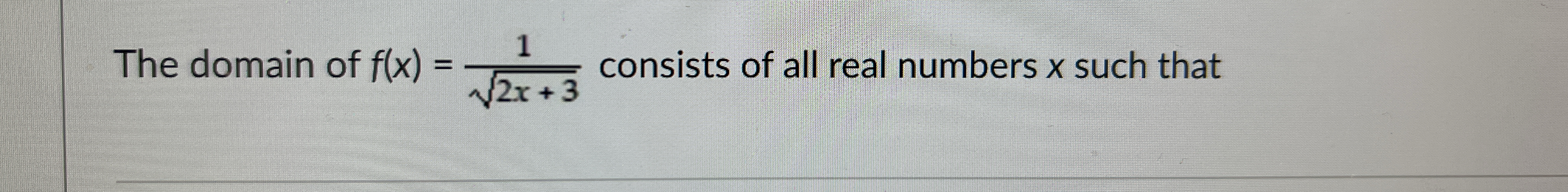
What is the domain of f(x) = 1 / sqrt(2x + 3)?
Understand the Problem
The question is asking to identify the domain of the function f(x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2x + 3}}. To solve this, we need to determine the values of x for which the expression is defined, focusing on the conditions under which the denominator is not zero and is defined.
Answer
The domain of $f(x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2x + 3}}$ is $x > -\frac{3}{2}$.
Answer for screen readers
The domain of $f(x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2x + 3}}$ is $x > -\frac{3}{2}$.
Steps to Solve
- Identify the denominator condition
Since the function is defined as $f(x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2x + 3}}$, we need to ensure that the denominator $\sqrt{2x + 3}$ is greater than zero.
- Set the inequality
We require: $$ 2x + 3 > 0 $$
- Solve for x
To solve the inequality: $$ 2x > -3 $$
Dividing both sides by 2: $$ x > -\frac{3}{2} $$
- State the domain
The domain of $f(x)$ consists of all real numbers $x$ such that: $$ x > -\frac{3}{2} $$
The domain of $f(x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2x + 3}}$ is $x > -\frac{3}{2}$.
More Information
The domain indicates that the function is only defined for input values greater than $-\frac{3}{2}$ because the square root and the division cannot take non-positive values. This is a common consideration when dealing with rational and radical functions.
Tips
- Ignoring the square root condition: Some may forget that the expression inside the square root must be strictly greater than zero, not equal to zero.
- Incorrectly solving the inequality: It's crucial to carefully manage signs when dividing or multiplying by negative numbers, although that's not necessary in this case since the coefficient of $x$ is positive.
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information