What is the principle of the turn ratio of a transformer as explained in the lab experiment?
Understand the Problem
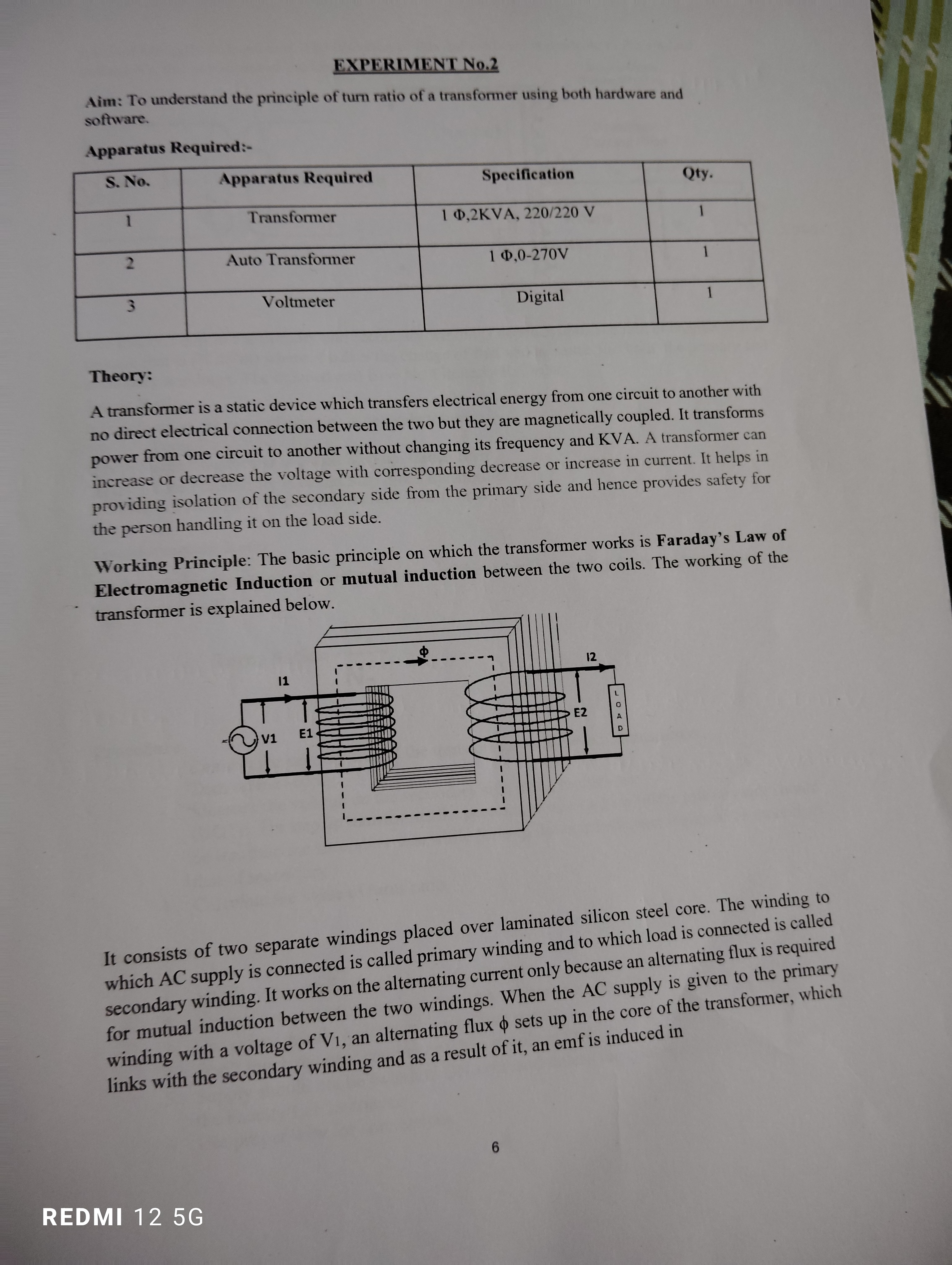
The question is describing an experiment aimed at understanding the principle of the turn ratio of a transformer using both hardware and software. It provides details about the necessary apparatus, the theory behind transformers, and their working principle, which involves Faraday's Law of Electromagnetic Induction.
Answer
The transformer's turn ratio is the ratio of the number of turns on the secondary to the primary winding.
The principle of the turn ratio of a transformer is that it is the ratio of the number of turns on the secondary winding to the number of turns on the primary winding. This ratio determines how the voltages and currents are transformed between the primary and secondary sides of a transformer.
Answer for screen readers
The principle of the turn ratio of a transformer is that it is the ratio of the number of turns on the secondary winding to the number of turns on the primary winding. This ratio determines how the voltages and currents are transformed between the primary and secondary sides of a transformer.
More Information
Transformers are crucial in electrical power systems for stepping up (increasing) or stepping down (decreasing) voltage levels efficiently. The turns ratio directly influences the voltage transformation and ensures the appropriate voltage levels for different applications.
Tips
A common mistake is confusing the turns ratio with the voltage ratio directly. Always relate the primary-to-secondary voltage ratio as per the transformer's turns ratio, i.e., V1/V2 = N1/N2.
Sources
- Transformers - Investigating the Turns Ratio Equation - YouTube - youtube.com
- Calculating the Turns Ratio of a Transformer - Technical Articles - eepower.com
- Transformation Ratio and Turn Ratio of Single-Phase Transformer - tutorialspoint.com
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information