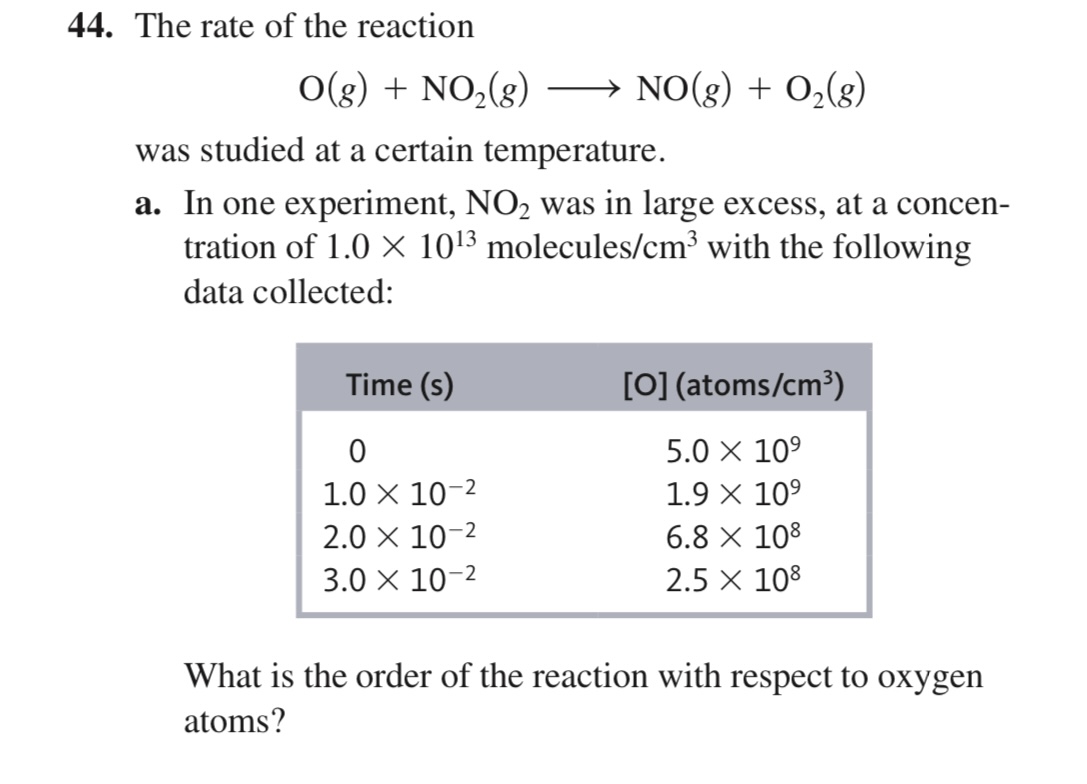
What is the order of the reaction with respect to oxygen atoms?
Understand the Problem
The question is asking for the determination of the order of a chemical reaction with respect to oxygen atoms, based on collected experimental data regarding the concentration of oxygen over time.
Answer
The reaction order with respect to oxygen is $n = 1$.
Answer for screen readers
The order of the reaction with respect to oxygen atoms is $n = 1$.
Steps to Solve
- Determine the change in concentration over time
Calculate the change in oxygen concentration, $[O]$, from the table provided. For example, at time $t = 0$, $[O] = 5.0 \times 10^9$, and at $t = 1.0 \times 10^{-2}$ s, $[O] = 1.9 \times 10^9$.
The change can be found as:
$$ \Delta [O] = [O]{\text{initial}} - [O]{\text{final}} $$
- Calculate the rate of reaction
Using the formula for the rate, we can express it as:
$$ \text{Rate} = -\frac{\Delta [O]}{\Delta t} $$
Calculate the rate for each time interval based on the change in concentration calculated.
- Set up a rate law expression
Assuming a general rate law of the form:
$$ \text{Rate} = k [O]^n $$
Where (n) is the order of the reaction with respect to $O$.
- Plug in values and solve for (n)
Using the calculated rates and corresponding concentrations from each time interval, set up equations to solve for (n). Since we will have multiple rates, we can compare two time intervals to solve for (n):
$$ \frac{\text{Rate}_1}{\text{Rate}_2} = \frac{[O]_1^n}{[O]_2^n} $$
- Take logarithms to simplify
To solve for (n), take the logarithm of both sides:
$$ \log \left( \frac{\text{Rate}_1}{\text{Rate}_2} \right) = n \log \left( \frac{[O]_1}{[O]_2} \right) $$
This will allow you to isolate (n).
- Calculate (n) using your values
Substituting values into the logarithmic equation will yield the reaction order.
The order of the reaction with respect to oxygen atoms is $n = 1$.
More Information
This result indicates that the reaction is first-order in oxygen, meaning that the rate is directly proportional to the concentration of oxygen.
Tips
- Incorrectly assuming order without calculations: Make sure to calculate the concentration changes and rates accurately before determining the order.
- Confusing the rate constant with reaction order: The order of the reaction is not the same as the rate constant (k).
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information