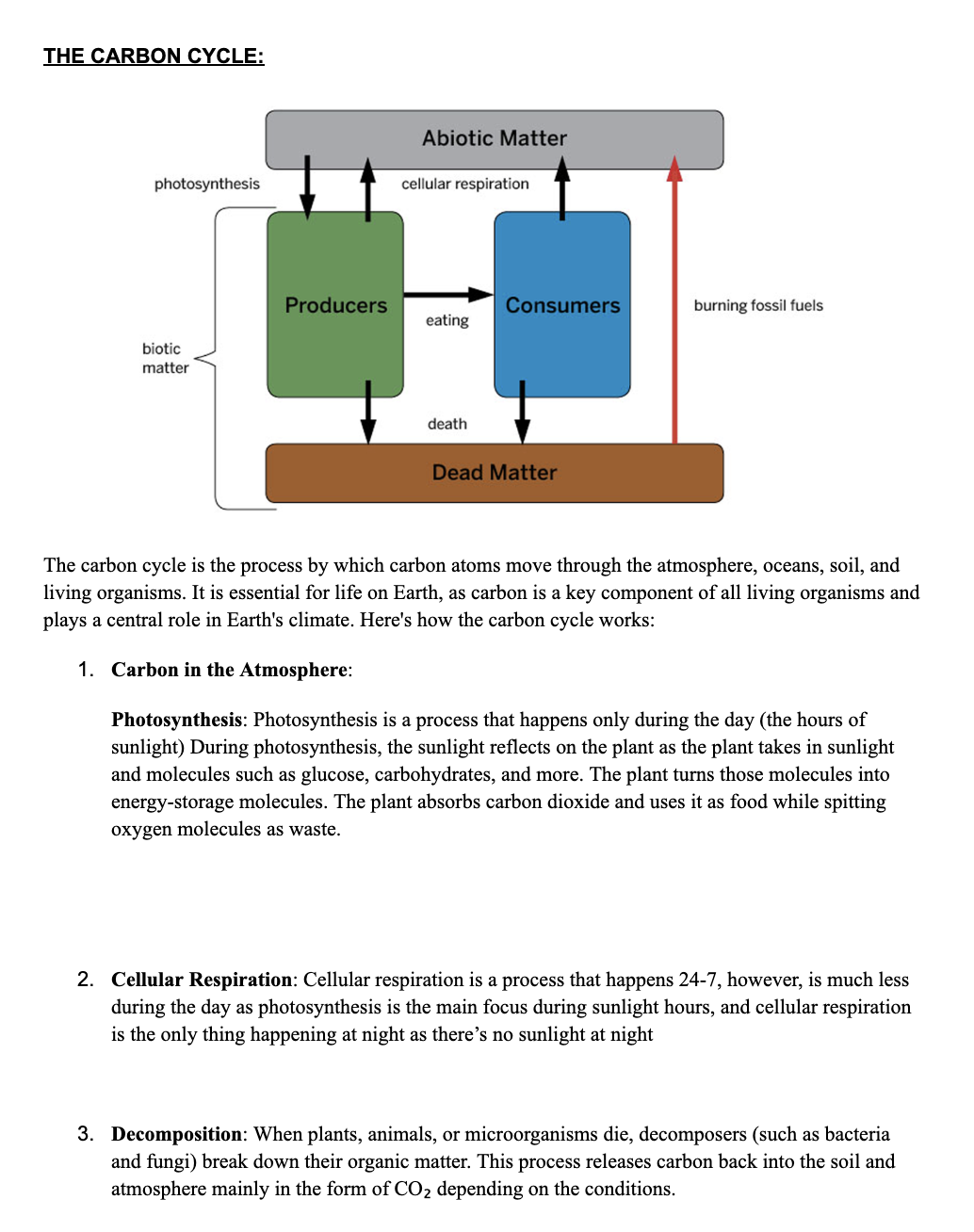
What is the carbon cycle and how do photosynthesis, cellular respiration, and decomposition contribute to it?
Understand the Problem
The question is asking for an explanation of the carbon cycle, detailing its components and processes such as photosynthesis, cellular respiration, and decomposition. It also seeks to understand the movement of carbon atoms through various components of the ecosystem.
Answer
The carbon cycle involves photosynthesis, cellular respiration, and decomposition moving carbon through the atmosphere, oceans, soil, and organisms.
The carbon cycle involves processes like photosynthesis, cellular respiration, and decomposition to move carbon between organisms, the atmosphere, soil, and oceans.
Answer for screen readers
The carbon cycle involves processes like photosynthesis, cellular respiration, and decomposition to move carbon between organisms, the atmosphere, soil, and oceans.
More Information
The carbon cycle is crucial for regulating Earth's climate and providing energy through carbon-based molecules. Photosynthesis absorbs carbon dioxide, while cellular respiration releases it. Decomposition breaks down organic matter, also adding carbon dioxide to the atmosphere.
Tips
A common mistake is misunderstanding the balance and flow between processes. Remember that each process plays a specific role in moving carbon.
Sources
- The carbon cycle (article) | Ecology - Khan Academy - khanacademy.org
- Carbon cycle | National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration - noaa.gov
- DOE Explains...the Carbon Cycle - Department of Energy - energy.gov
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information