What is the significance of histone modifications in transcription activation?
Understand the Problem
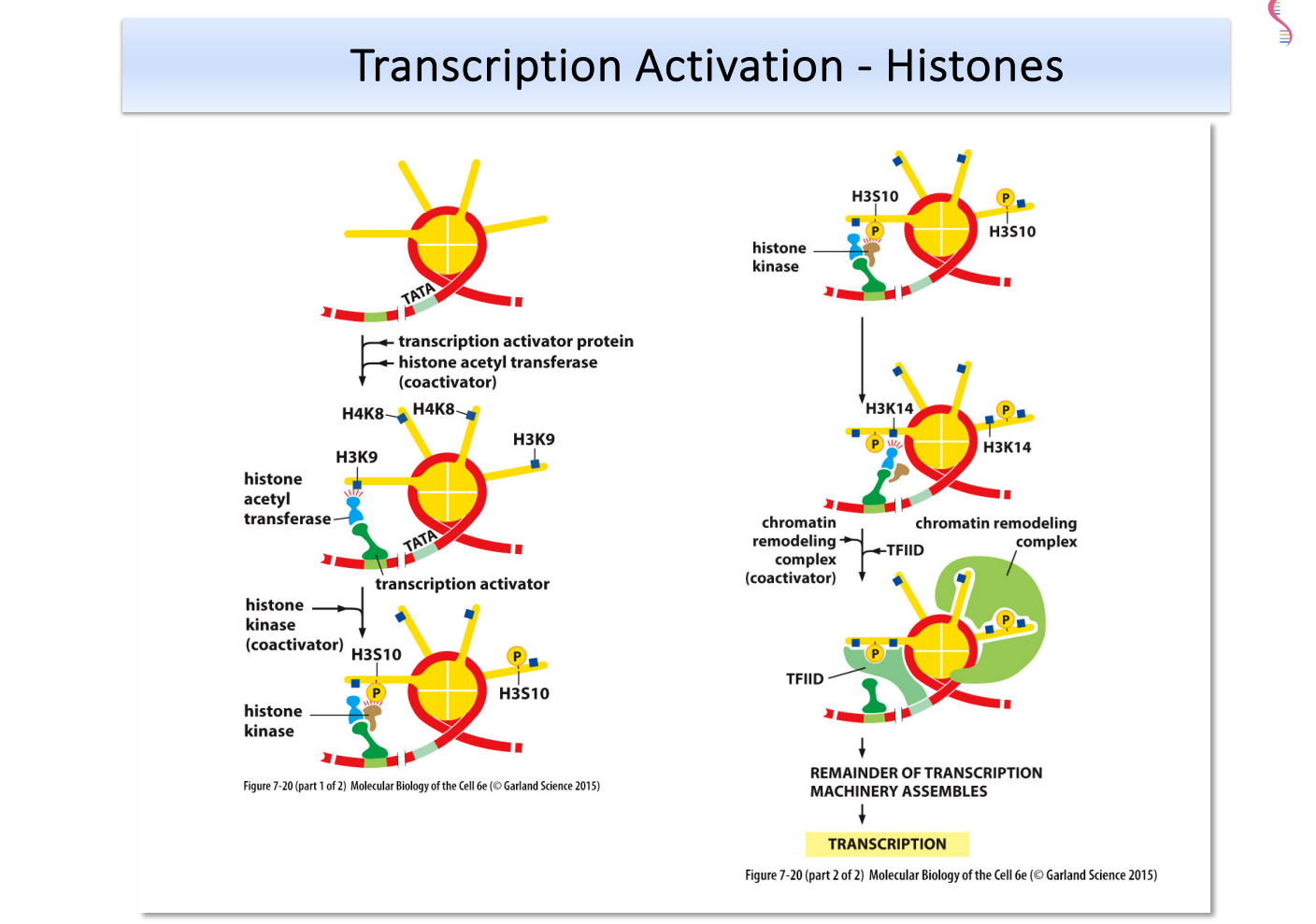
The image illustrates the process of transcription activation in relation to histones, detailing various proteins and modifications involved in the transcription process. It shows how transcription factors and coactivators interact with histones to facilitate transcription.
Answer
Histone modifications alter chromatin to enhance transcription.
Histone modifications like acetylation and phosphorylation play crucial roles in transcription activation by altering chromatin structure, making DNA more accessible for transcription machinery. Coactivators such as histone acetyltransferases and chromatin remodeling complexes facilitate these modifications, enhancing gene expression.
Answer for screen readers
Histone modifications like acetylation and phosphorylation play crucial roles in transcription activation by altering chromatin structure, making DNA more accessible for transcription machinery. Coactivators such as histone acetyltransferases and chromatin remodeling complexes facilitate these modifications, enhancing gene expression.
More Information
Histone acetylation reduces positive charges on histones, decreasing their affinity for DNA and allowing transcription factors to access genes. Phosphorylation often marks histones for specific cellular processes, such as transcription.
Tips
One common mistake is confusing histone acetylation with methylation. Acetylation generally loosens chromatin to activate transcription, while methylation can either activate or repress depending on the context.
Sources
- Regulation of chromatin by histone modifications | Cell Research - nature.com
- The Role of DNA Methylation and Histone Modifications in ... - pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Histone Modification - News-Medical - news-medical.net
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information