Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the two main functional components of the lower limb skeleton?
What are the two main functional components of the lower limb skeleton?
- Axial skeleton and pelvic girdle
- Appendicular skeleton and free lower limbs (correct)
- Pelvic girdle and thoracic cage
- Appendicular skeleton and pelvic girdle (correct)
What role does the pelvic girdle serve in the lower limb structure?
What role does the pelvic girdle serve in the lower limb structure?
- To serve as a weight-bearing structure
- To attach the free lower limb to the axial skeleton (correct)
- To provide protection for the lower organs
- To increase mobility of the leg
How is the pelvic girdle described in relation to the lower limbs?
How is the pelvic girdle described in relation to the lower limbs?
- It connects the free lower limb to the thoracic skeleton
- It is more mobile than the axial skeleton
- It is a bone structure primarily for support (correct)
- It does not contribute to the movement of the lower limb
Which of the following best describes the relationship between the pelvic girdle and the free lower limbs?
Which of the following best describes the relationship between the pelvic girdle and the free lower limbs?
What is a component of the lower limb skeleton not explicitly stated in the content provided?
What is a component of the lower limb skeleton not explicitly stated in the content provided?
What happens to the iliofemoral ligament during abduction?
What happens to the iliofemoral ligament during abduction?
Which muscle is NOT part of the anterior thigh muscles responsible for hip flexion?
Which muscle is NOT part of the anterior thigh muscles responsible for hip flexion?
Which ligament is stretched during adduction?
Which ligament is stretched during adduction?
What is the primary action of the pectineus muscle?
What is the primary action of the pectineus muscle?
What is the joint action occurring when the pubofemoral ligament is tightened?
What is the joint action occurring when the pubofemoral ligament is tightened?
What is the primary function of the greater trochanter of the femur?
What is the primary function of the greater trochanter of the femur?
What does the lesser trochanter primarily serve as an insertion point for?
What does the lesser trochanter primarily serve as an insertion point for?
What is the primary action of the iliopsoas muscle group?
What is the primary action of the iliopsoas muscle group?
What angle is formed between the femoral neck and femoral shaft in adults?
What angle is formed between the femoral neck and femoral shaft in adults?
Which structure contributes minimally to the mechanical stability of the femoral head in young individuals?
Which structure contributes minimally to the mechanical stability of the femoral head in young individuals?
Which structure connects the iliacus to the psoas major?
Which structure connects the iliacus to the psoas major?
Which muscle is responsible for lateral rotation and flexion of the thigh at the hip joint?
Which muscle is responsible for lateral rotation and flexion of the thigh at the hip joint?
What is the role of the ligamentum teres related to vascular supply?
What is the role of the ligamentum teres related to vascular supply?
From which vertebrae does the psoas major originate?
From which vertebrae does the psoas major originate?
In which position is the axis of the femoral neck oriented?
In which position is the axis of the femoral neck oriented?
What happens to the angle of the femoral neck with age and weight bearing?
What happens to the angle of the femoral neck with age and weight bearing?
What action does the psoas minor primarily stabilize?
What action does the psoas minor primarily stabilize?
What does the intertrochanteric line indicate?
What does the intertrochanteric line indicate?
Which muscle assists in stabilizing the hip during movement?
Which muscle assists in stabilizing the hip during movement?
What is the anatomical term for the hip joint?
What is the anatomical term for the hip joint?
What is the insertion point of the sartorius muscle?
What is the insertion point of the sartorius muscle?
Which of the following muscles is NOT a part of the iliopsoas group?
Which of the following muscles is NOT a part of the iliopsoas group?
How does the acetabulum contribute to hip stability?
How does the acetabulum contribute to hip stability?
What is a common consequence if the vascularization from the ligamentum teres is disrupted?
What is a common consequence if the vascularization from the ligamentum teres is disrupted?
What type of rotation does the iliacus assist with?
What type of rotation does the iliacus assist with?
What is the role of the iliopsoas muscle group during trunk movements?
What is the role of the iliopsoas muscle group during trunk movements?
What type of muscles attach to the greater trochanter?
What type of muscles attach to the greater trochanter?
What anatomical structure does the ligamentum teres originate from?
What anatomical structure does the ligamentum teres originate from?
Which muscle is primarily responsible for extending the hip joint from a flexed position?
Which muscle is primarily responsible for extending the hip joint from a flexed position?
What is the primary action of the gluteus medius muscle?
What is the primary action of the gluteus medius muscle?
From where does the tensor of fascia lata originate?
From where does the tensor of fascia lata originate?
What is the insertion point for most fibers of the gluteus maximus?
What is the insertion point for most fibers of the gluteus maximus?
Which muscle's primary role is to stabilize the pelvis during weight-bearing on the ipsilateral limb?
Which muscle's primary role is to stabilize the pelvis during weight-bearing on the ipsilateral limb?
