Which of the following best describes the effect of a greater number of cysteine amino acids on the stability of the proteins?
Understand the Problem
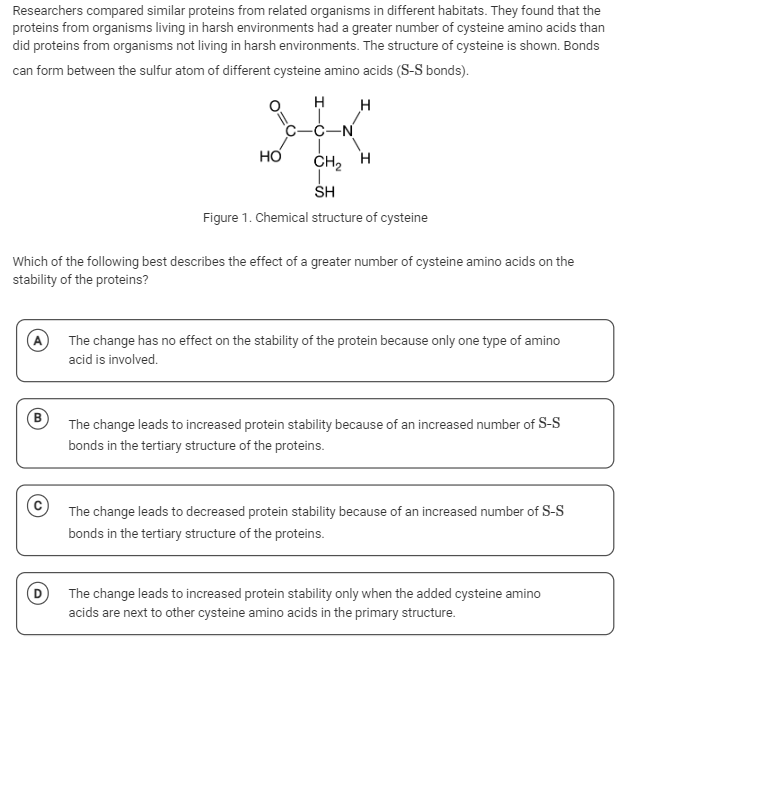
The question is asking about the effects of an increased number of cysteine amino acids on the stability of proteins, particularly focusing on the formation of disulfide bonds (S-S bonds) in the tertiary structure of proteins.
Answer
The change leads to increased protein stability because of an increased number of S-S bonds in the tertiary structure of the proteins.
The change leads to increased protein stability because of an increased number of S-S bonds in the tertiary structure of the proteins.
Answer for screen readers
The change leads to increased protein stability because of an increased number of S-S bonds in the tertiary structure of the proteins.
More Information
Cysteine amino acids can form disulfide bonds, which are covalent bonds that help stabilize the tertiary and quaternary structures of proteins. More cysteine residues mean more potential disulfide bonds, increasing overall protein stability.
Tips
A common mistake is to assume that only neighboring cysteine residues can form disulfide bonds. However, these bonds can form between cysteine residues at different locations in the protein chain.
Sources
- Which of the following best describes the effect of a greater number of cysteine amino acids on the stability of the proteins? - coursesidekick.com
- please answer truly! SH Figure 1. Chemical structure of cysteine... - coursehero.com
- Molecular Biology of the Cell - ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information