What is glycolysis and what are its steps in converting glucose to pyruvate?
Understand the Problem
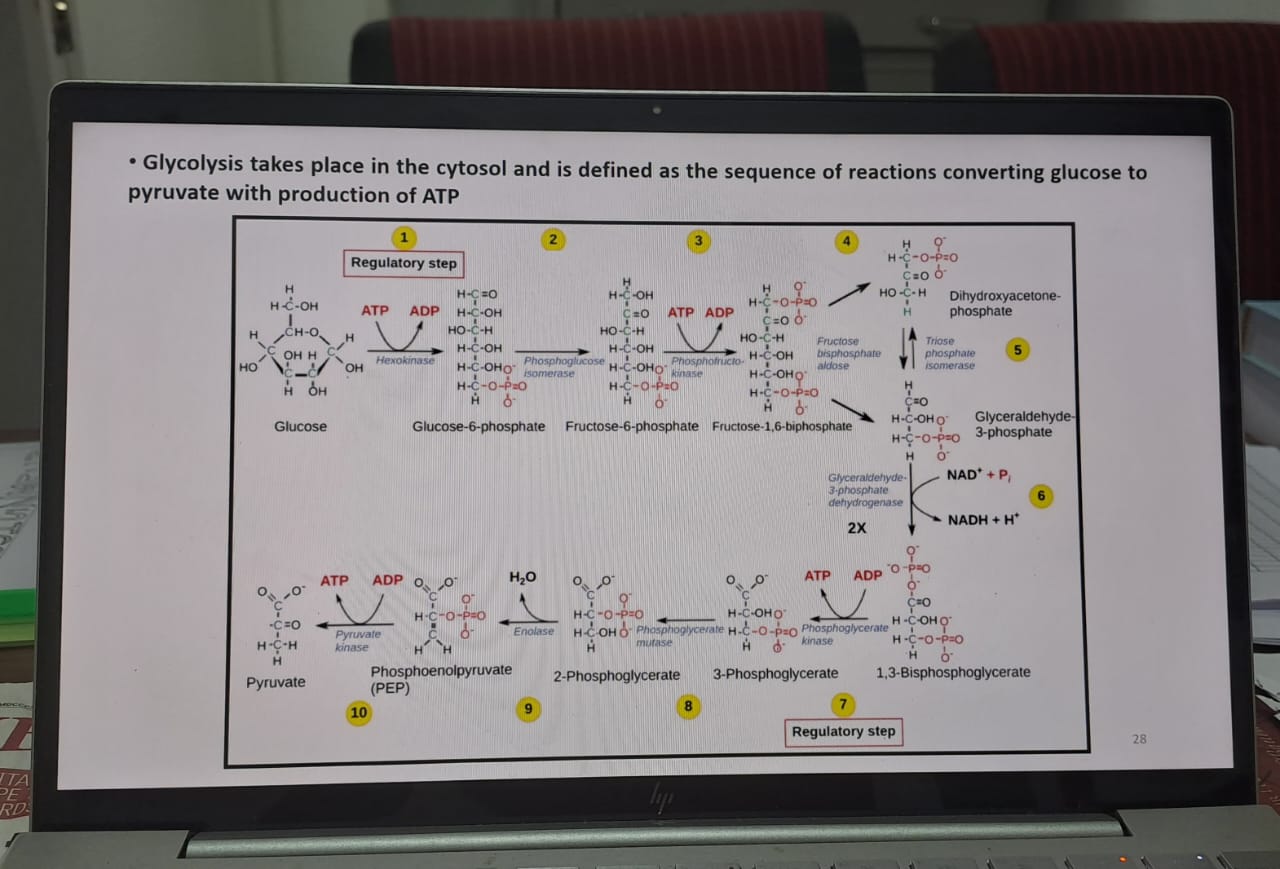
The image describes the glycolysis process, highlighting the sequence of reactions that convert glucose into pyruvate while producing ATP. It illustrates specific steps and enzymes involved in the process.
Answer
Glycolysis converts glucose to pyruvate in 10 steps, producing ATP and NADH.
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate through a series of 10 enzyme-catalyzed reactions in the cytosol, producing ATP and NADH.
Answer for screen readers
Glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate through a series of 10 enzyme-catalyzed reactions in the cytosol, producing ATP and NADH.
More Information
Glycolysis is an essential process for cellular respiration, providing energy in the form of ATP and reducing power in the form of NADH.
Tips
A common mistake is not balancing the input and output molecules correctly. Remember each glucose molecule leads to two molecules of pyruvate.
Sources
- Glycolysis | Cellular respiration | Biology (article) - Khan Academy - khanacademy.org
- Biochemistry, Glycolysis - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf - ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Glycolysis - Wikipedia - en.wikipedia.org
AI-generated content may contain errors. Please verify critical information