Which muscle is a deep layer muscle of the gluteal region and is responsible for external rotation of the hip?
Which muscle is a deep layer muscle of the gluteal region and is responsible for external rotation of the hip?
What is the primary role of the gluteus minimus?
What is the primary role of the gluteus minimus?
Which of the following muscles assists in lateral rotation of the hip joint?
Which of the following muscles assists in lateral rotation of the hip joint?
Which muscle group includes piriformis and quadratus femoris?
Which muscle group includes piriformis and quadratus femoris?
What action does the tensor of fascia lata perform at the hip joint?
What action does the tensor of fascia lata perform at the hip joint?
What is the primary function of the lateral rotators in the deep layer of the gluteal region?
What is the primary function of the lateral rotators in the deep layer of the gluteal region?
Which muscle originates from the anterior surface of the sacrum?
Which muscle originates from the anterior surface of the sacrum?
Which muscle acts as both a lateral rotator and an abductor of the hip joint?
Which muscle acts as both a lateral rotator and an abductor of the hip joint?
What is the insertion point for the obturator internus muscle?
What is the insertion point for the obturator internus muscle?
Which two muscles originate from the ischial tuberosity?
Which two muscles originate from the ischial tuberosity?
How do the deep layer muscles of the gluteal region contribute to hip joint function?
How do the deep layer muscles of the gluteal region contribute to hip joint function?
Which muscle's primary attachment is to the ischial spine?
Which muscle's primary attachment is to the ischial spine?
What is the role of the quadratus femoris muscle in relation to the hip joint?
What is the role of the quadratus femoris muscle in relation to the hip joint?
Flashcards
Lower limb skeleton components
Lower limb skeleton components
The lower limb's skeleton is divided into the axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton, connected via the pelvic girdle.
Pelvic girdle connection
Pelvic girdle connection
The pelvic girdle links the axial skeleton to the free lower limbs.
Pelvic Girdle Structure
Pelvic Girdle Structure
The pelvic girdle comprises two halves, connected to the axial skeleton.
Axial Skeleton
Axial Skeleton
Signup and view all the flashcards
Appendicular Skeleton
Appendicular Skeleton
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pubofemoral Ligament & Abduction
Pubofemoral Ligament & Abduction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Iliofemoral Ligament & Abduction
Iliofemoral Ligament & Abduction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ischiofemoral Ligament & Abduction
Ischiofemoral Ligament & Abduction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pectineus Muscle Function
Pectineus Muscle Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anterior Thigh Compartment
Anterior Thigh Compartment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Greater trochanter
Greater trochanter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lesser trochanter
Lesser trochanter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intertrochanteric line (crest)
Intertrochanteric line (crest)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral neck angle
Femoral neck angle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral anteversion
Femoral anteversion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip joint
Hip joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ligamentum teres
Ligamentum teres
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hip fracture
Hip fracture
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acetabulum
Acetabulum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Abductors
Abductors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Rotators
Rotators
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vascularization (hip)
Vascularization (hip)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Osteotomies
Osteotomies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Psoas major and Iliacus
Psoas major and Iliacus
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the muscles of the anterior thigh?
What are the muscles of the anterior thigh?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What action does the iliopsoas group perform?
What action does the iliopsoas group perform?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the origin of the psoas major?
What is the origin of the psoas major?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the insertion of the psoas major?
What is the insertion of the psoas major?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the action of the psoas minor?
What is the action of the psoas minor?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the origin of the iliacus?
What is the origin of the iliacus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the insertion of the iliacus?
What is the insertion of the iliacus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the action of the sartorius?
What is the action of the sartorius?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the origin of the sartorius?
What is the origin of the sartorius?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the insertion of the sartorius?
What is the insertion of the sartorius?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gluteus Maximus
Gluteus Maximus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gluteus Medius
Gluteus Medius
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gluteus Minimus
Gluteus Minimus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tensor Fascia Lata
Tensor Fascia Lata
Signup and view all the flashcards
Piriformis
Piriformis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Obturator Internus
Obturator Internus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Superior & Inferior Gemelli
Superior & Inferior Gemelli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Quadratus Femoris
Quadratus Femoris
Signup and view all the flashcards
What do these deep external rotators do?
What do these deep external rotators do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why are deep gluteal muscles important?
