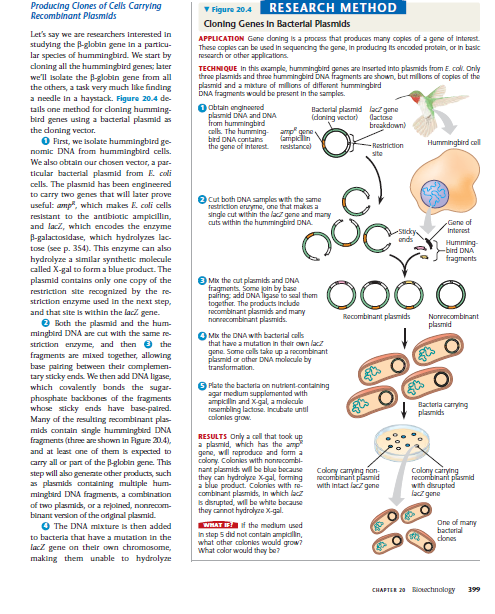
What is the process of cloning genes in bacterial plasmids, and what are the steps involved?
Understand the Problem
The question is asking for an explanation of the cloning process involving bacterial plasmids and the steps taken to produce clones carrying a specific gene. It aims to elucidate how genes from hummingbirds can be cloned into bacterial cells using various methods, including DNA isolation and plasmid manipulation.
Answer
Gene cloning in bacterial plasmids: 1) Obtain plasmid and target gene. 2) Cut with restriction enzymes. 3) Ligate fragments to form recombinant plasmids. 4) Transform bacteria. 5) Select transformed bacteria. 6) Screen for desired clones.
The process of cloning genes in bacterial plasmids involves obtaining the target gene and plasmid, cutting both with restriction enzymes, ligating them to form recombinant plasmids, transforming them into bacterial cells, selecting for successful transformations, and screening for desired clones.
Answer for screen readers
The process of cloning genes in bacterial plasmids involves obtaining the target gene and plasmid, cutting both with restriction enzymes, ligating them to form recombinant plasmids, transforming them into bacterial cells, selecting for successful transformations, and screening for desired clones.
More Information
Cloning genes into plasmids is a fundamental technique in molecular biology, allowing for the amplification and manipulation of specific genes. It is a cornerstone of genetic engineering and biotechnology, enabling the production of therapeutic proteins, genetically modified organisms, and advanced research studies.
Tips
Common mistakes include inefficient DNA ligation due to incorrect enzyme usage, failure in transformation process, or improper antibiotic selection resulting in background bacterial growth.
Sources
- The Plasmid Cloning Cycle - snapgene.com
- Overview: DNA cloning (article) - Khan Academy - khanacademy.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information