Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the duodenum?
What is the primary function of the duodenum?
What is the consequence of slowed blood flow through the liver?
What is the consequence of slowed blood flow through the liver?
What is the main function of the gallbladder?
What is the main function of the gallbladder?
What is the role of the liver in digestion?
What is the role of the liver in digestion?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the large intestine?
What is the primary function of the large intestine?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the duration of the entire process of digestion?
What is the duration of the entire process of digestion?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the spleen in the lymphatic system?
What is the primary function of the spleen in the lymphatic system?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the term for the sudden onset of abdominal pain that indicates an irritation of the perenium or peritonitis?
What is the term for the sudden onset of abdominal pain that indicates an irritation of the perenium or peritonitis?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the primary function of the nephrons in the kidney?
What is the primary function of the nephrons in the kidney?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the characteristic of peritonitis that can cause hypovolemic shock?
What is the characteristic of peritonitis that can cause hypovolemic shock?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the term for painful sensations that occur because of an irritated visceral perenium and may be perceived at a distant point on the surface of the body?
What is the term for painful sensations that occur because of an irritated visceral perenium and may be perceived at a distant point on the surface of the body?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the typical prehospital care for many diseases and conditions of the renal and urologic systems?
What is the typical prehospital care for many diseases and conditions of the renal and urologic systems?
Signup and view all the answers
Study Notes
• Abdominal pain is a common complaint, and its cause can be difficult to identify, especially prehospital, but it's essential to recognize life-threatening problems and act swiftly.
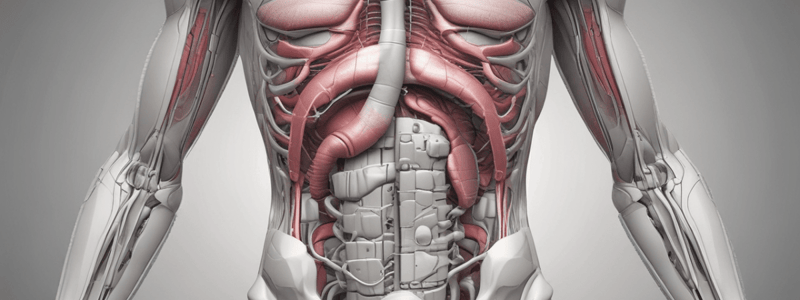
• The abdominal cavity contains solid and hollow organs that make up the GI, genital, and urinary systems, and injury to a solid organ can cause shock and bleeding.
• The GI tract consists of the mouth, salivary glands, esophagus, stomach, intestines, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, rectum, and anus, and the entire process of digestion takes 8-72 hours.
• The liver plays a crucial role in processing nutrients, and if blood flow through the liver slows down, blood may back up throughout the entire GI system.
• The duodenum is the first part of the small intestine and absorbs resources for use by other cells in the body, and it's where the pancreas, liver, and gallbladder connect to the digestive system.
• The liver is responsible for secreting bile, filtering toxic substances, and creating glucose stores, and it also produces substances for blood clotting and immune function.
• The gallbladder acts as a reservoir for bile, and the small intestine produces enzymes that turn food into substances that can be absorbed by the capillaries.
• The large intestine is responsible for completing the reabsorption of water and solidifying the digested material, and it's also the site of bacterial digestion.
• The spleen is part of the lymphatic system, assists in the filtration of blood, and aids in the development of red blood cells and serves as a blood reservoir.
• The kidneys regulate electrolytes, water content, and acid in the blood, and remove metabolic wastes, drug metabolites, and excess fluids, and they produce hormones that generate new red blood cells.
• Nephrons are the structural and functional units of the kidney that aid in forming urine and play a major role in maintaining homeostasis.
• Acute abdomen refers to the sudden onset of abdominal pain that indicates an irritation of the perenium or peritonitis.
• Peritonitis can be caused by infection, penetrating abdominal wound, blunt injury, or diseases, and it's characterized by severe pain in the major systems.
• The perenium consists of two membranes: the parietal perenium, which lies along the walls of the abdominal cavity, and the visceral perenium, which covers the surface of each of the organs within the abdominal cavity.
• Visceral pain is usually associated with urologic problems, and pinpointing the source of such pain is challenging because only a few nerve fibers may be involved in pain transmission.
• Referred pain is painful sensations that occur because of an irritated visceral perenium and may be perceived at a distant point on the surface of the body, such as the back or shoulder.
• Peritonitis usually causes ilas vomiting, which is associated with the loss of fluids into the abdominal cavity, potentially causing hypemic shock.
• Patients with acute appendicitis may have normal vital signs or present with signs of shock, and a fever may or may not be present.
• Diseases and conditions of the renal and urologic systems range from UTI to acute kidney injury, and prehospital care for many of these diseases is supportive.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Test your knowledge of the abdominal cavity, including the GI tract, liver, pancreas, and kidneys. Learn about the causes and symptoms of abdominal pain, including peritonitis, acute appendicitis, and urologic problems. This quiz is perfect for medical students and healthcare professionals.