Why are deep gluteal muscles important?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Deep Gluteal Muscles
Deep Gluteal Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Piriformis Muscle
Piriformis Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Obturator Internus Muscle
Obturator Internus Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Superior & Inferior Gemelli Muscles
Superior & Inferior Gemelli Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Quadratus Femoris Muscle
Quadratus Femoris Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral Rotation of Hip
Lateral Rotation of Hip
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral Head Stabilization
Femoral Head Stabilization
Signup and view all the flashcards
Function of Deep Gluteal Muscles
Function of Deep Gluteal Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Lower Limb 1
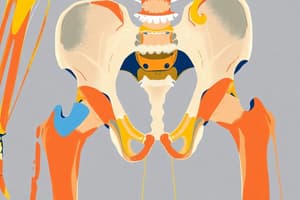
- The skeleton of the lower limb is divided into two functional components:
- the pelvic girdle (bony pelvis)
- the bones of the free lower limbs
The Pelvic Girdle
- Attaches the free lower limb to the axial skeleton
- Two identical half-connected components:
- posterior: sacrum
- anterior: pubic symphysis
- Ilium, Ischium, and Pubis are the three primary bones that form the hip bone.
- These fuse to form the acetabulum.
- The iliac crest is a thick, prominent border.
- The iliac fossa is a large medial depression that provides proximal attachment for the iliacus muscle.
- There are anterior superior and inferior iliac spines offering ligament and tendon attachment.
- The greater sciatic notch is formed by the posterior border of the ischium.
- The ischial tuberosity is a large, bony projection that helps connect the body of the ischium to its ramus.
- The pubic bone is part of the anteromedial hip bone
- Pubis forms the anteromedial portion of the hip bone and contributes to the formation of the acetabulum.
- The pubis is divided into a body (flattened, medial) and superior and inferior rami projecting laterally.
- The pubic symphysis is where the two pubic bones are joined medially.
- The pubic crest originates from the pubic tubercles, and helps attach abdominal muscles.
The Hip
- The acetabulum is large, cup-shaped cavity, on the lateral side of the hip bone that articulates with the head of the femur.
- The acetabulum is formed by the fusion of the ilium, ischium, and pubis.
- The acetabular notch and fossa contribute to the lunate surface of the acetabulum.
- The acetabular labrum is a fibrocartilaginous ring that deepens the acetabulum.
- The acetabular axis forms a 30° to 40° angle with the horizontal plane.
- The anterior orientation of the acetabulum is 15° to 20° from the frontal plane.
The Femur
- The femur is the longest and heaviest bone in the body.
- It transmits body weight from the hip bone to the tibia.
- Its length is roughly a quarter of the person's height.
- The femur has a midshaft and two epiphyseal ends (proximal and distal).
- The proximal end has a head, neck, and two trochanters (greater and lesser).
- The femoral head is spherical and covered in articular cartilage.
- The fovea is a depression where the ligament of the head attaches to the acetabulum.
- The femoral neck is trapezoidal, with a narrow head and broader base
- The greater trochanter is a large, irregular, quadrilateral eminence.
- The lesser trochanter is a conical eminence projecting from the base of the neck.
- The intertrochanteric line (or crest) marks where the neck and shaft meet.
The Ligamentum Teres
- The ligament of the femur head is a flattened fibrous band.
- It is implanted, by its apex, into the antero-superior part of the fovea capitis femoris.
- The base of the ligament connects to the acetabular notch, by two separate bands.
- Its role is negligible in terms of mechanical support, although it plays a part in the vascularization of the femoral head.
- The obturator artery often contributes to the vascularization.
The Hip Joint
- The hip joint is a synovial joint (enarthrosis).
- It's formed by the acetabulum and the proximal epiphysis of the femur.
- It is very stable in part due to its conformation, capsule, and ligaments.
The Hip Capsule
- The capsule runs from the iliac bone to the upper end of the femur.
- It is made up of two kinds of fibres: longitudinal and circular.
- Medially, the capsular ligament is inserted into the acetabular rim.
- The transverse ligament and the peripheral surface of the labrum are also involved.
- Laterally, the capsule is not attached to the edges of the articular cartilage but attaches to the base of the neck.
- There are three important ligaments: iliofemoral, pubofemoral, and ischiofemoral supporting the hip.
Hip Movements & Ligament Roles
-
Flexion: decreases the angle between the hip bones
-
Extension: increases the angle between the hip bones
-
Abduction: limb moving away from the midline
-
Adduction: limb moving towards the midline
-
Lateral Rotation: limb rotated away from the midline
-
Medial Rotation: limb rotated towards the midline
-
During various movements of the hip joint, the different ligaments act to support it to maintain stability in the hip
Muscles
- The anterior thigh muscles include the hip flexors and knee extensors. -Examples: Iliopsoas, Sartorius
- Medial thigh muscles include the adductor group. -Examples: Adductor longus, brevis, magnus, gracilis, obturator externus
- Muscles of the gluteal region are divided into superficial and deep layers -Examples include: gluteus maximus, medius, minimus, tensor fasciae latae, piriformis, obturator internus, superior and inferior gemelli, and quadratus femoris.
- The posterior thigh muscles mainly comprise the hip extensors and knee flexors -Examples: Semitendinosus, Semimembranosus, and Biceps femurs
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.