone marrow?
The iliac crest is used for which medical procedure due to its large amount of red bone marrow?
Study Notes
Gateways to the Lower Limb
- There are four major routes by which structures pass from the abdomen and pelvis into and out of the lower limb.
- The greater sciatic foramen is a posterior gate for the passage of the sciatic nerve.
- The inguinal gate is an anterior gate for the passage of the femoral vein, artery, and nerve.
Muscles of the Pelvic Girdle
- The gluteus maximus muscle originates from the ilium and sacrum, and inserts into the gluteal tuberosity of the femur.
- It is innervated by the gluteal nerve and acts to externally rotate the lower limb.
Muscles of the Thigh
- The quadriceps femoris muscle has four separate heads: rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius, and vastus medialis.
- It originates mainly from the femur and inserts into the tibial tuberosity.
- It is innervated by the femoral nerve and acts to extend the knee.
Muscles of the Posterior Compartment of the Thigh
- The hamstring muscles consist of three muscles: biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus.
- They have a common origin from the ischial tuberosity and insert into the upper end of the fibula and tibia.
- They are innervated by the sciatic nerve and act to flex the knee.
Muscles of the Anterior Compartment of the Leg
- The tibialis anterior muscle originates from the tibia and inserts into the first metatarsal bones of the foot.
- It is innervated by a branch of the sciatic nerve and acts to dorsiflex the foot.
Muscles of the Posterior Compartment of the Leg
- The gastrocnemius muscle originates from the femur and inserts into the calcaneus via the tendo calcaneus (Achilles tendon).
- It is innervated by a branch of the sciatic nerve and acts to plantar flex the foot.
- The soleus muscle originates from the fibula and tibia and inserts into the calcaneus via the tendo calcaneus (Achilles tendon).
- It is innervated by a branch of the sciatic nerve and acts to plantar flex the foot.
Muscles of the Anterior Abdominal Wall
- The muscles of the anterior abdominal wall consist of four muscles on each side: external oblique, internal oblique, transverse abdominal, and rectus abdominis.
- They originate from the side of the abdomen and insert into the linea alba in the midline.
- The rectus abdominis muscle is surrounded by the rectus sheath formed by the aponeurosis of the other three muscles.
Inguinal Ligament
- The inguinal ligament is formed by the lower boundary of the external abdominal oblique aponeurosis.
Nerve Plexuses
- The brachial plexus originates from C5-8 and T1, and mainly supplies the upper limb.
- The lumbosacral plexus originates from L1-5, S1-5, and Coc.1, and mainly supplies the lower limb.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Carpal tunnel syndrome results from increased pressure inside the tunnel compressing structures affecting the median nerve.
Joints of the Upper Limb
- The shoulder joint is an articulation of the humerus head with the glenoid cavity of the scapula.
- The elbow joint is an articulation of the humerus with the ulna and radius.
- The wrist joint is an articulation of the radius and triangular articular disc with the carpal bones.
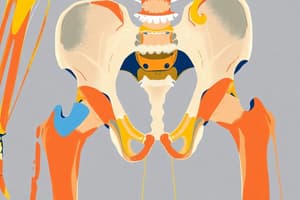
Pelvic Girdle
- The pelvic girdle consists of one bone on each side, called the hip bone.
- It forms the pelvic cavity with the sacrum posteriorly.
- The acetabulum is a socket for articulation with the head of the femur, forming the hip joint.
Iliac Crest and Ischial Spine
- The iliac crest has a large amount of red bone marrow, and is used in bone marrow transplantation.
- The top of the iliac crests marks the level of the fourth lumbar vertebral body (L4).
- The ischial spine is a landmark for the plane of the obstetric outlet (plane of least pelvic dimensions).
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Explore the major routes for structures passing between the abdomen, pelvis, and lower limb including the greater sciatic foramen and inguinal gate. Learn about the muscles of the pelvic girdle such as the Gluteus maximus muscle with origins, insertions, and nerve supply. Prepared by Dr. Hussam Hussein.