What is osmosis and how does it affect cells in different solution concentrations?
Understand the Problem
The question refers to osmosis in cells, focusing on the movement of water and solutes through semi-permeable membranes. It discusses concepts like isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solutions and how these affect cell structure and function. The high-level approach would involve explaining the definitions and implications of these terms, as well as their impact on living cells.
Answer
Osmosis is water movement across a membrane affecting cells differently in hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic solutions.
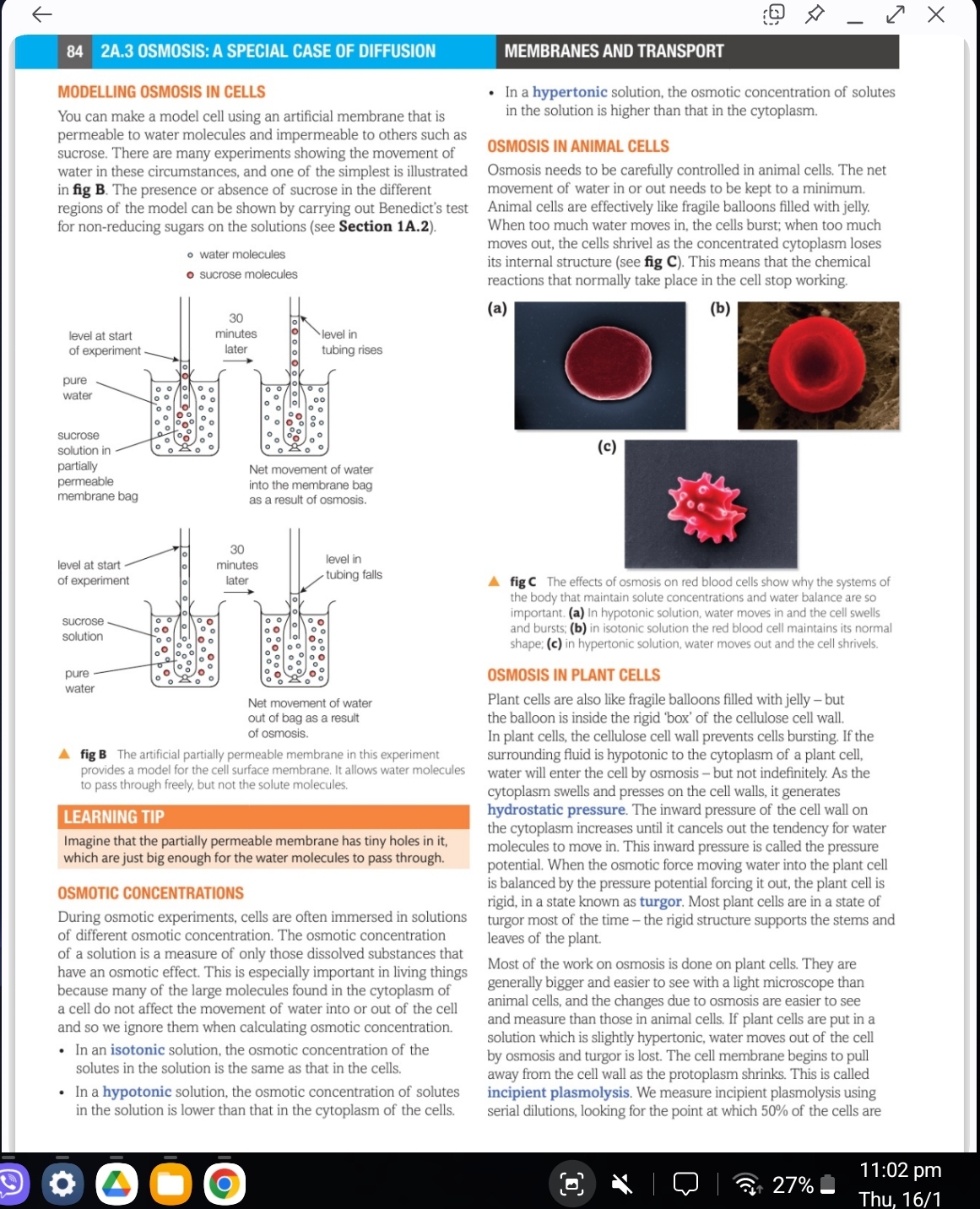
Osmosis is the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from a region of lower solute concentration to higher solute concentration. In hypotonic solutions, cells swell; in hypertonic, they shrink; in isotonic, they maintain their size. Plant and animal cells react differently due to structural differences.
Answer for screen readers
Osmosis is the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane from a region of lower solute concentration to higher solute concentration. In hypotonic solutions, cells swell; in hypertonic, they shrink; in isotonic, they maintain their size. Plant and animal cells react differently due to structural differences.
More Information
Animal cells may burst in hypotonic solutions due to lack of cell walls, while plant cells develop turgor pressure. Hypertonic solutions cause water loss, leading to cell shrinkage.
Tips
A common mistake is confusing the effects of hypertonic and hypotonic solutions on cells.
Sources
- Physiology, Osmosis - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf - ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Tonicity: hypertonic, isotonic & hypotonic solutions (article) - khanacademy.org
- Osmosis, osmolarity, and tonicity (article) | Khan Academy - khanacademy.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information